Repetitive Patterns in Proteins
... -> An evolutionary path from “simple” scaffold proteins to fully ...
... -> An evolutionary path from “simple” scaffold proteins to fully ...
Fluorescent proteins Green Fluorescence Protein
... dual peaked excitation spectra, poor photo-stability, and poor folding at 37°C. ...
... dual peaked excitation spectra, poor photo-stability, and poor folding at 37°C. ...
Sports and Protein Metabolism
... Effect of Exercise on Protein Metabolism Exercise changes the rates of protein synthesis and the proteolysis in muscle During hard resistance exercise , the rat of protein synthesis will increase, provide a.a. in contracting muscle Moderate-intensity endurance exercise seem to increase the rate of ...
... Effect of Exercise on Protein Metabolism Exercise changes the rates of protein synthesis and the proteolysis in muscle During hard resistance exercise , the rat of protein synthesis will increase, provide a.a. in contracting muscle Moderate-intensity endurance exercise seem to increase the rate of ...
taqman protein assays
... (*) It includes sample processing, consumables, qPCR machine utilization and preliminary qPCR data quality control and analysis. ...
... (*) It includes sample processing, consumables, qPCR machine utilization and preliminary qPCR data quality control and analysis. ...
Presentation (PowerPoint File)
... In almost all cases, for all ranges of initial RMSD, even when starting from the “best” structural alignment, the final results are better than the initial template- the models move closer to native Based on a comprehensive folding benchmark, we expect low resolution structures for ~ 2/3 of proteins ...
... In almost all cases, for all ranges of initial RMSD, even when starting from the “best” structural alignment, the final results are better than the initial template- the models move closer to native Based on a comprehensive folding benchmark, we expect low resolution structures for ~ 2/3 of proteins ...
How to start to crystallise proteins
... crystallizing agent, the limit of nucleation/precipitation and locate the concentration range on which to focus. This search is based on the net charge of the protein and the chemical nature of the crystallizing agent (Hofmeister series). In addition it is more efficient by screening ranges of salts ...
... crystallizing agent, the limit of nucleation/precipitation and locate the concentration range on which to focus. This search is based on the net charge of the protein and the chemical nature of the crystallizing agent (Hofmeister series). In addition it is more efficient by screening ranges of salts ...
simplified models for proteins in coarse
... And aggregation takes place in a very long time scale. LONG TIME Therefore, an explicit-solvent atomistic molecular dynamics simulation is unfeasible. Solution: use simplified models of the proteins and make coarse-grained simulations (reduced number of particles + implicit solvent) Aim: study the g ...
... And aggregation takes place in a very long time scale. LONG TIME Therefore, an explicit-solvent atomistic molecular dynamics simulation is unfeasible. Solution: use simplified models of the proteins and make coarse-grained simulations (reduced number of particles + implicit solvent) Aim: study the g ...
Principles of Life
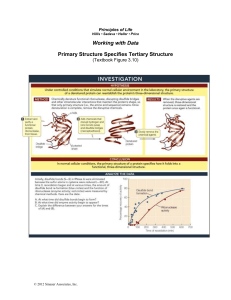
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
Protein Structure - George Mason University
... • Boundary Conditions – If water molecules are not being explicitly included in the potential function, the solvent boundary conditions must be imposed. The water molecules must not diffuse away from the protein. Also, usually a limited number of solvent molecules are included. ...
... • Boundary Conditions – If water molecules are not being explicitly included in the potential function, the solvent boundary conditions must be imposed. The water molecules must not diffuse away from the protein. Also, usually a limited number of solvent molecules are included. ...
Erin Margaret Schuman
... A news feed on the cell’s proteins could tell scientists when a protein of interest was synthesized, which may have been 30 seconds or an hour ago, and where the protein is. In a neuron, for example, there is always uncertainty about where something was made and Erin Margaret Schuman where it ends u ...
... A news feed on the cell’s proteins could tell scientists when a protein of interest was synthesized, which may have been 30 seconds or an hour ago, and where the protein is. In a neuron, for example, there is always uncertainty about where something was made and Erin Margaret Schuman where it ends u ...
