Differences between a voltage balun and a current balun
... line without experiencing large losses, therefore a BALUN is required to provide an unbalanced to a balanced match. Voltage BALUNS: A voltage BALUN forces voltage potentials equal in amplitude but opposite in sign with reference to ground that is present at its output terminals. A voltage BALUN may ...
... line without experiencing large losses, therefore a BALUN is required to provide an unbalanced to a balanced match. Voltage BALUNS: A voltage BALUN forces voltage potentials equal in amplitude but opposite in sign with reference to ground that is present at its output terminals. A voltage BALUN may ...
2.6.4 Interfacing Outputs Word Document | GCE AS/A
... Motors are used in a wide range of electronic products where motion is the required result. The power of the motors varies considerably depending on the application but they all require quite large currents to make them work successfully, particularly at startup where the load current can be very hi ...
... Motors are used in a wide range of electronic products where motion is the required result. The power of the motors varies considerably depending on the application but they all require quite large currents to make them work successfully, particularly at startup where the load current can be very hi ...
Digital Insulation Resistance Testers
... Digital insulation testing up to 5000 Volts The Fluke 1550 is a digital insulation tester capable of testing switchgear, motors, generators and cables at up to 5000 V DC. It can be used for a wide range of tests: from simple spot checks to timed tests and breakdown tests. Measurement storage and PC ...
... Digital insulation testing up to 5000 Volts The Fluke 1550 is a digital insulation tester capable of testing switchgear, motors, generators and cables at up to 5000 V DC. It can be used for a wide range of tests: from simple spot checks to timed tests and breakdown tests. Measurement storage and PC ...
8-bit analog-to-digital converters with differential inputs
... successive-approximation logic to match an analog differential input voltage (VI+ – VI –) to a corresponding tap on the 256-resistor network. The most significant bit (MSB) is tested first. After eight comparisons (64 clock periods), an 8-bit binary code (1111 1111 = full scale) is transferred to an ...
... successive-approximation logic to match an analog differential input voltage (VI+ – VI –) to a corresponding tap on the 256-resistor network. The most significant bit (MSB) is tested first. After eight comparisons (64 clock periods), an 8-bit binary code (1111 1111 = full scale) is transferred to an ...
Digital Multi-meter and Oscilloscope
... oscilloscope”, but adapting the computer to act as an oscilloscope the function is not quite the same. The computer is acting more like a DMM, measuring voltage, but with time resolution, (e.g. 5000 samples per second). The Power Amplifier can produce voltage waveforms that are periodic in time. It ...
... oscilloscope”, but adapting the computer to act as an oscilloscope the function is not quite the same. The computer is acting more like a DMM, measuring voltage, but with time resolution, (e.g. 5000 samples per second). The Power Amplifier can produce voltage waveforms that are periodic in time. It ...
Results
... response consisted of a transient and steady state part. The type of transient response was dependent on the resistor used. It was shown that for resistors with small values, the system was underdamped, and the transient response of the output was a voltage oscillating around its steady state value. ...
... response consisted of a transient and steady state part. The type of transient response was dependent on the resistor used. It was shown that for resistors with small values, the system was underdamped, and the transient response of the output was a voltage oscillating around its steady state value. ...
Form B - PowerStream
... - certain abnormal system conditions such as over/under voltage , over/under frequency, open phase(s); - islanding Document Number: ...
... - certain abnormal system conditions such as over/under voltage , over/under frequency, open phase(s); - islanding Document Number: ...
Electrical Components and Circuits
... Electrical charge will not move through a conducting path unless there is a potential difference between the ends of the conductors ...
... Electrical charge will not move through a conducting path unless there is a potential difference between the ends of the conductors ...
ADM660 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Figure 1 shows the voltage inverting configuration, while Figure 2 shows the configuration for voltage doubling. An oscillator generating antiphase signals φ1 and φ2 controls switches S1, S2, and S3, S4. During φ1, switches S1 and S2 are closed charging C1 up to the voltage at V+. During φ2, S1 and ...
... Figure 1 shows the voltage inverting configuration, while Figure 2 shows the configuration for voltage doubling. An oscillator generating antiphase signals φ1 and φ2 controls switches S1, S2, and S3, S4. During φ1, switches S1 and S2 are closed charging C1 up to the voltage at V+. During φ2, S1 and ...
Action PAK AP4380 ® DC Input,
... status. Active line power is indicated by an illuminated LED. If the input signal is 10% more than full scale range, the LED will flash at 8Hz. Below 0%, the flash rate is 4Hz. ...
... status. Active line power is indicated by an illuminated LED. If the input signal is 10% more than full scale range, the LED will flash at 8Hz. Below 0%, the flash rate is 4Hz. ...
