Study Guide 1
... Compare and contrast the various philosophies of Keynesian and Monetarist Economics (i.e. macroeconomic equilibrium, fiscal and monetary policy, flexibility of prices and wages, etc.) Discuss the difference between the Keynesian and Monetarist LRAS curves and why and how their assumptions guide thei ...
... Compare and contrast the various philosophies of Keynesian and Monetarist Economics (i.e. macroeconomic equilibrium, fiscal and monetary policy, flexibility of prices and wages, etc.) Discuss the difference between the Keynesian and Monetarist LRAS curves and why and how their assumptions guide thei ...
Study Questions for Section 4
... result is the same as the long run. 4) b. An inflation / unemployment tradeoff was evident in the 1960’s. This led economists to believe that the Phillips Curve was an accurate description of the way the economy worked. It also led them to believe there would never be another recession. 5) a. Econom ...
... result is the same as the long run. 4) b. An inflation / unemployment tradeoff was evident in the 1960’s. This led economists to believe that the Phillips Curve was an accurate description of the way the economy worked. It also led them to believe there would never be another recession. 5) a. Econom ...
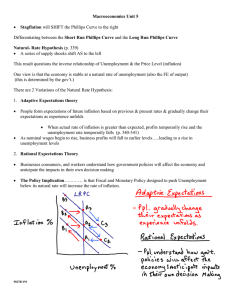
The Phillips Curve: Short Run and Long Run
... It suggested that if governments wanted to reduce unemployment it had to accept higher inflation as a trade-off. ...
... It suggested that if governments wanted to reduce unemployment it had to accept higher inflation as a trade-off. ...
Phillips curve

In economics, the Phillips curve is a historical inverse relationship between rates of unemployment and corresponding rates of inflation that result in an economy. Stated simply, decreased unemployment, (i.e., increased levels of employment) in an economy will correlate with higher rates of inflation.While there is a short run tradeoff between unemployment and inflation, it has not been observed in the long run. In 1968, Milton Friedman asserted that the Phillips Curve was only applicable in the short-run and that in the long-run, inflationary policies will not decrease unemployment. Friedman then correctly predicted that, in the upcoming years after 1968, both inflation and unemployment would increase. The long-run Phillips Curve is now seen as a vertical line at the natural rate of unemployment, where the rate of inflation has no effect on unemployment. Accordingly, the Phillips curve is now seen as too simplistic, with the unemployment rate supplanted by more accurate predictors of inflation based on velocity of money supply measures such as the MZM (""money zero maturity"") velocity, which is affected by unemployment in the short but not the long term.