FoldNucleus: web server for the prediction of RNA
... free energy landscape. Because the function of RNA depends on its conformation, which is analogous to the relationship between the function and folding structure of proteins, researchers have successfully applied methods developed for proteins, such as the A analysis (Matouschek et al., 1990). In th ...
... free energy landscape. Because the function of RNA depends on its conformation, which is analogous to the relationship between the function and folding structure of proteins, researchers have successfully applied methods developed for proteins, such as the A analysis (Matouschek et al., 1990). In th ...
Hidden Markov models for detecting remote protein homologies
... and a probability distribution for each position. The structure of a protein can be predicted by using a homology to sequences for which the structure is known. Proteins with similar structure assumed to have similar functionclassification of proteins into families according their function. ...
... and a probability distribution for each position. The structure of a protein can be predicted by using a homology to sequences for which the structure is known. Proteins with similar structure assumed to have similar functionclassification of proteins into families according their function. ...
new window
... Lipisorb liquid: 1.35 kcals/cc; 57grams protein/L, 85%of fat as MCT (medium chain triglycerides do not require bile acids or enzymatic breakdown) E. Immune Enhancing i. Impact: 3 patented ingredient are Arginine, omega-3 fatty acids, and dietary nucleotides. 1 kcal/cc, 56 grams protein/L. • Arginine ...
... Lipisorb liquid: 1.35 kcals/cc; 57grams protein/L, 85%of fat as MCT (medium chain triglycerides do not require bile acids or enzymatic breakdown) E. Immune Enhancing i. Impact: 3 patented ingredient are Arginine, omega-3 fatty acids, and dietary nucleotides. 1 kcal/cc, 56 grams protein/L. • Arginine ...
Genetically Modified Organism
... interactions that stabilize protein quaternary and tertiary structures, facilitates denaturation. 2. SDS also has a negative electrical charge and binds to proteins in a constant mass ratio of 1.4 : 1, so that the total amount of detergent bound is directly proportional to the molecular weight of th ...
... interactions that stabilize protein quaternary and tertiary structures, facilitates denaturation. 2. SDS also has a negative electrical charge and binds to proteins in a constant mass ratio of 1.4 : 1, so that the total amount of detergent bound is directly proportional to the molecular weight of th ...
File - Elko Science
... (water soluble) side chain are often found on the surface of the molecule while amino acids with nonpolar (water insoluble) side chain are buried in the interior. This means that the folded protein is soluble in water or aqueous solutions. + Disulfide Bonds: The polypeptide chains of some proteins a ...
... (water soluble) side chain are often found on the surface of the molecule while amino acids with nonpolar (water insoluble) side chain are buried in the interior. This means that the folded protein is soluble in water or aqueous solutions. + Disulfide Bonds: The polypeptide chains of some proteins a ...
Recombinant Human Platelet Derived Growth Factor Subunit B Cat
... Platelet Derived Growth Factor Subunit B (PDGFB) belongs to the PDGF/VEGF growth factor family. Platelet-derived growth factor is a potent mitogen for cells of mesenchymal origin. PDGFB can exist either as a homodimer (PDGF-BB) or as a heterodimer with the platelet-derived growth factor alpha polype ...
... Platelet Derived Growth Factor Subunit B (PDGFB) belongs to the PDGF/VEGF growth factor family. Platelet-derived growth factor is a potent mitogen for cells of mesenchymal origin. PDGFB can exist either as a homodimer (PDGF-BB) or as a heterodimer with the platelet-derived growth factor alpha polype ...
How Enzymes Work
... some cases by shielding the had persistent structure and that catalytic site from contact with Elucidating the active site. In the crystal structure of a lysozyme mutant bound to destruction of that structure could a synthetic sugar substrate, the sugar ring in the active site is distorted, and the ...
... some cases by shielding the had persistent structure and that catalytic site from contact with Elucidating the active site. In the crystal structure of a lysozyme mutant bound to destruction of that structure could a synthetic sugar substrate, the sugar ring in the active site is distorted, and the ...
