And the measurement of inflation
... Output and employment decline while the price level is rising Supply shocks have been a major source of cost-push inflation, typically due to dramatic increases in the price of raw materials or energy • EX: Oil embargoes of the early 1970s caused cost-push inflation ...
... Output and employment decline while the price level is rising Supply shocks have been a major source of cost-push inflation, typically due to dramatic increases in the price of raw materials or energy • EX: Oil embargoes of the early 1970s caused cost-push inflation ...
Practice Midterm 2
... 2. When the Fed buys and sells bonds to private bank to increase or decrease the money supply. 3. both increase 4. Monetary policy is controlled by the Fed and is less subject to political pressure than fiscal policy, but monetary policy. 5. inflation 6. it equals #unemployed/total labor force 7. th ...
... 2. When the Fed buys and sells bonds to private bank to increase or decrease the money supply. 3. both increase 4. Monetary policy is controlled by the Fed and is less subject to political pressure than fiscal policy, but monetary policy. 5. inflation 6. it equals #unemployed/total labor force 7. th ...
Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Definition
... Definition: An index designed to measure the change in price of a fixed market basket of goods and services. The market basket of goods and services is representative of the purchases of a typical urban consumer. The index is intended to measure pure price change only; attempts are made to remove ch ...
... Definition: An index designed to measure the change in price of a fixed market basket of goods and services. The market basket of goods and services is representative of the purchases of a typical urban consumer. The index is intended to measure pure price change only; attempts are made to remove ch ...
Mrs. Thompson`s Notes on Defining, Calculating, and Measuring
... a. The CPI reflects how costs of purchases by families change over time b. The CPI is based on the period 1982-1984 (aggregate “base year”). To measure the prices, the Bureau of Labor Statistics sends employees to 23,000 stores in 87 cities and tabulates approximately 80,000 prices each month. The g ...
... a. The CPI reflects how costs of purchases by families change over time b. The CPI is based on the period 1982-1984 (aggregate “base year”). To measure the prices, the Bureau of Labor Statistics sends employees to 23,000 stores in 87 cities and tabulates approximately 80,000 prices each month. The g ...
the July Review - Blue Water Capital Advisors
... This report is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute an offer or solicitation to purchase or sell any security or commodity and is not intended to provide specific advice or recommendations for any individual. To determine which investment(s) may be appropriate for you, co ...
... This report is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute an offer or solicitation to purchase or sell any security or commodity and is not intended to provide specific advice or recommendations for any individual. To determine which investment(s) may be appropriate for you, co ...
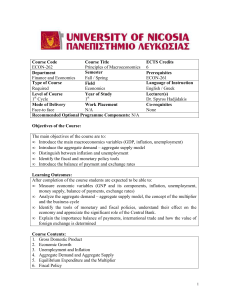
ECON-262 Principles of Macroeconomics
... • Distinguish between inflation and unemployment • Identify the fiscal and monetary policy tools • Introduce the balance of payment and exchange rates Learning Outcomes: After completion of the course students are expected to be able to: • Measure economic variables (GNP and its components, inflatio ...
... • Distinguish between inflation and unemployment • Identify the fiscal and monetary policy tools • Introduce the balance of payment and exchange rates Learning Outcomes: After completion of the course students are expected to be able to: • Measure economic variables (GNP and its components, inflatio ...
Name: KEY Date: ______ Class Period: ______ Chapter 3 Review
... B.) What is the purpose of the GDP? To determine how well an economy is performing in a given country. ...
... B.) What is the purpose of the GDP? To determine how well an economy is performing in a given country. ...
Slide 1
... AS is Phillips curve with substitution for expected inflation Note that we have moved up one derivative in prices from introductory AS-AD because Phillips curve related to inflation. ...
... AS is Phillips curve with substitution for expected inflation Note that we have moved up one derivative in prices from introductory AS-AD because Phillips curve related to inflation. ...
投影片 1
... ‧ Gul-Pesendorfer is very unexplored model, and many people like it more than hyperbolics. Does it lead to different results than hyperbolics? It’s not well understood. ‧ Frederick, Loewenstein, and O’Donoghue (JEL 2002) — review of time discounting. ...
... ‧ Gul-Pesendorfer is very unexplored model, and many people like it more than hyperbolics. Does it lead to different results than hyperbolics? It’s not well understood. ‧ Frederick, Loewenstein, and O’Donoghue (JEL 2002) — review of time discounting. ...
Presentation
... Lack of lots, gun shy lenders, high prices, rising rates, SF gets better slowly ...
... Lack of lots, gun shy lenders, high prices, rising rates, SF gets better slowly ...
William A. Niskanen POLITICAL GUIDANCE ON MONETARY POLICY
... tions, and a price rule can lead to considerable instability in other markets. The long experience with the several types of gold standards, for example, included several short periods ofinflation caused by major gold discoveries, long periods of deflation, frequent recessions, and the Great Depress ...
... tions, and a price rule can lead to considerable instability in other markets. The long experience with the several types of gold standards, for example, included several short periods ofinflation caused by major gold discoveries, long periods of deflation, frequent recessions, and the Great Depress ...
study guide > the ascent of money part 1
... COMPARATIVELY SPEAKING FAILING TO PAY DEBT OBLIGATIONS IN MEMPHIS HAVE LESS _______________ STIGMA AND IT IS CONSIDERABLY ________________ TO RID YOURSELF OF DEBT PAYMENTS. WHAT IS THE PHILOSOPHY BEHIND THE EASE OF BANKRUPTCY IN THE UNITED STATES? ...
