GEOGRAPHY Chap – 7 VOLCANOES STD. 8 Q1. What is a volcano
... Hot springs are also called thermal springs. They are associated with areas where ground water has sunk and is heated underground by internal forces. Such water usually rises without any explosion. It is of medical value as certain minerals are dissolved in it. Eg. Manikaran in the Kulu valley of th ...
... Hot springs are also called thermal springs. They are associated with areas where ground water has sunk and is heated underground by internal forces. Such water usually rises without any explosion. It is of medical value as certain minerals are dissolved in it. Eg. Manikaran in the Kulu valley of th ...
about volcanoes Power point
... What a volcano is. Understand that there are 3 main types of volcanoes. ...
... What a volcano is. Understand that there are 3 main types of volcanoes. ...
Basalt has a high melting point and is very runny (like honey) – in
... and it flows like cold treacle. Because if flows more slowly than basalt, it forms volcanic cones with a much steeper shape, called cone volcanoes. Examples of cone volcanoes include Mt Taranaki and Mt Ruapehu. Rhyolite magma is the most viscous type of magma – it flows like tar. It is light in colo ...
... and it flows like cold treacle. Because if flows more slowly than basalt, it forms volcanic cones with a much steeper shape, called cone volcanoes. Examples of cone volcanoes include Mt Taranaki and Mt Ruapehu. Rhyolite magma is the most viscous type of magma – it flows like tar. It is light in colo ...
Active
... There are 33 active volcanoes in the US Most are at convergent plate boundaries in Alaska and N. California, Oregon, and Washington. These are all stratovolcanoes, which are the most dangerous in terms of explosive activity. Some are on or near hotspots: Hawaii’s volcanoes, and Yellowstone Some are ...
... There are 33 active volcanoes in the US Most are at convergent plate boundaries in Alaska and N. California, Oregon, and Washington. These are all stratovolcanoes, which are the most dangerous in terms of explosive activity. Some are on or near hotspots: Hawaii’s volcanoes, and Yellowstone Some are ...
Chapter 13 Section 2 Directed Reading
... 12. Pyroclastic particles less than 2 mm in diameter that mostly fall on the land that immediately surrounds the volcano are called ____________________________. 13. Pyroclastic particles less than 0.25 mm in diameter that are so small they might travel around Earth in the upper atmosphere are calle ...
... 12. Pyroclastic particles less than 2 mm in diameter that mostly fall on the land that immediately surrounds the volcano are called ____________________________. 13. Pyroclastic particles less than 0.25 mm in diameter that are so small they might travel around Earth in the upper atmosphere are calle ...
Science Education Reform - American Geosciences Institute
... Understand that most volcanism occurs beneath the ocean. ...
... Understand that most volcanism occurs beneath the ocean. ...
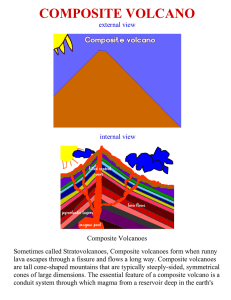
composite volcano
... tens of kilometers. There are many composite volcano chains on earth, notably around the Pacific rim, known as the "Rim of Fire". Other examples of composite volcanoes and their locations are: ...
... tens of kilometers. There are many composite volcano chains on earth, notably around the Pacific rim, known as the "Rim of Fire". Other examples of composite volcanoes and their locations are: ...
Chapter 6 Study Guide
... What forms when magma hardens in a volcano’s pipe and is later exposed? ______________. California’s Mount Shasta and Lassen Peak are volcanoes caused by __________ of the Juan de Fuca plate. A(n) _____________ happens when an explosive eruption hurls ash, cinders, bombs, and gases out of a volcano. ...
... What forms when magma hardens in a volcano’s pipe and is later exposed? ______________. California’s Mount Shasta and Lassen Peak are volcanoes caused by __________ of the Juan de Fuca plate. A(n) _____________ happens when an explosive eruption hurls ash, cinders, bombs, and gases out of a volcano. ...
Chapter 12
... Active – Dormant - Extinct Active – is a volcano that has had at least one eruption during the past 10,000 years. May be dormant or erupting. Dormant – have note erupted recently, but may at any time Extinct – have not erupted in over 10,000 years. ...
... Active – Dormant - Extinct Active – is a volcano that has had at least one eruption during the past 10,000 years. May be dormant or erupting. Dormant – have note erupted recently, but may at any time Extinct – have not erupted in over 10,000 years. ...
Volcano types and projectiles
... Aa is jagged and blocky. Pillow lava is circular and cools quickly. ...
... Aa is jagged and blocky. Pillow lava is circular and cools quickly. ...
document
... Volcanoes are mountains that build higher and higher as they erupt. Once a volcano erupts it might produce ash or lava. Volcanoes can make many types of rocks. There are as many 1,500 active volcanoes around the world. The most important volcano in the United States is Mt. Ranier. ...
