General Outline for Antibiotics (a good study guide)
... similar – stable in gastric acid and readily absorbed after oral administration; can also be administered parenterally for serious cases of staphylococcal disease; food interferes with absorption b) nafcillin is inactivated by acid pH so its given parenterally 3. fate after absorption a) all bind pl ...
... similar – stable in gastric acid and readily absorbed after oral administration; can also be administered parenterally for serious cases of staphylococcal disease; food interferes with absorption b) nafcillin is inactivated by acid pH so its given parenterally 3. fate after absorption a) all bind pl ...
Fluoroquinolone resistance in mycobacterium tuberculosis strains
... are also added to the regimen based on first-line DST results 5, 6. In Kenya flouroquinolones are used in the treatment of MDR-TB patients according to WHO standards and are also used in the treatment of other bacterial infections. Treatment of MDR-TB takes 18 to 24 months and must be done on the b ...
... are also added to the regimen based on first-line DST results 5, 6. In Kenya flouroquinolones are used in the treatment of MDR-TB patients according to WHO standards and are also used in the treatment of other bacterial infections. Treatment of MDR-TB takes 18 to 24 months and must be done on the b ...
beta lactam antibiotics and other cell wall synthesis
... the combination widens the antimicrobial spectrum B. Sulbactam Pivoxil and Ampicillin ( Unasyn) C. Tazobactam and Piperacillin (Tazocin) ...
... the combination widens the antimicrobial spectrum B. Sulbactam Pivoxil and Ampicillin ( Unasyn) C. Tazobactam and Piperacillin (Tazocin) ...
Antibiotic Choices - CriticalCareMedicine / FrontPage
... Statistically non-inferior to vancomycin and vancomycin/ceftazidime for the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections STRAUSS 1 and 2 trials Current indications: complicated skin and skin structure infections (cSSSI), DM foot infections, ?nosocomial pneumonia (awaiting further trials) Dose: 500 ...
... Statistically non-inferior to vancomycin and vancomycin/ceftazidime for the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections STRAUSS 1 and 2 trials Current indications: complicated skin and skin structure infections (cSSSI), DM foot infections, ?nosocomial pneumonia (awaiting further trials) Dose: 500 ...
Dirithromycin (Dynabac): same as erythromycin base but once daily
... 1. Presence of Clostridia difficile in GI tract 2. Altered gastrointestinal flora 3. Presence of Toxin A and B - must have toxin receptors in gut 4. Predisposing factors * potential adverse effect of all antimicrobial agents - especially ones that affect obligate anaerobes (ampicillin, Augmentin, ce ...
... 1. Presence of Clostridia difficile in GI tract 2. Altered gastrointestinal flora 3. Presence of Toxin A and B - must have toxin receptors in gut 4. Predisposing factors * potential adverse effect of all antimicrobial agents - especially ones that affect obligate anaerobes (ampicillin, Augmentin, ce ...
Bez nadpisu - Dr.Fatimah Al.Shehri
... – that blood concentrations of a drug remain above the MIC. – increasing the concentration of ATB to higher multiples of the MIC does not significantly increase the rate of kill – E.g., for PNC and cephalosporins, dosing schedules that ensure blood levels greater than MIC for 60 – 70 % of the time w ...
... – that blood concentrations of a drug remain above the MIC. – increasing the concentration of ATB to higher multiples of the MIC does not significantly increase the rate of kill – E.g., for PNC and cephalosporins, dosing schedules that ensure blood levels greater than MIC for 60 – 70 % of the time w ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... Levofloxacin [Fig. 1 a], (S)-(-)-9-fluro-2,3,-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7Hpyrido[1,2,3-de][1,4]benzoxazine-6-carboxylic acid, a third-generation fluoroquinolone, is the active levoisomer of ofloxacin and is twice as active as the parent drug. It is active against both Gram-p ...
... Levofloxacin [Fig. 1 a], (S)-(-)-9-fluro-2,3,-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7Hpyrido[1,2,3-de][1,4]benzoxazine-6-carboxylic acid, a third-generation fluoroquinolone, is the active levoisomer of ofloxacin and is twice as active as the parent drug. It is active against both Gram-p ...
