Marine Mammal Dive Response
... to the eyes, brain, and spinal cord. Which of the following is the most likely reason for this adaptation? A. To increase the number of red blood cells in the nervous system B. To increase the amount of oxygen reaching the skeletomuscular system C. To increase the amount of oxygen reaching the centr ...
... to the eyes, brain, and spinal cord. Which of the following is the most likely reason for this adaptation? A. To increase the number of red blood cells in the nervous system B. To increase the amount of oxygen reaching the skeletomuscular system C. To increase the amount of oxygen reaching the centr ...
Fructose 6
... Figure 2. Using the non-oxidative branch of the pentose pathway to produce ribose-5-phosphate for the nucleic acid pathways (Mode 1). ...
... Figure 2. Using the non-oxidative branch of the pentose pathway to produce ribose-5-phosphate for the nucleic acid pathways (Mode 1). ...
Mitochondrial DNA
... Mutation rate in mtDNA is very high: 10 times the nuclear rate. mtDNA is associated with the inner membrane, the site of oxidative phosphorylation. Oxidative phosphorylation generates large amounts of “reactive oxygen species” (peroxide and superoxide), which are quite mutagenic. ...
... Mutation rate in mtDNA is very high: 10 times the nuclear rate. mtDNA is associated with the inner membrane, the site of oxidative phosphorylation. Oxidative phosphorylation generates large amounts of “reactive oxygen species” (peroxide and superoxide), which are quite mutagenic. ...
SfRBM UAB 2017 Regional Redox Symposium, Abstract/Poster
... Peroxiredoxin-2 recycling is inhibited in sickle cell disease on mice and human Ouyang An essential role of nuclear receptor binding factor-2 (NRBF-2) in learning and memory Pati HDAC1, NOS3, and circadian clock gene expression in the endothelium Quiles Differential Regulation of miRNA and mRNA Exp ...
... Peroxiredoxin-2 recycling is inhibited in sickle cell disease on mice and human Ouyang An essential role of nuclear receptor binding factor-2 (NRBF-2) in learning and memory Pati HDAC1, NOS3, and circadian clock gene expression in the endothelium Quiles Differential Regulation of miRNA and mRNA Exp ...
professional certificate in gerontology
... Prerequisite: Consent of instructor. This course is designed to sensitize students to the needs of the frail elderly, the most vulnerable portion of the elderly population. Students will learn to assess the physical, psychological and social factors which contribute to the maintenance of the frail e ...
... Prerequisite: Consent of instructor. This course is designed to sensitize students to the needs of the frail elderly, the most vulnerable portion of the elderly population. Students will learn to assess the physical, psychological and social factors which contribute to the maintenance of the frail e ...
oxidation, reduction, redox potential, citric acid cycle, respiratory
... Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are high reactive atoms or molecules containing free unpaired electrons. ROS include reactive molecules such are oxygen radicals, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), hydroxyl radical OH. and superoxide O2-. Reactive nitrogen species (RNS) have similar characteristic and function ...
... Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are high reactive atoms or molecules containing free unpaired electrons. ROS include reactive molecules such are oxygen radicals, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), hydroxyl radical OH. and superoxide O2-. Reactive nitrogen species (RNS) have similar characteristic and function ...
What is Mitochondrial Disease?
... abnormalities in the brain stem, cerebellum, and basal ganglia, and often accompanied by elevated lactic acid levels in the blood or cerebrospinal fluid. Leigh syndrome may be caused by the NARP mutation, the MERRF mutation, complex I deficiency, cytochrome oxidase (COX) deficiency, pyruvate dehydro ...
... abnormalities in the brain stem, cerebellum, and basal ganglia, and often accompanied by elevated lactic acid levels in the blood or cerebrospinal fluid. Leigh syndrome may be caused by the NARP mutation, the MERRF mutation, complex I deficiency, cytochrome oxidase (COX) deficiency, pyruvate dehydro ...
Genetic and molecular determinants of human ageing and longevity
... - DANISH AGING RESEARCH CENTER www.sdu.dk/darc ...
... - DANISH AGING RESEARCH CENTER www.sdu.dk/darc ...
Cell death in PD-the case for mitochondria
... • Mutations in this gene encoding PTEN (Phosphatase and tensin homologue)-induced putative kinase 1(PINK-1) cause aut. recessive PD. • Mitochondrial protein kinase, substrates unknown • Targets to mitochondria • K/O in Drosophila assoc. with mitochondrial dysfunction, reduced respiratory chain activ ...
