Volcanoes
... size of cinders into the air High in gas-rich basaltic magma small, usually only erupt once (maybe a few times) ...
... size of cinders into the air High in gas-rich basaltic magma small, usually only erupt once (maybe a few times) ...
Did a Massive Volcano Cause Massive Extinction?!
... • Produce both lava and pyroclastic material that can reach up to 120 mph! • Usually found in the Ring of Fire, which is a zone of volcanoes that circles the Pacific Ocean. ...
... • Produce both lava and pyroclastic material that can reach up to 120 mph! • Usually found in the Ring of Fire, which is a zone of volcanoes that circles the Pacific Ocean. ...
Volcanic Eruptions
... • What causes these different types of volcanoes to form? • The different ways in which they erupt and the different materials that are erupted. ...
... • What causes these different types of volcanoes to form? • The different ways in which they erupt and the different materials that are erupted. ...
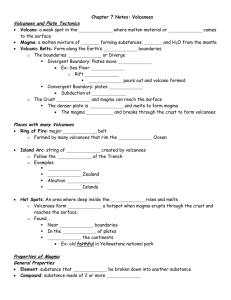
Chapter 7 Notes: Volcanoes Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcano Magma
... Volcano: a weak spot in the _______________ where molten material or _______________ comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of ________ forming substances, ________ and H2O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form along the Earth’s _______________ boundaries o The boundaries _______________ or Div ...
... Volcano: a weak spot in the _______________ where molten material or _______________ comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of ________ forming substances, ________ and H2O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form along the Earth’s _______________ boundaries o The boundaries _______________ or Div ...
Geology Final Exam Review 1st Semester What drives Earth`s rock
... a. Describe what causes the different textures. 3. Tell the differences between gabbro and granite. 4. List the 3 main compositional types of igneous rocks. a. Describe the mineral differences for each type. 5. List the 3 main types of volcanoes. a. Describe the differences between each volcano. (Hi ...
... a. Describe what causes the different textures. 3. Tell the differences between gabbro and granite. 4. List the 3 main compositional types of igneous rocks. a. Describe the mineral differences for each type. 5. List the 3 main types of volcanoes. a. Describe the differences between each volcano. (Hi ...
Geo Fun - Latitude Festival
... Examine volcanic rocks, learn about the planet through a geologist’s lens, and understand volcanic hazards through a series of safe experiments with our Earth Science team. KS2 Curriculum Link: Develop understanding of the nature, processes and methods of science through different types of science e ...
... Examine volcanic rocks, learn about the planet through a geologist’s lens, and understand volcanic hazards through a series of safe experiments with our Earth Science team. KS2 Curriculum Link: Develop understanding of the nature, processes and methods of science through different types of science e ...
Earthquakes originate at a point
... Hypothesis that Earth’s continents were joined as a single landmass that broke apart about 200 mya (million years ago) and slowly moved to their present locations Alfred Wegener 25. What evidence was there for continental drift? Explain. Fossils-Similar fossils of several different plants and animal ...
... Hypothesis that Earth’s continents were joined as a single landmass that broke apart about 200 mya (million years ago) and slowly moved to their present locations Alfred Wegener 25. What evidence was there for continental drift? Explain. Fossils-Similar fossils of several different plants and animal ...
VOLCANO NOTES
... lava. They are small volcanoes, about a mile across and up to a thousand feet high. They have very steep sides and usually have a small crater on top. These have a medium to explosive eruption ...
... lava. They are small volcanoes, about a mile across and up to a thousand feet high. They have very steep sides and usually have a small crater on top. These have a medium to explosive eruption ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... Beginning violent eruption with bombs, cinders, and ash from vent Followed by quiet eruption with lava flow that covers rock particles Large cone-shaped mountain result of many alternating eruptions Mount Vesuvius in Italy and Mount Etna in Sicily ...
... Beginning violent eruption with bombs, cinders, and ash from vent Followed by quiet eruption with lava flow that covers rock particles Large cone-shaped mountain result of many alternating eruptions Mount Vesuvius in Italy and Mount Etna in Sicily ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth - Chapter 4
... • Primarily water • Cause rock to melt at a lower temperature • Play an important role in subducting ocean plates ...
... • Primarily water • Cause rock to melt at a lower temperature • Play an important role in subducting ocean plates ...
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 9 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck
... • Primarily water • Cause rock to melt at a lower temperature • Play an important role in subducting ocean plates ...
... • Primarily water • Cause rock to melt at a lower temperature • Play an important role in subducting ocean plates ...
Nature and Products of Volcanic Eruptions
... Lava Flows • Basaltic lavas are much more fluid • Types of basaltic flows – Pahoehoe lava (resembles a twisted or ropey texture) – Aa lava (rough, jagged blocky texture) ...