Baytril 10% Oral Solution - Veterinary Medicines Directorate
... Calculate the daily quantity (ml) of Baytril 10% Oral Solution required for treatment period as follows: Total number of birds x Average body weight in kg x 0.1= Total volume (ml) per day Baytril 10% Oral Solution may be put directly into the header tank or introduced via a water proportioner pump. ...
... Calculate the daily quantity (ml) of Baytril 10% Oral Solution required for treatment period as follows: Total number of birds x Average body weight in kg x 0.1= Total volume (ml) per day Baytril 10% Oral Solution may be put directly into the header tank or introduced via a water proportioner pump. ...
ZYMAXID® Prescribing Information
... was found in the breast milk of rats following oral administration of gatifloxacin during lactation. However, systemic levels of gatifloxacin following topical ocular administration are low [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], and it is not known whether gatifloxacin would be present in maternal milk ...
... was found in the breast milk of rats following oral administration of gatifloxacin during lactation. However, systemic levels of gatifloxacin following topical ocular administration are low [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], and it is not known whether gatifloxacin would be present in maternal milk ...
Aminoglycosides
... Polymyxins are produced from Bacillus spp. They include: 1- Polymyxin B . Used in the form of polymyxin B sulfate. It is stable. Aqueous solutions of polymyxin B may be stored up to 12 months without significant loss of potency if kept under refrigeration. 2- Polymyxin E (Colistin). Colist ...
... Polymyxins are produced from Bacillus spp. They include: 1- Polymyxin B . Used in the form of polymyxin B sulfate. It is stable. Aqueous solutions of polymyxin B may be stored up to 12 months without significant loss of potency if kept under refrigeration. 2- Polymyxin E (Colistin). Colist ...
β-Lactam Antibiotics
... Used in treatment of pulmonary & extrapulmonary tuberculosis Causes serious dose related C.N.S. toxicity ( headaches, tremors, acute psychosis, convulsions) Contraindicated in epileptic & psychotic patients ...
... Used in treatment of pulmonary & extrapulmonary tuberculosis Causes serious dose related C.N.S. toxicity ( headaches, tremors, acute psychosis, convulsions) Contraindicated in epileptic & psychotic patients ...
L3_protein synthesis..
... Chloramphenicol is metabolized by the liver to chloramphenicol glucuronate (which is inactive). In liver impairment, the dose of chloramphenicol must therefore be reduced. The majority of the chloramphenicol dose is excreted by the kidneys as the inactive metabolite, chloramphenicol glucuronate. ...
... Chloramphenicol is metabolized by the liver to chloramphenicol glucuronate (which is inactive). In liver impairment, the dose of chloramphenicol must therefore be reduced. The majority of the chloramphenicol dose is excreted by the kidneys as the inactive metabolite, chloramphenicol glucuronate. ...
Revised: April 2014 AN. 01865/2013 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT
... Calculate the daily quantity (ml) of the product required for treatment period as follows: Total number of rabbits x Average body weight in kg x 0.1 = Total volume (ml) per day Medicated drinking water should be replaced every 24 hours. 4.10 Overdose (symptoms, emergency procedures, antidotes), if n ...
... Calculate the daily quantity (ml) of the product required for treatment period as follows: Total number of rabbits x Average body weight in kg x 0.1 = Total volume (ml) per day Medicated drinking water should be replaced every 24 hours. 4.10 Overdose (symptoms, emergency procedures, antidotes), if n ...
or 500 mg po bid
... syndromes that are not caused by bacteria (e.g., “colds,” acute bronchitis, most sore throats, “fever”). Administration of an antibacterial with a broader-than-necessary spectrum of activity. Failure to consider likely pathogens and resistance patterns in selecting empiric antibiotic regimen. ...
... syndromes that are not caused by bacteria (e.g., “colds,” acute bronchitis, most sore throats, “fever”). Administration of an antibacterial with a broader-than-necessary spectrum of activity. Failure to consider likely pathogens and resistance patterns in selecting empiric antibiotic regimen. ...