... • Mutations in this gene encoding PTEN (Phosphatase and tensin homologue)-induced putative kinase 1(PINK-1) cause aut. recessive PD. • Mitochondrial protein kinase, substrates unknown • Targets to mitochondria • K/O in Drosophila assoc. with mitochondrial dysfunction, reduced respiratory chain activ ...
... isocitrate can be facilitated by NADPH-linked IDH2, resulting in increased citrate synthesis. Mitochondrial citrate can be exported into the cytosol, where isocitrate can be converted to αKG by NADP+-linked IDH1. Mutant IDH1 or IDH2 oxidize NADPH back to NADP+ and reduce αKG to R(–)-2-hydroxyglutara ...
Healthy Aging Communities Dimensions
... This will most likely be achieved when communities are safe, promote health and wellbeing and use health services and community programs to prevent or minimize disease. (Adapted from WV Rural Healthy Aging Network, West Virginia University Center on Aging: www.hsc.wvu.edu/coa/rhan/ ) ...
... This will most likely be achieved when communities are safe, promote health and wellbeing and use health services and community programs to prevent or minimize disease. (Adapted from WV Rural Healthy Aging Network, West Virginia University Center on Aging: www.hsc.wvu.edu/coa/rhan/ ) ...
Mechanisms
... Reactions with target molecules Cellular deregulation Repair mechanisms “Essentials of Toxicology” by Klaassen Curtis D. and Watkins John B ...
... Reactions with target molecules Cellular deregulation Repair mechanisms “Essentials of Toxicology” by Klaassen Curtis D. and Watkins John B ...
Document
... for an extended period of time (many hours to many days; or all the time…) then they will produce a variety of inflammatory signaling molecules that produces an inflammatory response… Leading to even more disregulated S-T activity and more ROS… ...
... for an extended period of time (many hours to many days; or all the time…) then they will produce a variety of inflammatory signaling molecules that produces an inflammatory response… Leading to even more disregulated S-T activity and more ROS… ...
Ubiquinone
... The role of mitochondria in apoptosis • When cell receives a signal for apoptosis, one consequence is the permeability of the outer mitochondrial membrane will increase, allowing cytochrome c release. • The release of cytochrome c will activate caspase 9, which will initiate the protein ...
... The role of mitochondria in apoptosis • When cell receives a signal for apoptosis, one consequence is the permeability of the outer mitochondrial membrane will increase, allowing cytochrome c release. • The release of cytochrome c will activate caspase 9, which will initiate the protein ...
Healthy Aging
... Chronic and Degenerative diseaseheart disease, stroke, neoplastic diseases, respiratory diseases. Gender related-females have lower mortality rates, but this decreases with age and begins to even out with some exceptions-stroke and suicide-read pages 16-21 in the Fact Book ...
... Chronic and Degenerative diseaseheart disease, stroke, neoplastic diseases, respiratory diseases. Gender related-females have lower mortality rates, but this decreases with age and begins to even out with some exceptions-stroke and suicide-read pages 16-21 in the Fact Book ...
Stroma
... 8. Name three(3) ways that pyruvate is modified as it moves into to mitochondrion and prepares to enter Kreb’s cycle. 9. Describe the formation of citric acid in Kreb’s cycle. How many carbons does citric acid have? 10. For glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle and electron transport, list the following: locatio ...
... 8. Name three(3) ways that pyruvate is modified as it moves into to mitochondrion and prepares to enter Kreb’s cycle. 9. Describe the formation of citric acid in Kreb’s cycle. How many carbons does citric acid have? 10. For glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle and electron transport, list the following: locatio ...
Stroma
... What is the source of electrons for the electron transport chain? Describe how ATP is made in the electron transport chain. What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain? Provide the summary chemical equation for cellular respiration and explain the origin of each of the reacta ...
... What is the source of electrons for the electron transport chain? Describe how ATP is made in the electron transport chain. What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain? Provide the summary chemical equation for cellular respiration and explain the origin of each of the reacta ...
Ethical Issues on Aging and Longevity
... Technology The mechanism of aging is now more understood. This results in attempts to prolong and extend ‘healthy lifespan.’ Main motivation of modern medicine: avoid death at all cost. ...
