Presentation
... What is the anatomy of a volcano? •Vent: opening from which lava flows •Crater: funnel-shaped pit or depression at top of volcano •Caldera:craters whose walls have collapsed ...
... What is the anatomy of a volcano? •Vent: opening from which lava flows •Crater: funnel-shaped pit or depression at top of volcano •Caldera:craters whose walls have collapsed ...
Types of Volcanoes
... text inAthe first row. 11. Delete this text box when you are done. erupting or expected to erupt eventually. ...
... text inAthe first row. 11. Delete this text box when you are done. erupting or expected to erupt eventually. ...
Volcanoes - LambertEarth
... through which magma and volcanic gases pass. Explosion of a volcanic eruption can turn an entire ...
... through which magma and volcanic gases pass. Explosion of a volcanic eruption can turn an entire ...
MAR110 LECTURE #10 Plate Tectonics Volcanoes
... “bombs” (small to large pieces of solidified magma) and at times huge amounts of smoke (fine particles) and somewhat larger ash which tends to settle back to earth in the region. Besides slower lava flows, this kind of volcanic action can also produce superheated, high-speed pyroclastic flows that i ...
... “bombs” (small to large pieces of solidified magma) and at times huge amounts of smoke (fine particles) and somewhat larger ash which tends to settle back to earth in the region. Besides slower lava flows, this kind of volcanic action can also produce superheated, high-speed pyroclastic flows that i ...
Volcanoes lesson 2
... collapse of an ancient volcano, posthumously named Mount Mazama. This volcano violently erupted approximately 7700 years ago. The basin was formed after the top 5000 feet of the volcano collapsed. Subsequent lava flows sealed the bottom, allowing the caldera to fill with approximately 4.6 trillion g ...
... collapse of an ancient volcano, posthumously named Mount Mazama. This volcano violently erupted approximately 7700 years ago. The basin was formed after the top 5000 feet of the volcano collapsed. Subsequent lava flows sealed the bottom, allowing the caldera to fill with approximately 4.6 trillion g ...
Types of Volcanoes Article File
... Shield volcanoes, the third type of volcano, are built almost entirely of fluid lava flows. Flow after flow pours out in all directions from a central summit vent, or group of vents, building a broad, gently sloping cone of flat, domical shape, with a profile much like that of a warrior's shield. Th ...
... Shield volcanoes, the third type of volcano, are built almost entirely of fluid lava flows. Flow after flow pours out in all directions from a central summit vent, or group of vents, building a broad, gently sloping cone of flat, domical shape, with a profile much like that of a warrior's shield. Th ...
Principal Types of Volcanoes
... Flow after flow pours out in all directions from a central summit vent, or group of vents, ...
... Flow after flow pours out in all directions from a central summit vent, or group of vents, ...
Volcano Glossary III
... of magma with external water (groundwater or surface water). Ash can rise very high during an eruption and form a very dense ash cloud. ...
... of magma with external water (groundwater or surface water). Ash can rise very high during an eruption and form a very dense ash cloud. ...
32 - Cal State LA - Instructional Web Server
... • Describe the landscapes that result from volcanism ...
... • Describe the landscapes that result from volcanism ...
volcano powerpoint final
... Today two million people live in the immediate vicinity of Mount Vesuvius. This mountain has erupted more than 50 times since the eruption in 79 A.D., when it buried Pompeii and its sister city, Herculaneum. After Pompeii was buried and lost to history, the volcano continued to erupt every 100 yea ...
... Today two million people live in the immediate vicinity of Mount Vesuvius. This mountain has erupted more than 50 times since the eruption in 79 A.D., when it buried Pompeii and its sister city, Herculaneum. After Pompeii was buried and lost to history, the volcano continued to erupt every 100 yea ...
Review for Chapter 9 – Volcanoes
... 1. What kind of eruptions come from … a. Basaltic lava? b. Andesedic Lava? c. Rhyolitic lava? 2. How much silica is in… a. Basaltic lava? b. Andesedic Lava? c. Rhyolitic lava? 3. Out of the 3 above, what has the coolest magma? What formed Shasta, Vesuvius (Italy), Pompei? 4. What forms at a hot spot ...
... 1. What kind of eruptions come from … a. Basaltic lava? b. Andesedic Lava? c. Rhyolitic lava? 2. How much silica is in… a. Basaltic lava? b. Andesedic Lava? c. Rhyolitic lava? 3. Out of the 3 above, what has the coolest magma? What formed Shasta, Vesuvius (Italy), Pompei? 4. What forms at a hot spot ...
Chapter 12 Section 4
... What is the most common volcanic gas? Water vapor What other gases can be expected? Carbon dioxide and sulfur compounds All of gasses that are expelled are super heated!! Evidence has shown that volcanoes contribute enough greenhouse gas to affect climate long after the eruption has ended! ...
... What is the most common volcanic gas? Water vapor What other gases can be expected? Carbon dioxide and sulfur compounds All of gasses that are expelled are super heated!! Evidence has shown that volcanoes contribute enough greenhouse gas to affect climate long after the eruption has ended! ...