... Lava Flows • Basaltic lavas are much more fluid • Types of basaltic flows – Pahoehoe lava (resembles a twisted or ropey texture) – Aa lava (rough, jagged blocky texture) ...
Warm up question What hypothesis is Alfred Wegener known for
... A place where material from the earths mantle has burned a whole through the crust ...
... A place where material from the earths mantle has burned a whole through the crust ...
Rock Cycle - The School District of Palm Beach County
... 7th Grade Science Summer Activity Week 1 Parent Information ...
... 7th Grade Science Summer Activity Week 1 Parent Information ...
DICHOTOMOUS KEY TO THE IGNEOUS ROCKS
... Igneous rocks break-up into two categories, Volcanic (extrusive) or Magmatic (underground from magmaintrusive). In general Extrusive or volcanic rocks either have holes (created from the gases that are released during and eruption) and are light weight or can be glassy and sharp. Intrusive, cool slo ...
... Igneous rocks break-up into two categories, Volcanic (extrusive) or Magmatic (underground from magmaintrusive). In general Extrusive or volcanic rocks either have holes (created from the gases that are released during and eruption) and are light weight or can be glassy and sharp. Intrusive, cool slo ...
lesson 24 effects of ash fall
... Magma is buoyont, and lighter than the solid rock that surrounds it, which is why it rises. ...
... Magma is buoyont, and lighter than the solid rock that surrounds it, which is why it rises. ...
Lassen Volcanic National Park
... Lassen Volcanic National Park is home to smoking fumaroles, meadows freckled with wildflowers, clear mountain lakes, and numerous volcanoes. Jagged peaks tell the story of its eruptive past while hot water continues to mold the land. Lassen Volcanic offers opportunities to discover the wonder and my ...
... Lassen Volcanic National Park is home to smoking fumaroles, meadows freckled with wildflowers, clear mountain lakes, and numerous volcanoes. Jagged peaks tell the story of its eruptive past while hot water continues to mold the land. Lassen Volcanic offers opportunities to discover the wonder and my ...
Lecture11_volcanic_landforms
... the gas is dissolved within the magma when the magma is under pressure. Gas bubbles and froth on surface of the lava, similar to bubbles on top of soda. Obsidian flow, Long Valley Caldera, California, was created by crustal collapse associated with an explosive eruption about 650,000 years ago. Sinc ...
... the gas is dissolved within the magma when the magma is under pressure. Gas bubbles and froth on surface of the lava, similar to bubbles on top of soda. Obsidian flow, Long Valley Caldera, California, was created by crustal collapse associated with an explosive eruption about 650,000 years ago. Sinc ...
Document
... Lahars are fast-moving mud flows. Two things together make a lahar: Thick, loose deposits of volcanic ash and water. The water can come in several ways: - A major rainstorm dumps water on the volcano. - An eruption melts large amounts of snow and ice on the flanks of the volcano. Lahars are more da ...
... Lahars are fast-moving mud flows. Two things together make a lahar: Thick, loose deposits of volcanic ash and water. The water can come in several ways: - A major rainstorm dumps water on the volcano. - An eruption melts large amounts of snow and ice on the flanks of the volcano. Lahars are more da ...
Word format
... When the pyroclastic material first gets ejected sideways from the volcano, the type of eruption is called a _____________________ (happened at Mt. St. Helens in 1980). ...
... When the pyroclastic material first gets ejected sideways from the volcano, the type of eruption is called a _____________________ (happened at Mt. St. Helens in 1980). ...
Super Volcanoes
... – this eruption was 2,500 times larger than the 1980 eruption of Mt. St. Helens – the caldera formed by this eruption was bigger than the state of Rhode Island – produced Huckleberry Ridge tuff, 500 – 2500 foot thick sheet of volcanic rock ...
... – this eruption was 2,500 times larger than the 1980 eruption of Mt. St. Helens – the caldera formed by this eruption was bigger than the state of Rhode Island – produced Huckleberry Ridge tuff, 500 – 2500 foot thick sheet of volcanic rock ...
VOLCANOES MR.OCHOA CHAPTER 6
... create dome mountains which form with rising magma being blocked by horizontal layers of rock . The magma pushes the layers to bend upward into a dome shape. Eventually the rock above the dome wears away, leaving it exposed. One example is the Black Hills in South Dakota. ...
... create dome mountains which form with rising magma being blocked by horizontal layers of rock . The magma pushes the layers to bend upward into a dome shape. Eventually the rock above the dome wears away, leaving it exposed. One example is the Black Hills in South Dakota. ...
Mount Pleasant Caldera

The Mount Pleasant Caldera is a large eroded Late Devonian volcanic caldera complex, located in the northern Appalachian Mountains of southwestern New Brunswick, Canada. It is one of few noticeable pre-Cenozoic calderas, and its formation is associated to a period of crustal thinning that followed the Acadian orogeny in the northern Appalachian Mountains.It sits relatively near to the coastline.