... Technology The mechanism of aging is now more understood. This results in attempts to prolong and extend ‘healthy lifespan.’ Main motivation of modern medicine: avoid death at all cost. ...
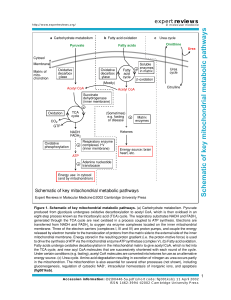
Schematic of key mitochondrial metabolic pathways
... generated through the TCA cycle are next oxidised in a process coupled to ATP synthesis. Electrons are transferred from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen via enzyme complexes located on the inner mitochondrial membrane. Three of the electron carriers (complexes I, III and IV) are proton pumps, and couple the ...
... generated through the TCA cycle are next oxidised in a process coupled to ATP synthesis. Electrons are transferred from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen via enzyme complexes located on the inner mitochondrial membrane. Three of the electron carriers (complexes I, III and IV) are proton pumps, and couple the ...
Muscular mitochondrial respiratory chain dysfunction in a rodent
... ipsilateral and contralateral limbs; this is most likely due to the 'spill-over' of toxin crossing the midline during the injection of 6-OHDA (Sliwinski et al., 2005). The present study suggests a correlation, in PD, between the effects of the lesion to the substantia nigra and the observed skeletal ...
... ipsilateral and contralateral limbs; this is most likely due to the 'spill-over' of toxin crossing the midline during the injection of 6-OHDA (Sliwinski et al., 2005). The present study suggests a correlation, in PD, between the effects of the lesion to the substantia nigra and the observed skeletal ...
mitochondria and aging - American Federation for Aging Research
... turn decreases the life span of the insects from two months to about a week. The injury caused by free radicals initiates a self-perpetuating cycle in which oxidative damage impairs mitochondrial function, which results in the generation of even greater amounts of oxygen-free radicals. Over time, ...
... turn decreases the life span of the insects from two months to about a week. The injury caused by free radicals initiates a self-perpetuating cycle in which oxidative damage impairs mitochondrial function, which results in the generation of even greater amounts of oxygen-free radicals. Over time, ...
mitochondria and aging - American Federation for Aging Research
... turn decreases the life span of the insects from two months to about a week. The injury caused by free radicals initiates a self-perpetuating cycle in which oxidative damage impairs mitochondrial function, which results in the generation of even greater amounts of oxygen-free radicals. Over time, ...
... turn decreases the life span of the insects from two months to about a week. The injury caused by free radicals initiates a self-perpetuating cycle in which oxidative damage impairs mitochondrial function, which results in the generation of even greater amounts of oxygen-free radicals. Over time, ...
Château Hostens-Picant blanc 2008
... The harvest was made by hand, followed by a selective hand sorting. The vinification The grapes have had a pelicullar maceration for 24 hours followed by a gentle pneumatic press out. The fermentation is made in oak barrels (100% brand new). Aging will be made on fine lees together with periodic sti ...
... The harvest was made by hand, followed by a selective hand sorting. The vinification The grapes have had a pelicullar maceration for 24 hours followed by a gentle pneumatic press out. The fermentation is made in oak barrels (100% brand new). Aging will be made on fine lees together with periodic sti ...
Free-radical theory of aging

The free radical theory of aging (FRTA) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time. A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell. While a few free radicals such as melanin are not chemically reactive, most biologically-relevant free radicals are highly reactive. For most biological structures, free radical damage is closely associated with oxidative damage. Antioxidants are reducing agents, and limit oxidative damage to biological structures by passivating them from free radicals.Strictly speaking, the free radical theory is only concerned with free radicals such as superoxide ( O2− ), but it has since been expanded to encompass oxidative damage from other reactive oxygen species such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), or peroxynitrite (OONO−).Denham Harman first proposed the free radical theory of aging in the 1950s, and in the 1970s extended the idea to implicate mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species.In some model organisms, such as yeast and Drosophila, there is evidence that reducing oxidative damage can extend lifespan. In mice, interventions that enhance oxidative damage generally shorten lifespan. However, in roundworms (Caenorhabditis elegans), blocking the production of the naturally occurring antioxidant superoxide dismutase has recently been shown to increase lifespan. Whether reducing oxidative damage below normal levels is sufficient to extend lifespan remains an open and controversial question.