2 Effects of Volcanic Eruptions
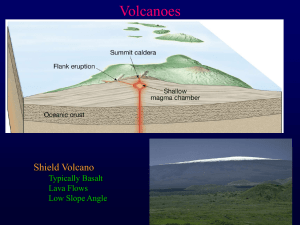
... volcanoes themselves. There are three main kinds of volcanoes: shield volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, and composite volcanoes. Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. ...
... volcanoes themselves. There are three main kinds of volcanoes: shield volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, and composite volcanoes. Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. ...
Chapter 13 Section 2
... Volcanic Eruptions Types of Magma/Lava • Mafic - describes magma or igneous rock that is rich in magnesium and iron and that is generally dark in color • Felsic - describes magma or igneous rock that is rich in feldspar and silica and that is generally light in color • Mafic rock commonly makes up t ...
... Volcanic Eruptions Types of Magma/Lava • Mafic - describes magma or igneous rock that is rich in magnesium and iron and that is generally dark in color • Felsic - describes magma or igneous rock that is rich in feldspar and silica and that is generally light in color • Mafic rock commonly makes up t ...
Volcanic Eruption Hazard Annex
... summit that contains a central vent or a clustered group of vents. Lava either flows through breaks in the crater wall or from fissures on the flanks of the cone. Lava, solidified within the fissu ...
... summit that contains a central vent or a clustered group of vents. Lava either flows through breaks in the crater wall or from fissures on the flanks of the cone. Lava, solidified within the fissu ...
Document
... Halema’uma’u Crater, within the larger caldera of Kilauea, is now about one-half mile across and 300 feet deep. From 1905 to 1924, a huge lava lake occupied the crater, often barely 100 feet below the rim (the prominent line marked by the yellow arrow shows where the lava stood at one time). In 192 ...
... Halema’uma’u Crater, within the larger caldera of Kilauea, is now about one-half mile across and 300 feet deep. From 1905 to 1924, a huge lava lake occupied the crater, often barely 100 feet below the rim (the prominent line marked by the yellow arrow shows where the lava stood at one time). In 192 ...
Lab 3: Volcanic Hazards
... In order to understand, predict, and plan for hazards associated with a particular volcano, it is necessary to know the type of volcano (in our case either shield or composite) and the composition of the magma. Magma composition plays a primary role in determining whether the eruption will be effusi ...
... In order to understand, predict, and plan for hazards associated with a particular volcano, it is necessary to know the type of volcano (in our case either shield or composite) and the composition of the magma. Magma composition plays a primary role in determining whether the eruption will be effusi ...
Activity Plan Example
... volcanoes are volcanoes are volcanoes are volcano is listed listed listed listed The three shapes of Only two shapes of No shapes of Only one shape of volcanoes are volcanoes are volcanoes are volcano is listed listed listed listed The type of The type of The type of eruption eruption is listed No t ...
... volcanoes are volcanoes are volcanoes are volcano is listed listed listed listed The three shapes of Only two shapes of No shapes of Only one shape of volcanoes are volcanoes are volcanoes are volcano is listed listed listed listed The type of The type of The type of eruption eruption is listed No t ...
Build a Volcano
... abruptly, there is a miniature explosion of gas and liquid. The gases in lava behave in somewhat the same way. Their sudden expansion causes the terrible explosions that throw out great masses of solid rock as well as lava, dust, and ashes. The violent separation of gas from lava may produce rock fr ...
... abruptly, there is a miniature explosion of gas and liquid. The gases in lava behave in somewhat the same way. Their sudden expansion causes the terrible explosions that throw out great masses of solid rock as well as lava, dust, and ashes. The violent separation of gas from lava may produce rock fr ...
Types of Magma - Teacher Notes
... Viscosity • Viscosity – internal resistance to flow • Low Viscosity ...
... Viscosity • Viscosity – internal resistance to flow • Low Viscosity ...
Volcanoes - leavingcertgeography
... These flows occur when the vent area or ash column collapses. Because pyroclastic flows can reach 1500 degrees F and travel at high speeds (160-250 kilometres per hour and up), they are extremely destructive and deadly. Pyroclastic flows are typical of composite volcano eruptions, but are also assoc ...
... These flows occur when the vent area or ash column collapses. Because pyroclastic flows can reach 1500 degrees F and travel at high speeds (160-250 kilometres per hour and up), they are extremely destructive and deadly. Pyroclastic flows are typical of composite volcano eruptions, but are also assoc ...
Tectonic Activity
... These flows occur when the vent area or ash column collapses. Because pyroclastic flows can reach 1500 degrees F and travel at high speeds (160-250 kilometres per hour and up), they are extremely destructive and deadly. Pyroclastic flows are typical of composite volcano eruptions, but are also assoc ...
... These flows occur when the vent area or ash column collapses. Because pyroclastic flows can reach 1500 degrees F and travel at high speeds (160-250 kilometres per hour and up), they are extremely destructive and deadly. Pyroclastic flows are typical of composite volcano eruptions, but are also assoc ...
Lassen Peak Volcanic National Park
... On Sunday, May 18, 1980, the largest volcanic eruption to occur in North American historic times transformed a picturesque volcano into a decapitated remnant. On this date in southwestern Washington State, Mount St. Helens erupted with tremendous force. ...