Volcano Activity
... Form a hypothesis about where you think the most hazardous volcanoes are located on Earth. Think about the potential risk to people and property near the volcano when formulating your hypothesis. Objectives ...
... Form a hypothesis about where you think the most hazardous volcanoes are located on Earth. Think about the potential risk to people and property near the volcano when formulating your hypothesis. Objectives ...
What do we expect in a volcanic eruption?
... • Lava flows from from others (called some pyroclastics. Better • Range from mafic than fireworks? (e.g. basalt) to • You bet!!! felsic, like all ign rx • Rocks may form from ...
... • Lava flows from from others (called some pyroclastics. Better • Range from mafic than fireworks? (e.g. basalt) to • You bet!!! felsic, like all ign rx • Rocks may form from ...
Volcanic Activity
... • Site of volcano warning system 1991 - 43 scientists and journalists were killed by a three-mile-long pyroclastic flow, a fast-moving river of hot gas and rock that can speed along at speeds up to 450 miles per hour. ...
... • Site of volcano warning system 1991 - 43 scientists and journalists were killed by a three-mile-long pyroclastic flow, a fast-moving river of hot gas and rock that can speed along at speeds up to 450 miles per hour. ...
Volcanic Landforms
... layers by multiple eruptions, sometimes recurring over hundreds of thousands of years, sometimes over a few hundred. Andesite magma (the most common but not the only magma type), tends to form composite cones. During some eruptions, cinders, bombs and blocks form a mountain or add height to one that ...
... layers by multiple eruptions, sometimes recurring over hundreds of thousands of years, sometimes over a few hundred. Andesite magma (the most common but not the only magma type), tends to form composite cones. During some eruptions, cinders, bombs and blocks form a mountain or add height to one that ...
Document
... Nuee ardente: pyroclastic flow, of searing superheated gas and incandescent volcanic ash and dust Mount Pelee, on the Carribean island of Martinique, 1902 eruption. All but 2 of the more than 20,000 people in the town of St. Pierre were killed. ...
... Nuee ardente: pyroclastic flow, of searing superheated gas and incandescent volcanic ash and dust Mount Pelee, on the Carribean island of Martinique, 1902 eruption. All but 2 of the more than 20,000 people in the town of St. Pierre were killed. ...
Faizan - WordPress.com
... A bowl or sheild shaped Volcano in the middle with long-gentle slopes made by basaltic lava flows,called flood basalt. ...
... A bowl or sheild shaped Volcano in the middle with long-gentle slopes made by basaltic lava flows,called flood basalt. ...
Volcano ppt that goes with notes
... Active volcanoes are erupting, have erupted recently, or have had at least one eruption in the last 10,000 years and are expected to erupt again in the near future. A dormant volcano is a sleeping volcano. Dormant volcanoes are not active now, but may become active again in the future. ...
... Active volcanoes are erupting, have erupted recently, or have had at least one eruption in the last 10,000 years and are expected to erupt again in the near future. A dormant volcano is a sleeping volcano. Dormant volcanoes are not active now, but may become active again in the future. ...
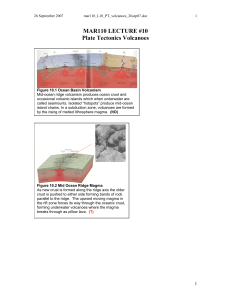
Axial Seamount

Axial Seamount (also Coaxial Seamount or Axial Volcano) is a seamount and submarine volcano located on the Juan de Fuca Ridge, approximately 480 km (298 mi) west of Cannon Beach, Oregon. Standing 1,100 m (3,609 ft) high, Axial Seamount is the youngest volcano and current eruptive center of the Cobb-Eickelberg Seamount chain. Located at the center of both a geological hotspot and a mid-ocean ridge, the seamount is geologically complex, and its origins are still poorly understood. Axial Seamount is set on a long, low-lying plateau, with two large rift zones trending 50 km (31 mi) to the northeast and southwest of its center. The volcano features an unusual rectangular caldera, and its flanks are pockmarked by fissures, vents, sheet flows, and pit craters up to 100 m (328 ft) deep; its geology is further complicated by its intersection with several smaller seamounts surrounding it.Axial Seamount was first detected in the 1970s by satellite altimetry, and mapped and explored by Pisces IV, DSV Alvin, and others through the 1980s. A large package of sensors was dropped on the seamount through 1992, and the New Millennium Observatory was established on its flanks in 1996. Axial Seamount received significant scientific attention following the seismic detection of a submarine eruption at the volcano in January 1998, the first time a submarine eruption had been detected and followed in situ. Subsequent cruises and analysis showed that the volcano had generated lava flows up to 13 m (43 ft) thick, and the total eruptive volume was found to be 18,000–76,000 km3 (4,300–18,200 cu mi). Axial Seamount erupted again in April 2011, producing a mile-wide lava flow and fulfilling a 16-year cycle that had been predicted in 2006.