... COMPARATIVELY SPEAKING FAILING TO PAY DEBT OBLIGATIONS IN MEMPHIS HAVE LESS _______________ STIGMA AND IT IS CONSIDERABLY ________________ TO RID YOURSELF OF DEBT PAYMENTS. WHAT IS THE PHILOSOPHY BEHIND THE EASE OF BANKRUPTCY IN THE UNITED STATES? ...
Business Cycles and Fluctuations
... change in the operations of the economy reduces a demand for workers & their skills • Consumer tastes change and therefore causes certain goods to no longer be demanded. ...
... change in the operations of the economy reduces a demand for workers & their skills • Consumer tastes change and therefore causes certain goods to no longer be demanded. ...
inflasi - E-conosmart.com
... Inflation is a rising prices of goods and services in general and continuously over a certain period ...
... Inflation is a rising prices of goods and services in general and continuously over a certain period ...
Inflation
... goods and services in an economy over a period of time. • The term "inflation" once referred to increases in the money supply (monetary inflation); however, the relationship between money supply and price levels have led to its primary use today in describing price inflation. • A loss of purchasing ...
... goods and services in an economy over a period of time. • The term "inflation" once referred to increases in the money supply (monetary inflation); however, the relationship between money supply and price levels have led to its primary use today in describing price inflation. • A loss of purchasing ...
Exam I from Summer 2006
... recently, both, Ford and GM made announcements that they will be closing their plants in Atlanta leading to unemployment amongst their workers c) In 2002 the tourism industry suffered a decline and many hotel/restaurant workers lost their jobs. In less than two years the recession in the industry en ...
... recently, both, Ford and GM made announcements that they will be closing their plants in Atlanta leading to unemployment amongst their workers c) In 2002 the tourism industry suffered a decline and many hotel/restaurant workers lost their jobs. In less than two years the recession in the industry en ...
Workshop in economic terms
... • Rising wages and material costs may lead to the upward pressure on price – cost-push inflation. • Furthermore, excessive spending and/or heavy borrowing due to a budget deficit by the federal government can be inflationary. ...
... • Rising wages and material costs may lead to the upward pressure on price – cost-push inflation. • Furthermore, excessive spending and/or heavy borrowing due to a budget deficit by the federal government can be inflationary. ...
Document
... Stop-Go Policy Cycle Policy that switches from expansionary to contractionary, and so on ...
... Stop-Go Policy Cycle Policy that switches from expansionary to contractionary, and so on ...
Phoenix Society of Financial Analysts and Arizona State University Business... ASU, Memorial Union - Ventana Room
... Now, one thing that helps keep inflation expectations low is public confidence that the Fed means what it says about pledging to keep inflationary pressures in check. I'd say it's possible that this change in expectations is due at least partly to the Fed's credibility on this point. ...
... Now, one thing that helps keep inflation expectations low is public confidence that the Fed means what it says about pledging to keep inflationary pressures in check. I'd say it's possible that this change in expectations is due at least partly to the Fed's credibility on this point. ...
The Phillips Curve: Short Run and Long Run
... It suggested that if governments wanted to reduce unemployment it had to accept higher inflation as a trade-off. ...
... It suggested that if governments wanted to reduce unemployment it had to accept higher inflation as a trade-off. ...
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation reflects a reduction in the purchasing power per unit of money – a loss of real value in the medium of exchange and unit of account within the economy. A chief measure of price inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index (normally the consumer price index) over time. The opposite of inflation is deflation.Inflation affects an economy in various ways, both positive and negative. Negative effects of inflation include an increase in the opportunity cost of holding money, uncertainty over future inflation which may discourage investment and savings, and if inflation were rapid enough, shortages of goods as consumers begin hoarding out of concern that prices will increase in the future.Inflation also has positive effects: Fundamentally, inflation gives everyone an incentive to spend and invest, because if they don't, their money will be worth less in the future. This increase in spending and investment can benefit the economy. However it may also lead to sub-optimal use of resources. Inflation reduces the real burden of debt, both public and private. If you have a fixed-rate mortgage on your house, your salary is likely to increase over time due to wage inflation, but your mortgage payment will stay the same. Over time, your mortgage payment will become a smaller percentage of your earnings, which means that you will have more money to spend. Inflation keeps nominal interest rates above zero, so that central banks can reduce interest rates, when necessary, to stimulate the economy. Inflation reduces unemployment to the extent that unemployment is caused by nominal wage rigidity. When demand for labor falls but nominal wages do not, as typically occurs during a recession, the supply and demand for labor cannot reach equilibrium, and unemployment results. By reducing the real value of a given nominal wage, inflation increases the demand for labor, and therefore reduces unemployment.Economists generally believe that high rates of inflation and hyperinflation are caused by an excessive growth of the money supply. However, money supply growth does not necessarily cause inflation. Some economists maintain that under the conditions of a liquidity trap, large monetary injections are like ""pushing on a string"". Views on which factors determine low to moderate rates of inflation are more varied. Low or moderate inflation may be attributed to fluctuations in real demand for goods and services, or changes in available supplies such as during scarcities. However, the consensus view is that a long sustained period of inflation is caused by money supply growing faster than the rate of economic growth.Today, most economists favor a low and steady rate of inflation. Low (as opposed to zero or negative) inflation reduces the severity of economic recessions by enabling the labor market to adjust more quickly in a downturn, and reduces the risk that a liquidity trap prevents monetary policy from stabilizing the economy. The task of keeping the rate of inflation low and stable is usually given to monetary authorities. Generally, these monetary authorities are the central banks that control monetary policy through the setting of interest rates, through open market operations, and through the setting of banking reserve requirements.