... Volcanoes are mountains that build higher and higher as they erupt. Once a volcano erupts it might produce ash or lava. Volcanoes can make many types of rocks. There are as many 1,500 active volcanoes around the world. The most important volcano in the United States is Mt. Ranier. ...
volcanoes - TeacherXin
... the crater’s rim – Quiet eruption: • Lava flows from vents, setting fire to and then burying everything in its path. It can cover large areas with a thick layer of lava ...
... the crater’s rim – Quiet eruption: • Lava flows from vents, setting fire to and then burying everything in its path. It can cover large areas with a thick layer of lava ...
volcano
... a magma chamber below the surface of the Earth. Volcanoes are generally found at different places on Earth. For example, in the oceans, Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust. For example the Hawaii was created from magma 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Erupting volc ...
... a magma chamber below the surface of the Earth. Volcanoes are generally found at different places on Earth. For example, in the oceans, Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust. For example the Hawaii was created from magma 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Erupting volc ...
Introduction to Volcanism and Plate Tectonic Overview
... rocks, gases, and events observed at modern eruptions are! compared to similar ancient lavas to infer past activity ! ...
... rocks, gases, and events observed at modern eruptions are! compared to similar ancient lavas to infer past activity ! ...
File
... Landforms From Magma Features formed by magma include volcanic necks, dikes, and sills, as well as batholiths and dome mountains. ...
... Landforms From Magma Features formed by magma include volcanic necks, dikes, and sills, as well as batholiths and dome mountains. ...
volcanoes - boykinhonors
... hot springs: water is heated by the hot rock and reaches Earth’s surface ...
... hot springs: water is heated by the hot rock and reaches Earth’s surface ...
VOLCANO CHAPARRASTIQUE ERUPTS IN EL SALVADOR
... the San Miguel municipality about 140 km (87 miles) east of San Salvador, the capital, spewed ash over a wide area known for its coffee plantations. ...
... the San Miguel municipality about 140 km (87 miles) east of San Salvador, the capital, spewed ash over a wide area known for its coffee plantations. ...
Ch. 7.2 Volcanic Eruptions
... Only a few hundred meters high at most; very steep sides. Result from explosive eruptions of solid fragments. ...
... Only a few hundred meters high at most; very steep sides. Result from explosive eruptions of solid fragments. ...
Volcanoes - BrainPOP
... 1. Which of the following is an opinion about volcanic activity? a. Volcanoes are made of hardened lava b. A large number of volcanoes can be found along the edge of the Pacific Ocean c. The 1991 eruption of Mt. Pinatubo was the scariest volcanic event in history d. Shield volcanoes can actually cre ...
... 1. Which of the following is an opinion about volcanic activity? a. Volcanoes are made of hardened lava b. A large number of volcanoes can be found along the edge of the Pacific Ocean c. The 1991 eruption of Mt. Pinatubo was the scariest volcanic event in history d. Shield volcanoes can actually cre ...
Volcanoes
... • 3 classifications of volcanic activity: extinct (does not erupt), dormant (sleeping), and active (currently erupting). • The most active volcano on the Earth is Kilauea on the big island of Hawaii because it has been erupting almost daily since 1983! ...
... • 3 classifications of volcanic activity: extinct (does not erupt), dormant (sleeping), and active (currently erupting). • The most active volcano on the Earth is Kilauea on the big island of Hawaii because it has been erupting almost daily since 1983! ...
Silverthrone Caldera

The Silverthrone Caldera is a potentially active caldera complex in southwestern British Columbia, Canada, located over 350 kilometres (220 mi) northwest of the city of Vancouver and about 50 kilometres (31 mi) west of Mount Waddington in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains. The caldera is one of the largest of the few calderas in western Canada, measuring about 30 kilometres (19 mi) long (north-south) and 20 kilometres (12 mi) wide (east-west). Mount Silverthrone, an eroded lava dome on the caldera's northern flank that is 2,864 metres (9,396 ft) high may be the highest volcano in Canada.The main glaciers in the Silverthrone area are the Pashleth, Kingcome, Trudel, Klinaklini and Silverthrone glaciers. Most of the caldera lies in the Ha-Iltzuk Icefield, which is the largest icefield in the southern half of the Coast Mountains; it is one of the five icefields in southwestern British Columbia that thinned between the mid-1980s and 1999 due to global warming. Nearly half of the icefield is drained by the Klinaklini Glacier, which feeds the Klinaklini River.The Silverthrone Caldera is very remote and rarely visited or studied by geoscientists, such as volcanologists. It can be reached by helicopter or — with major difficulty — by hiking along one of the several river valleys extending from the British Columbia Coast or from the Interior Plateau.