7.5 Proteins - HS Biology IB
... primary structure is sequence / number of amino acids; determined by base sequence in the gene; (largely) determines higher level structures/secondary structure/tertiary structure; secondary structure is regular repeating patterns; such as alpha/α helix and beta/β (pleated) sheet; determined by H bo ...
... primary structure is sequence / number of amino acids; determined by base sequence in the gene; (largely) determines higher level structures/secondary structure/tertiary structure; secondary structure is regular repeating patterns; such as alpha/α helix and beta/β (pleated) sheet; determined by H bo ...
Determination of Proteins
... those which contain a non amino acid component in addition to the amino acids. e.g. lipoprotein , phosphoproteins etc. ...
... those which contain a non amino acid component in addition to the amino acids. e.g. lipoprotein , phosphoproteins etc. ...
Protein structure homework: FAQ
... the screen and what is in the actual pdb-file. That's why I suggested that you open this file with notepad or any other text editor. Q: When I open a protein in notepad I don’t understand what all the acronyms mean. A: There are many acronyms there. Some of them are intuitive, but some aren’t. The m ...
... the screen and what is in the actual pdb-file. That's why I suggested that you open this file with notepad or any other text editor. Q: When I open a protein in notepad I don’t understand what all the acronyms mean. A: There are many acronyms there. Some of them are intuitive, but some aren’t. The m ...
Computational Structural Genomics of a Complete Minimal Organism
... with functionally characterized homologues, using a structural alignment tool such as MINAREA [3]. Another method is analysis of the surface properties of the protein, possibly coupled with an analysis of conservation among homologues of a protein from multiple species. A more thorough means of usin ...
... with functionally characterized homologues, using a structural alignment tool such as MINAREA [3]. Another method is analysis of the surface properties of the protein, possibly coupled with an analysis of conservation among homologues of a protein from multiple species. A more thorough means of usin ...
C H E M I S T R Y
... released from the ribosome, a number of modifications are made in order for the protein to perform it’s intended function. The protein must fold into it’s appropriate 3-dimensional shape. ...
... released from the ribosome, a number of modifications are made in order for the protein to perform it’s intended function. The protein must fold into it’s appropriate 3-dimensional shape. ...
class test 2 prot synth aminos
... c) What collective name is given to the triplet of mRNA bases that correspond to each amino acid? ...
... c) What collective name is given to the triplet of mRNA bases that correspond to each amino acid? ...
cell - Zoology, UBC
... Cell membranes are semipermeable, and thus subject to osmotic forces. Animal cell membranes are flexible, and allow for inflation and deflation depending on the movement of water ...
... Cell membranes are semipermeable, and thus subject to osmotic forces. Animal cell membranes are flexible, and allow for inflation and deflation depending on the movement of water ...
Protein folding

Protein folding is the process by which a protein structure assumes its functional shape or conformation. It is the physical process by which a polypeptide folds into its characteristic and functional three-dimensional structure from random coil.Each protein exists as an unfolded polypeptide or random coil when translated from a sequence of mRNA to a linear chain of amino acids. This polypeptide lacks any stable (long-lasting) three-dimensional structure (the left hand side of the first figure). Amino acids interact with each other to produce a well-defined three-dimensional structure, the folded protein (the right hand side of the figure), known as the native state. The resulting three-dimensional structure is determined by the amino acid sequence (Anfinsen's dogma). Experiments beginning in the 1980s indicate the codon for an amino acid can also influence protein structure.The correct three-dimensional structure is essential to function, although some parts of functional proteins may remain unfolded, so that protein dynamics is important. Failure to fold into native structure generally produces inactive proteins, but in some instances misfolded proteins have modified or toxic functionality. Several neurodegenerative and other diseases are believed to result from the accumulation of amyloid fibrils formed by misfolded proteins. Many allergies are caused by incorrect folding of some proteins, because the immune system does not produce antibodies for certain protein structures.