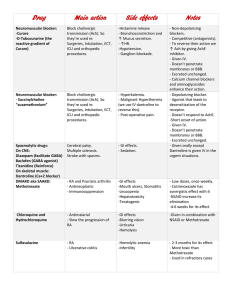
Drug Main action Side effects Notes
... - LT (Zafrilukast) inhibitor are given with it in asthmatic patients (any allergy, ex: Urticaria). - Celecoxib are used instead of NSAID in patients with peptic ulcer ...
... - LT (Zafrilukast) inhibitor are given with it in asthmatic patients (any allergy, ex: Urticaria). - Celecoxib are used instead of NSAID in patients with peptic ulcer ...
Nursing 3703 Pharmacology
... Synthetic bactericidal drugs with activity against gram positive and gram negative organisms Most are given orally Excreted via kidneys Mechanism of action is by interfering with DNA gyrase, an enzyme necessary for synthesis of bacterial DNA ...
... Synthetic bactericidal drugs with activity against gram positive and gram negative organisms Most are given orally Excreted via kidneys Mechanism of action is by interfering with DNA gyrase, an enzyme necessary for synthesis of bacterial DNA ...
Moxifloxacin 0.5 % eye drop solution - Gobierno
... not free of methodological errors, showed superior clinical efficacy after 48 hours of treatment but not after 7 days. The safety profile is similar to other fluoroquinolones presenting the risk of corneal deposits and connective tissue alterations as reflected in the risk plan. The doses employed i ...
... not free of methodological errors, showed superior clinical efficacy after 48 hours of treatment but not after 7 days. The safety profile is similar to other fluoroquinolones presenting the risk of corneal deposits and connective tissue alterations as reflected in the risk plan. The doses employed i ...
Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy
... Americans every year (∼19,000) than emphysema, HIV/AIDS, Parkinson's disease, and homicide combined – most serious MRSA infections, an estimated 85%, are associated with a healthcare exposure, but nearly 14% of the infections are communityassociated. • Almost 2 million Americans per year develop h ...
... Americans every year (∼19,000) than emphysema, HIV/AIDS, Parkinson's disease, and homicide combined – most serious MRSA infections, an estimated 85%, are associated with a healthcare exposure, but nearly 14% of the infections are communityassociated. • Almost 2 million Americans per year develop h ...
A) ATB inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis
... enteric fever, extra-intestinal salmonellosis zoonoses (tularemia, brucellosis etc.) prostatitis acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis lower respiratory tract infections in cystic fibrosis common UTI gastroenteritis, enterocolitis biliary infections (+ prophylaxis) uretritis (STD) nosocomial infe ...
... enteric fever, extra-intestinal salmonellosis zoonoses (tularemia, brucellosis etc.) prostatitis acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis lower respiratory tract infections in cystic fibrosis common UTI gastroenteritis, enterocolitis biliary infections (+ prophylaxis) uretritis (STD) nosocomial infe ...
Doxacil
... Doxacil® may produce gastrointestinal irritation to a varying degree in some individuals. Epigastric distress, abdominal discomfort, nausea, and vomiting may occur. Long term therapy with Doxacil® may produce changes in the peripheral blood. Various skin reactions including rashes, urticaria, exfoli ...
... Doxacil® may produce gastrointestinal irritation to a varying degree in some individuals. Epigastric distress, abdominal discomfort, nausea, and vomiting may occur. Long term therapy with Doxacil® may produce changes in the peripheral blood. Various skin reactions including rashes, urticaria, exfoli ...
Antibiotic interactions: Answers to 4 common questions
... Of note, metronidazole was not included in this study endpoint. The study’s secondary endpoint of INR >4 found that 10% of patients taking metronidazole and 8% of patients taking TMP/SMX in addition to warfarin had INRs >4. Almost 10% (9.7%) of patients prescribed fluconazole had a peak INR value >6 ...