... On Sunday, May 18, 1980, the largest volcanic eruption to occur in North American historic times transformed a picturesque volcano into a decapitated remnant. On this date in southwestern Washington State, Mount St. Helens erupted with tremendous force. ...
All About Volcanoes - Library Video Company
... Teacher’s Guide and Program Copyright 2000 by Schlessinger Media, a division of Library Video Company ...
... Teacher’s Guide and Program Copyright 2000 by Schlessinger Media, a division of Library Video Company ...
Chapter 9 Volcanoes Test Study Guide: Geology 1P, Mr. Traeger
... composite volcanoes? Where does each type form? Relate this to plate viscosity lab § How Volcanoes Work website: tectonics! § What are the major volcanic hazards? http://www.geology.sdsu.edu/how_volcanoes_ § What things do volcanologists look for work/ when forecasting a volcanic eruption? § Traeger ...
... composite volcanoes? Where does each type form? Relate this to plate viscosity lab § How Volcanoes Work website: tectonics! § What are the major volcanic hazards? http://www.geology.sdsu.edu/how_volcanoes_ § What things do volcanologists look for work/ when forecasting a volcanic eruption? § Traeger ...
Magma
... Volcaniclastic Classification • Epiclastic – Transport by a hydrologic system – Volcanic sandstone, shale, etc ...
... Volcaniclastic Classification • Epiclastic – Transport by a hydrologic system – Volcanic sandstone, shale, etc ...
volcanoes
... other volcanic materials. (T in composite for Tall volcano) SHIELD VOLCANO – Wide gently-sloping mountain made of layers of lava and formed by QUIET eruptions. (SH makes the sh sound like when you tell someone to be quiet – sh) GEYSER – Fountain of water and steam that builds up pressure underground ...
... other volcanic materials. (T in composite for Tall volcano) SHIELD VOLCANO – Wide gently-sloping mountain made of layers of lava and formed by QUIET eruptions. (SH makes the sh sound like when you tell someone to be quiet – sh) GEYSER – Fountain of water and steam that builds up pressure underground ...
Chapter 8 section 2
... How do cinder cone volcanoes form? Gases build up in magma as it rises to Earth’s surface. When the gas builds up enough pressure, the volcano erupts. The eruption throws ash, cinders, and lava into the air. The lava cools quickly and particles of solid lava, ash, and cinders fall to the surface. Th ...
... How do cinder cone volcanoes form? Gases build up in magma as it rises to Earth’s surface. When the gas builds up enough pressure, the volcano erupts. The eruption throws ash, cinders, and lava into the air. The lava cools quickly and particles of solid lava, ash, and cinders fall to the surface. Th ...
Presentation
... This laccolith in Red and White Mountain, Colorado, is of Tertiary age. Overlying layers of rock have been eroded. ...
... This laccolith in Red and White Mountain, Colorado, is of Tertiary age. Overlying layers of rock have been eroded. ...
Erupting Volcano Model (916k PDF file)
... 1. Composite Cone Volcanoes (Strato volcanoes) have some of the most explosive eruptions. The volcano is built of lava, cinders and ash, and the overall size of the volcano tends to increase after an eruption. Strato volcanoes have very steep sides and are a sort of transportation system for magma t ...
... 1. Composite Cone Volcanoes (Strato volcanoes) have some of the most explosive eruptions. The volcano is built of lava, cinders and ash, and the overall size of the volcano tends to increase after an eruption. Strato volcanoes have very steep sides and are a sort of transportation system for magma t ...
2430 Volcano GUD v2 - Learning Resources
... Seismograph – An instrument that records the vibrations of Earth, also known as seismic waves. Seismologist – A scientist who studies earthquake waves and what they tell us about the inside of our planet. Shield Volcano – A type of volcano that is shaped like a flattened dome, resembling the look of ...
... Seismograph – An instrument that records the vibrations of Earth, also known as seismic waves. Seismologist – A scientist who studies earthquake waves and what they tell us about the inside of our planet. Shield Volcano – A type of volcano that is shaped like a flattened dome, resembling the look of ...
Note - ees.nmt.edu
... Cascades • Subduction of Juan de Fuca plate beneath North America • Water released from slab aids melting above • Magma travels toward surface, some cools, other erupts • 6-7 of these volcanoes have erupted in last 200 years ...
... Cascades • Subduction of Juan de Fuca plate beneath North America • Water released from slab aids melting above • Magma travels toward surface, some cools, other erupts • 6-7 of these volcanoes have erupted in last 200 years ...
Krakatoa

Krakatoa, or Krakatau (Indonesian: Krakatau), is a volcanic island situated in the Sunda Strait between the islands of Java and Sumatra in the Indonesian province of Lampung. The name is also used for the surrounding island group comprising the remnants of a much larger island of three volcanic peaks which was obliterated in a cataclysmic 1883 eruption, unleashing huge tsunamis (killing more than 36,000 people) and destroying over two-thirds of the island. The explosion is considered to be the loudest sound ever heard in modern history, with reports of it being heard up to 3,000 miles (4,800 km) from its point of origin. The shock waves from the explosion were recorded on barographs worldwide.In 1927 a new island, Anak Krakatau, or ""Child of Krakatoa"", emerged from the caldera formed in 1883 and is the current location of eruptive activity.