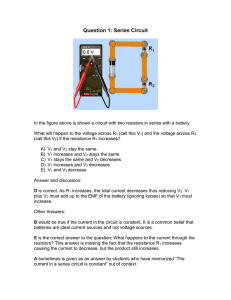
Question 1 - cloudfront.net
... D is correct. As R1 increases, the total current decreases thus reducing V2. V1 plus V2 must add up to the EMF of the battery (ignoring losses) so that V1 must increase. Other Answers: B would be true if the current in the circuit is constant. It is a common belief that batteries are ideal current s ...
... D is correct. As R1 increases, the total current decreases thus reducing V2. V1 plus V2 must add up to the EMF of the battery (ignoring losses) so that V1 must increase. Other Answers: B would be true if the current in the circuit is constant. It is a common belief that batteries are ideal current s ...
Common units of measure Introduction Reference Electrical
... Where appropriate, conversion factors are also given. This document presents some of the most common quantities used in electrical engineering, with an example of typical use. ...
... Where appropriate, conversion factors are also given. This document presents some of the most common quantities used in electrical engineering, with an example of typical use. ...
A Single-phase-to-three-phase Power Converter with an Active
... Figure 1(b) shows a conventional single-phase-to-three-phase power converter circuit with power factor correction (PFC) circuit. In order to suppress the harmonic currents, a boost chopper circuit is added to DC link in Figure 1(a). This circuit can obtain sinusoidal waveform of the input current be ...
... Figure 1(b) shows a conventional single-phase-to-three-phase power converter circuit with power factor correction (PFC) circuit. In order to suppress the harmonic currents, a boost chopper circuit is added to DC link in Figure 1(a). This circuit can obtain sinusoidal waveform of the input current be ...
DM-II PRO Digital Recorder / Data Logger
... • Comes as a complete kit, CT’s and PC software are included with product • Works with single and three phase systems (Y and delta) • Capable of recording all parameters (single or three phase) simultaneously • All readings are True RMS (TRMS) • User selectable rates allow recording from one hour to ...
... • Comes as a complete kit, CT’s and PC software are included with product • Works with single and three phase systems (Y and delta) • Capable of recording all parameters (single or three phase) simultaneously • All readings are True RMS (TRMS) • User selectable rates allow recording from one hour to ...
Naim Discrete Regulator
... the reference voltage and the regulator output voltage) and a single, common-emitter connected transistor with an active load that provides most of the open-loop voltage gain. Differences include the output stage where, because the output is DC rather than AC, a compound follower replaces the power ...
... the reference voltage and the regulator output voltage) and a single, common-emitter connected transistor with an active load that provides most of the open-loop voltage gain. Differences include the output stage where, because the output is DC rather than AC, a compound follower replaces the power ...
MX Programmable Power Source flyer
... The MX Series controller has a powerful AC and DC transient generation system that allows complex sequences of voltage, frequency and waveshapes to be generated. This further enhances the MX’s capability to simulate AC line conditions or DC disturbances. When combined with the multiphase arbitrary w ...
... The MX Series controller has a powerful AC and DC transient generation system that allows complex sequences of voltage, frequency and waveshapes to be generated. This further enhances the MX’s capability to simulate AC line conditions or DC disturbances. When combined with the multiphase arbitrary w ...
Electricity
... blown fuse with a new one. Too many appliances in use at the _____________________ is the most likely cause for the overheating of the circuit. Household Fuse Box ...
... blown fuse with a new one. Too many appliances in use at the _____________________ is the most likely cause for the overheating of the circuit. Household Fuse Box ...
ADA4850-1
... The ADA4850 family provides users with a true single-supply capability, allowing input signals to extend 200 mV below the negative rail and to within 2.2 V of the positive rail. The output of the amplifier can swing within 80 mV of either supply rail. With its combination of low price, excellent dif ...
... The ADA4850 family provides users with a true single-supply capability, allowing input signals to extend 200 mV below the negative rail and to within 2.2 V of the positive rail. The output of the amplifier can swing within 80 mV of either supply rail. With its combination of low price, excellent dif ...
Switched-mode power supply

A switched-mode power supply (switching-mode power supply, switch-mode power supply, SMPS, or switcher) is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently. Like other power supplies, an SMPS transfers power from a source, like mains power, to a load, such as a personal computer, while converting voltage and current characteristics. Unlike a linear power supply, the pass transistor of a switching-mode supply continually switches between low-dissipation, full-on and full-off states, and spends very little time in the high dissipation transitions, which minimizes wasted energy. Ideally, a switched-mode power supply dissipates no power. Voltage regulation is achieved by varying the ratio of on-to-off time. In contrast, a linear power supply regulates the output voltage by continually dissipating power in the pass transistor. This higher power conversion efficiency is an important advantage of a switched-mode power supply. Switched-mode power supplies may also be substantially smaller and lighter than a linear supply due to the smaller transformer size and weight.Switching regulators are used as replacements for linear regulators when higher efficiency, smaller size or lighter weight are required. They are, however, more complicated; their switching currents can cause electrical noise problems if not carefully suppressed, and simple designs may have a poor power factor.