Volcanic Activity
... long tube in the ground that connects the magma chamber to Earth’s surface. Vent - an opening in the volcano where gases and molten rock leave. Lava flow – The area covered by lava as it pours out of a vent. Crater – A bowl-shaped area that may form at the top of a volcano around the volcano’s ...
... long tube in the ground that connects the magma chamber to Earth’s surface. Vent - an opening in the volcano where gases and molten rock leave. Lava flow – The area covered by lava as it pours out of a vent. Crater – A bowl-shaped area that may form at the top of a volcano around the volcano’s ...
Chapter 4 - Igneous Rocks
... crystallization of andesitic magma – Granitic magmas are more viscous than other magmas so they tend to lose their mobility before reaching the surface – Tend to produce large plutonic structures ...
... crystallization of andesitic magma – Granitic magmas are more viscous than other magmas so they tend to lose their mobility before reaching the surface – Tend to produce large plutonic structures ...
Igneous Rocks: Born of Fire
... – May be produced by interaction of basaltic magmas and more silica-rich rocks in the crust – May also evolve by magmatic differentiation – And incorporation of volatiles into the magma ...
... – May be produced by interaction of basaltic magmas and more silica-rich rocks in the crust – May also evolve by magmatic differentiation – And incorporation of volatiles into the magma ...
1 GS104 Lab Quiz 2 Study Guide - Taylor Sections Use your lecture
... Extrusive igneous rock = lava cools to form rock, via volcanic eruption fast cooling, small / microscopic crystals Intrusive igneous rock = magma cools to form rock, beneath Earth's surface slow cooling, large mineral crystals Porphyritic igneous rock = large mineral crystals floating in micro-cryst ...
... Extrusive igneous rock = lava cools to form rock, via volcanic eruption fast cooling, small / microscopic crystals Intrusive igneous rock = magma cools to form rock, beneath Earth's surface slow cooling, large mineral crystals Porphyritic igneous rock = large mineral crystals floating in micro-cryst ...
Volcano Science Highlights
... V44A-02: Magma reservoirs: How well do we know them, why does it matter, and how can we do better? (Invited) ...
... V44A-02: Magma reservoirs: How well do we know them, why does it matter, and how can we do better? (Invited) ...
The Critical Zone What is a caldera? The Valles Caldera
... area is prone to wildfire. Fire has been a common occurrence in forests of the Southwest for a long time, and at low intensity, it can be healthy for growth of the forest. However, recently the fires have intensified by burning hotter, and across more acreage. What might be causing this change? 7. V ...
... area is prone to wildfire. Fire has been a common occurrence in forests of the Southwest for a long time, and at low intensity, it can be healthy for growth of the forest. However, recently the fires have intensified by burning hotter, and across more acreage. What might be causing this change? 7. V ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... Materials associated with volcanic eruptions Pyroclastic materials • "Fire fragments" • Types of pyroclastic material ...
... Materials associated with volcanic eruptions Pyroclastic materials • "Fire fragments" • Types of pyroclastic material ...
ES11_Ch09_Lecture
... Materials associated with volcanic eruptions Pyroclastic materials • "Fire fragments" • Types of pyroclastic material ...
... Materials associated with volcanic eruptions Pyroclastic materials • "Fire fragments" • Types of pyroclastic material ...
volcanic activity guided notes
... a long tube in the ground that connects the magma chamber to Earth’s surface. __________ - an opening in the volcano where gases and molten rock leave. __________ ________ – The area covered by lava as it pours out of a vent. Crater – A _________-__________ area that may form at the top of a v ...
... a long tube in the ground that connects the magma chamber to Earth’s surface. __________ - an opening in the volcano where gases and molten rock leave. __________ ________ – The area covered by lava as it pours out of a vent. Crater – A _________-__________ area that may form at the top of a v ...
VolcanicHazards2
... Few fatalities are typically associated with basaltic lava eruptions, as neighborhoods, such as the one shown here, can be evacuated. Buildings and other human-made structures are not so lucky! ...
... Few fatalities are typically associated with basaltic lava eruptions, as neighborhoods, such as the one shown here, can be evacuated. Buildings and other human-made structures are not so lucky! ...
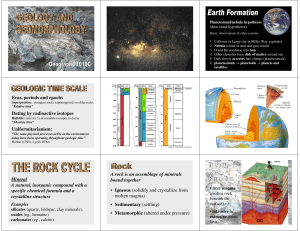
Eras, periods and epochs Dating by radioactive
... “The same physical processes active in the environment today have been operating throughout geologic time” Hutton (1795), Lyell (1830) Source: University of Calgary ...
... “The same physical processes active in the environment today have been operating throughout geologic time” Hutton (1795), Lyell (1830) Source: University of Calgary ...
