Problem Set 7
... b. An increase in government spending and a decrease in taxes. c. A decrease in government spending and an increase in taxes. d. A decrease in government spending and an decrease in taxes. 7. Evidence suggesting that prices and wages are slow to adjust in response to aggregate demand and supply chan ...
... b. An increase in government spending and a decrease in taxes. c. A decrease in government spending and an increase in taxes. d. A decrease in government spending and an decrease in taxes. 7. Evidence suggesting that prices and wages are slow to adjust in response to aggregate demand and supply chan ...
Economics 202.04 Macroeconomic Theory
... c. Suppose the government increases spending, reducing the country’s savings rate to 0.15. Calculate the new steadystate capital stock and output per worker. ...
... c. Suppose the government increases spending, reducing the country’s savings rate to 0.15. Calculate the new steadystate capital stock and output per worker. ...
Chapter 16 - Central Web Server 2
... matter when it comes to understanding the behavior of inflation and unemployment? • When unemployment is low, firms compete for workers and bid up wages sharply. • When unemployment is high, it is more difficult for firms to cut wages because workers tend to resist wage cuts. Result: Even if the tot ...
... matter when it comes to understanding the behavior of inflation and unemployment? • When unemployment is low, firms compete for workers and bid up wages sharply. • When unemployment is high, it is more difficult for firms to cut wages because workers tend to resist wage cuts. Result: Even if the tot ...
B-Inflation
... Factors Causing Inflation in GCC Stats 1. As a result of pegging GCC currencies - except the Kuwaiti dinar- to a weakening dollar there has been an increase in the cost of goods that are imported from countries whose currencies had appreciated against the dollar, like the EU, Japan and China. 2. Ri ...
... Factors Causing Inflation in GCC Stats 1. As a result of pegging GCC currencies - except the Kuwaiti dinar- to a weakening dollar there has been an increase in the cost of goods that are imported from countries whose currencies had appreciated against the dollar, like the EU, Japan and China. 2. Ri ...
ECON 521 Special Topics in Economic Policy
... • Inflation Rate is the growth or percentage change in the overall price level. • Inflation rate measures the price level (P), through: -- Consumer Price Index (CPI) -- GDP Deflator • Inflation Rate = Percentage Change in (P) • Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money, causes distortions in de ...
... • Inflation Rate is the growth or percentage change in the overall price level. • Inflation rate measures the price level (P), through: -- Consumer Price Index (CPI) -- GDP Deflator • Inflation Rate = Percentage Change in (P) • Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money, causes distortions in de ...
EC108 Macroeconomics 1 Review Class
... by a transitory shock that will have effect only at time t. This is shown with a shift in the DAS curve from DASt−1 to DASt (the shift is by exactly the size of the shock). The supply shock causes inflation to rise and output to fall. Note that according to the model, part of the effects of this shock ...
... by a transitory shock that will have effect only at time t. This is shown with a shift in the DAS curve from DASt−1 to DASt (the shift is by exactly the size of the shock). The supply shock causes inflation to rise and output to fall. Note that according to the model, part of the effects of this shock ...
More
... You take 70 and divide it by the interest rate. Ex: Most savings accounts earn an interest rate of 2%. How long will it take to double? 70/2=35 years! --------------------Fiscal Policy vs. Monetary Policy-------------------Fiscal Policy: stabilizing the economy through taxation and government spendi ...
... You take 70 and divide it by the interest rate. Ex: Most savings accounts earn an interest rate of 2%. How long will it take to double? 70/2=35 years! --------------------Fiscal Policy vs. Monetary Policy-------------------Fiscal Policy: stabilizing the economy through taxation and government spendi ...
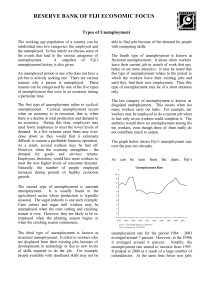
Types of Unemployment - Reserve Bank of Fiji
... which the workers leave their existing jobs and until they find their new employment. Thus this type of unemployment may be of a short duration only. The last category of unemployment is known as disguised unemployment. This occurs when too many workers carry out tasks. For example, ten workers may ...
... which the workers leave their existing jobs and until they find their new employment. Thus this type of unemployment may be of a short duration only. The last category of unemployment is known as disguised unemployment. This occurs when too many workers carry out tasks. For example, ten workers may ...
The Labor Market, Unemployment, and Inflation
... equilibrium wage will fall. • Anyone who wants a job at W1 will have one. There is always full employment in this sense. Principles of Economics, 7/e ...