... Of note, metronidazole was not included in this study endpoint. The study’s secondary endpoint of INR >4 found that 10% of patients taking metronidazole and 8% of patients taking TMP/SMX in addition to warfarin had INRs >4. Almost 10% (9.7%) of patients prescribed fluconazole had a peak INR value >6 ...
ANTISEPSIS Aspects of history: Since the middle of XIX century the
... Despite that these antibiotics are of low activity against many gramnegative microorganisms, an effective action against aerobic and facultatively anaerobic bacterial pathogens is important for the clinical use. In humans, significant concentrations were observed in bile, peritoneal, pleural fluids ...
... Despite that these antibiotics are of low activity against many gramnegative microorganisms, an effective action against aerobic and facultatively anaerobic bacterial pathogens is important for the clinical use. In humans, significant concentrations were observed in bile, peritoneal, pleural fluids ...
Oral Medications in Optometric Practice
... • Over the last 10 yrs, the %age of Americans who took at least one prescription drug in the past month increased from 44% to 48%. The use of 2 or more drugs increased from 25% to 31%. The use of five or more drugs/month increased from 6% to 11%. • In 2007-2008, 9 out of 10 Americans >60 yoa repor ...
... • Over the last 10 yrs, the %age of Americans who took at least one prescription drug in the past month increased from 44% to 48%. The use of 2 or more drugs increased from 25% to 31%. The use of five or more drugs/month increased from 6% to 11%. • In 2007-2008, 9 out of 10 Americans >60 yoa repor ...
Drugs for treating infections
... • Insufficient control on drug prescribing • Inadequate compliance with treatment regimens • Prescribing inappropriate doses • Lack of infection control • Increasing frequency and speed of travel ...
... • Insufficient control on drug prescribing • Inadequate compliance with treatment regimens • Prescribing inappropriate doses • Lack of infection control • Increasing frequency and speed of travel ...
2nd Term 11th Lecture
... Metronidazole has potent antibacterial activity against anaerobes, including bacteroides and clostridium species Metronidazole is indicated for treatment of anaerobic or mixed intra-abdominal infections, vaginitis (bacterial vaginosis), antibiotic-associated enterocolitis, acute gingivitis and o ...
... Metronidazole has potent antibacterial activity against anaerobes, including bacteroides and clostridium species Metronidazole is indicated for treatment of anaerobic or mixed intra-abdominal infections, vaginitis (bacterial vaginosis), antibiotic-associated enterocolitis, acute gingivitis and o ...
Levofloxacin
Levofloxacin (trade names Levaquin (US), Tavanic (EU), and others) is a broad-spectrum antibiotic of the fluoroquinolone drug class, and the levo isomer of its predecessor ofloxacin. Its spectrum of activity includes most strains of bacterial pathogens responsible for respiratory, urinary tract, gastrointestinal, and abdominal infections, including Gram negative (Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, Moraxella catarrhalis, Proteus mirabilis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa), Gram positive (methicillin-sensitive but not methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, and Streptococcus pyogenes), and atypical bacterial pathogens (Chlamydophila pneumoniae and Mycoplasma pneumoniae). Compared to earlier antibiotics of the fluoroquinoline class such as ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin exhibits greater activity towards Gram-positive bacteria but lesser activity toward Gram-negative bacteria, especially Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Levofloxacin and later generation fluoroquinolones are collectively referred to as ""respiratory quinolones"" to distinguish them from earlier fluoroquinolones which exhibited modest activity toward the important respiratory pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae.Levofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones are valued for their broad spectrum of activity, excellent tissue penetration, and for their availability in both oral and intravenous formulations. Levofloxacin is used alone or in combination with other antibacterial drugs to treat certain bacterial infections including pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and abdominal infections.Levofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones are generally well tolerated, but in rare instances have produced serious adverse reactions such as spontaneous tendon ruptures and irreversible peripheral neuropathy. Tendon damage may manifest months after therapy had been completed. Levofloxacin may cause worsening of myasthenia gravis symptoms, including muscle weakness and breathing problems.