Unit 3 Notes - Phoenix Union High School District
... an injection of new money into the economy. • Round 2: The $10 is income for resource suppliers and with an MPC = 0.80, households spend $8 and save $2. • Round 3: The $8 of new spending is income for other households and they spend 80 percent, or $6.40 and save $1.60. • Round 4: The new $6.40 is in ...
... an injection of new money into the economy. • Round 2: The $10 is income for resource suppliers and with an MPC = 0.80, households spend $8 and save $2. • Round 3: The $8 of new spending is income for other households and they spend 80 percent, or $6.40 and save $1.60. • Round 4: The new $6.40 is in ...
Ch25 - 山东大学课程中心
... military and hence government spending to be reduced. If the new classical view or the economy is correct and government spending does affect the aggregate demand curve, predict what will happen to aggregate output and the price level when government spending is reduced in line with the public's exp ...
... military and hence government spending to be reduced. If the new classical view or the economy is correct and government spending does affect the aggregate demand curve, predict what will happen to aggregate output and the price level when government spending is reduced in line with the public's exp ...
Sticky Prices and the Phillips Curve
... could still have short-run effects even if prices were flexible and people had rational expectations. Lucas’s model relied on the idea that firms had a difficulty in the short-run distinguishing between movements in their prices and movements in the overall price levels. For this reason, an increase ...
... could still have short-run effects even if prices were flexible and people had rational expectations. Lucas’s model relied on the idea that firms had a difficulty in the short-run distinguishing between movements in their prices and movements in the overall price levels. For this reason, an increase ...
Inflation Cycles
... exceeds its expected rate, and the economy behaves like it does in a demand-pull inflation. If aggregate demand grows more slowly than expected, real GDP falls below potential GDP, the inflation rate slows, and the economy behaves like it does in a costpush inflation. © 2012 Pearson Education ...
... exceeds its expected rate, and the economy behaves like it does in a demand-pull inflation. If aggregate demand grows more slowly than expected, real GDP falls below potential GDP, the inflation rate slows, and the economy behaves like it does in a costpush inflation. © 2012 Pearson Education ...
US RECESSION
... The Us economy shrank in three quarters in the early 2000s (the 3rd quarter of 2000), the first quarter of 2001, and the third quarter of 2001. The US economy was in recession from March 2001 to November 2001, a period of eight months. ...
... The Us economy shrank in three quarters in the early 2000s (the 3rd quarter of 2000), the first quarter of 2001, and the third quarter of 2001. The US economy was in recession from March 2001 to November 2001, a period of eight months. ...
Steinar Holden, ECON 4325
... Zero lower bound for the interest rate o Puts a lower bound for the real interest rate when recession is combined with low rate of inflation o If possible, avoid fiscal contractions as long as the monetary policy is constrained by the zero lower bound New Keynesian framework usually does not all ...
... Zero lower bound for the interest rate o Puts a lower bound for the real interest rate when recession is combined with low rate of inflation o If possible, avoid fiscal contractions as long as the monetary policy is constrained by the zero lower bound New Keynesian framework usually does not all ...
Inflation - Doral Academy Preparatory
... when prices are pushed up by rising costs to producers who compete with each other for increasingly scarce resources. The increased costs are passed onto ...
... when prices are pushed up by rising costs to producers who compete with each other for increasingly scarce resources. The increased costs are passed onto ...
Rate of interest
... 4. Rate of growth in GDP – affects domestic demand for agricultural products (remember the income elasticity of demand. 5. Rate of foreign exchange – reflects the value of the dollar relative to client nation currencies and hence the export demand for agricultural products. ...
... 4. Rate of growth in GDP – affects domestic demand for agricultural products (remember the income elasticity of demand. 5. Rate of foreign exchange – reflects the value of the dollar relative to client nation currencies and hence the export demand for agricultural products. ...
BHARAT SCHOOL OF BANKING INFLATION
... Suppose, you lived in "peace" (in context of your spending) in the year 2010, when you bought vegetables or fruits (or any other commodity) in much less price (than present). But at present i.e. in 2015, the prices of the same things have gone up which means you have to spend much more, than you use ...
... Suppose, you lived in "peace" (in context of your spending) in the year 2010, when you bought vegetables or fruits (or any other commodity) in much less price (than present). But at present i.e. in 2015, the prices of the same things have gone up which means you have to spend much more, than you use ...
Quiz: Introductory Macroeconomics
... Fridays was followed by a 12.5 percent fall in prices of fresh fish. From this it can be deduced that the a. demand curve for fish shifted to the left. b. demand curve shifted to the right. c. supply curve shifted to the left. d. supply curve shifted to the right. Technological change, such as the i ...
... Fridays was followed by a 12.5 percent fall in prices of fresh fish. From this it can be deduced that the a. demand curve for fish shifted to the left. b. demand curve shifted to the right. c. supply curve shifted to the left. d. supply curve shifted to the right. Technological change, such as the i ...