Volcano Notes _filled in_
... -Living things also play a role in the story of rocks and rock formation. -Fossils are traces of organisms that are preserved as rocks. They can not only tell us what living things were living in the area, but also provide us clues about the climate and other conditions of the past. Fossils can also ...
... -Living things also play a role in the story of rocks and rock formation. -Fossils are traces of organisms that are preserved as rocks. They can not only tell us what living things were living in the area, but also provide us clues about the climate and other conditions of the past. Fossils can also ...
Lithosphere L > E Heat flowing in Earth`s core below the lithosphere
... “old” magma that either remains below ground (for example, as an intrusion) or is rising toward the surface. In this case, gases may escape continuously into the atmosphere from the soil, volcanic vents, fumaroles, and hydrothermal systems. ...
... “old” magma that either remains below ground (for example, as an intrusion) or is rising toward the surface. In this case, gases may escape continuously into the atmosphere from the soil, volcanic vents, fumaroles, and hydrothermal systems. ...
Lesson 2 - Humanities.Com
... Well it’s all down to the lava that makes the volcano. Shield volcanoes are made from a thin runny lava (called basalt). This lava will not get stuck in the volcano vent. The eruption will be freely flowing and gentle (like pouring water from a jug). They are found on constructive boundaries. Compos ...
... Well it’s all down to the lava that makes the volcano. Shield volcanoes are made from a thin runny lava (called basalt). This lava will not get stuck in the volcano vent. The eruption will be freely flowing and gentle (like pouring water from a jug). They are found on constructive boundaries. Compos ...
What Types of Igneous Processes Are Occurring Here?
... Rock 7. This medium-grained rock is a plutonic rock. It has a salt-and-pepper appearance, caused by the presence of felsic minerals (feldspar and quartz) and mafic minerals (mostly biotite mica). It is intermediate in composition. ...
... Rock 7. This medium-grained rock is a plutonic rock. It has a salt-and-pepper appearance, caused by the presence of felsic minerals (feldspar and quartz) and mafic minerals (mostly biotite mica). It is intermediate in composition. ...
volcanos
... 10. Hearing aids, glasses, mobility aids for elderly or vulnerable members of your house. ...
... 10. Hearing aids, glasses, mobility aids for elderly or vulnerable members of your house. ...
Volcanoes
... What is a Volcano? • Volcano–a mountain that forms when magma (As well as volcanic gases) reaches the surface ...
... What is a Volcano? • Volcano–a mountain that forms when magma (As well as volcanic gases) reaches the surface ...
Volcano Study Guide Extinct – Unlikely to erupt ever again Active
... Active – Likely to erupt in the near future ...
... Active – Likely to erupt in the near future ...
Lassen Peak Volcanic National Park
... •Abundant pyroclastic activity •deadly airborne debris •Explosive eruptions – very hazardous ...
... •Abundant pyroclastic activity •deadly airborne debris •Explosive eruptions – very hazardous ...
File
... Lava – melted rock that flows down the volcano Magma – melted rock inside the Earth Molten – melted, liquid Vent – a crack on the side of a volcano where magma can escape ...
... Lava – melted rock that flows down the volcano Magma – melted rock inside the Earth Molten – melted, liquid Vent – a crack on the side of a volcano where magma can escape ...
Igneous Bodies: Intrusives
... 550 active volcanoes (60% on Ring of Fire, 20% in Mediterrean, rest mainly on divergent boundaries) ...
... 550 active volcanoes (60% on Ring of Fire, 20% in Mediterrean, rest mainly on divergent boundaries) ...
volcano
... A volcano allows hot lava and smoke to leave from a magma chamber below the surface of the Earth. Volcanoes are generally found at different places on Earth. For example, in the oceans, Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust. For example the Hawaii was created f ...
... A volcano allows hot lava and smoke to leave from a magma chamber below the surface of the Earth. Volcanoes are generally found at different places on Earth. For example, in the oceans, Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust. For example the Hawaii was created f ...
The Rock Cycle
... • The more silica in the magma, the more explosive the eruption • Granite (same silica content as obsidian) • Gabbro (silica- poor) • Obsidian, rhyolite (silica- rich, like granite) • Basalt (gentle flow of lava, small grains) ...
... • The more silica in the magma, the more explosive the eruption • Granite (same silica content as obsidian) • Gabbro (silica- poor) • Obsidian, rhyolite (silica- rich, like granite) • Basalt (gentle flow of lava, small grains) ...
Mount Pleasant Caldera

The Mount Pleasant Caldera is a large eroded Late Devonian volcanic caldera complex, located in the northern Appalachian Mountains of southwestern New Brunswick, Canada. It is one of few noticeable pre-Cenozoic calderas, and its formation is associated to a period of crustal thinning that followed the Acadian orogeny in the northern Appalachian Mountains.It sits relatively near to the coastline.