Questions Chapter 14
... 13. The rise in volatility in the late 1960s was caused by the large positive shock to demand that came from military spending on the Vietnam War. That shock resulted in a positive output gap and drove up volatility as shown in Figure 14-3. Figure 14-3 shows that the jumps in volatility in the early ...
... 13. The rise in volatility in the late 1960s was caused by the large positive shock to demand that came from military spending on the Vietnam War. That shock resulted in a positive output gap and drove up volatility as shown in Figure 14-3. Figure 14-3 shows that the jumps in volatility in the early ...
Presentation to the University of California at Berkeley Boalt School... San Francisco, California
... Worry #2—the trade gap. This has risen from near balance in the mid-1990s to a (nominal) deficit of almost $700 billion now. By reducing the need for domestic production of goods and services, the trade deficit subtracted about three quarters of a percentage point from real GDP growth in the first h ...
... Worry #2—the trade gap. This has risen from near balance in the mid-1990s to a (nominal) deficit of almost $700 billion now. By reducing the need for domestic production of goods and services, the trade deficit subtracted about three quarters of a percentage point from real GDP growth in the first h ...
Test 2
... 30. In the short run, the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of total output are determined by the intersection of A) the aggregate demand, the short-run aggregate supply and the long-run aggregate supply curves. B) the short-run aggregate supply and the long-run aggregate supply curv ...
... 30. In the short run, the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of total output are determined by the intersection of A) the aggregate demand, the short-run aggregate supply and the long-run aggregate supply curves. B) the short-run aggregate supply and the long-run aggregate supply curv ...
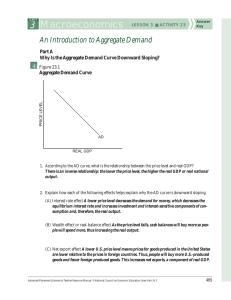
3 Macroeconomics LESSON 3 s ACTIVITY 23
... equilibrium interest rate and increases investment and interest-sensitive components of consumption and, therefore, the real output. (B) Wealth effect or real-balance effect As the price level falls, cash balances will buy more so people will spend more, thus increasing the real output. ...
... equilibrium interest rate and increases investment and interest-sensitive components of consumption and, therefore, the real output. (B) Wealth effect or real-balance effect As the price level falls, cash balances will buy more so people will spend more, thus increasing the real output. ...
105-notes inflation-stagflation-phillipscurve
... assumption is that people make the best possible decisions based on the information available to them. One implication is that they will not make persistent or systematic mistakes — their expectations are, on average, correct. ...
... assumption is that people make the best possible decisions based on the information available to them. One implication is that they will not make persistent or systematic mistakes — their expectations are, on average, correct. ...
CHAPTER 7 Wage and Price Adjustment: The Phillips Curve and
... the long-run AS-curve is vertical, a point that was emphasized in Chapter 3. Thus, the role of price expectations has to be discussed and the inflation-expectations-augmented Phillips curve can be used to show the analogies between the Phillips curve and the AS-curve. The AS-curve shows a relationsh ...
... the long-run AS-curve is vertical, a point that was emphasized in Chapter 3. Thus, the role of price expectations has to be discussed and the inflation-expectations-augmented Phillips curve can be used to show the analogies between the Phillips curve and the AS-curve. The AS-curve shows a relationsh ...
Practice for Exam 2 - Econ 304 - we will do this
... the effectiveness of monetary policy? Explain. ...
... the effectiveness of monetary policy? Explain. ...
Lecture 1
... Go to www.minneapolisfed.org and click on inflation calculator to find what goods worth $30,000 in 1980 would cost today. How can savers protect themselves from inflation? By demanding an inflation premium on the money they save. Nominal interest rate = real interest rate+ expected inflation rate In ...
... Go to www.minneapolisfed.org and click on inflation calculator to find what goods worth $30,000 in 1980 would cost today. How can savers protect themselves from inflation? By demanding an inflation premium on the money they save. Nominal interest rate = real interest rate+ expected inflation rate In ...
Phillips curve

In economics, the Phillips curve is a historical inverse relationship between rates of unemployment and corresponding rates of inflation that result in an economy. Stated simply, decreased unemployment, (i.e., increased levels of employment) in an economy will correlate with higher rates of inflation.While there is a short run tradeoff between unemployment and inflation, it has not been observed in the long run. In 1968, Milton Friedman asserted that the Phillips Curve was only applicable in the short-run and that in the long-run, inflationary policies will not decrease unemployment. Friedman then correctly predicted that, in the upcoming years after 1968, both inflation and unemployment would increase. The long-run Phillips Curve is now seen as a vertical line at the natural rate of unemployment, where the rate of inflation has no effect on unemployment. Accordingly, the Phillips curve is now seen as too simplistic, with the unemployment rate supplanted by more accurate predictors of inflation based on velocity of money supply measures such as the MZM (""money zero maturity"") velocity, which is affected by unemployment in the short but not the long term.