... equilibrium wage will fall. • Anyone who wants a job at W1 will have one. There is always full employment in this sense. Principles of Economics, 7/e ...
A Rise In The Price Of Oil Imports Has
... 24. What goes down when an economy goes into a recession in the short-run? a. output. b. unemployment. c. wages. d. both a and c. 25. What happens when there is a shortage in the labor market? a. wages rise. b. wages fall. c. wages stay the same. 26. If we are in an inflationary gap, the government ...
... 24. What goes down when an economy goes into a recession in the short-run? a. output. b. unemployment. c. wages. d. both a and c. 25. What happens when there is a shortage in the labor market? a. wages rise. b. wages fall. c. wages stay the same. 26. If we are in an inflationary gap, the government ...
Monetary Policy Effects
... affect their current price decisions. An increase in future price expectations may shift the AS curve to the left and thus act like a cost shock. Expectations can get “built into the system.” If every firm expects every other firm to raise prices by 10 percent, every firm will raise prices by about ...
... affect their current price decisions. An increase in future price expectations may shift the AS curve to the left and thus act like a cost shock. Expectations can get “built into the system.” If every firm expects every other firm to raise prices by 10 percent, every firm will raise prices by about ...
Chapter 4 -- The IS/LM Model
... Chapter 4 -The IS-LM Model Fundamental inflexibility assumptions: W -- inflexible P -- inflexible i -- flexible Overriding theme -- The interest rate changes as a result of monetary policy (money supply) as well as other factors. ...
... Chapter 4 -The IS-LM Model Fundamental inflexibility assumptions: W -- inflexible P -- inflexible i -- flexible Overriding theme -- The interest rate changes as a result of monetary policy (money supply) as well as other factors. ...
AS/AD Model
... People hold money for transactions purposes. Velocity (V) is constant, or, at least, stable (=1/k). Real output (Y) is constant w.r.t. labor supply. Therefore, changes in MS will only change P. • Aggregate Demand for output (AD) - derived from the demand for money, or - derived from the real ...
... People hold money for transactions purposes. Velocity (V) is constant, or, at least, stable (=1/k). Real output (Y) is constant w.r.t. labor supply. Therefore, changes in MS will only change P. • Aggregate Demand for output (AD) - derived from the demand for money, or - derived from the real ...
... Significant movements in house prices can be an issue for economic activity. Just as the run-up in house prices provided some support for consumer spending, slower increases, and especially outright decreases, could weaken that support. For example, back when house prices were rising so fast, people ...
Exam Answers
... money supply every year for the next 100 years. He’s come to you for advice. Which of the following predictions is FALSE? a. Although this policy might be effective at first, eventually, it could have devastating effects because it will generate very high levels of inflation. b. As long as he increa ...
... money supply every year for the next 100 years. He’s come to you for advice. Which of the following predictions is FALSE? a. Although this policy might be effective at first, eventually, it could have devastating effects because it will generate very high levels of inflation. b. As long as he increa ...
Study Guide
... CPI Practice* Using the values of the market baskets below, calculate the CPI for each year. Start with 2009 as the base year then recalculate with 2010 as the base year. Lastly, recalculate with 2011 as the base year. Market Base Year Base Year Base year Year Basket ...
... CPI Practice* Using the values of the market baskets below, calculate the CPI for each year. Start with 2009 as the base year then recalculate with 2010 as the base year. Lastly, recalculate with 2011 as the base year. Market Base Year Base Year Base year Year Basket ...
expand the income threshold for the 15 percent tax bracket so
... Treasury Yield Curve Spread policy of significant monetary restraint. It is clearly shown by the yield curve inversion, which is more than a year old. 10-Yr less Fed Funds ...
... Treasury Yield Curve Spread policy of significant monetary restraint. It is clearly shown by the yield curve inversion, which is more than a year old. 10-Yr less Fed Funds ...
Inflation, Disinflation, and Deflation
... off because as the Millers pay off their mortgage, the mortgage company will be able to lend to more potential homeowners. As the deflation continues, it will become harder and harder for the Millers to pay off their mortgage. Assuming wages are falling with deflation, the Millers will have to work ...
... off because as the Millers pay off their mortgage, the mortgage company will be able to lend to more potential homeowners. As the deflation continues, it will become harder and harder for the Millers to pay off their mortgage. Assuming wages are falling with deflation, the Millers will have to work ...
Chapter 25 - uob.edu.bh
... has no effect on the aggregate demand curve and cannot offset the leftward shift stemming from the reduction in the money supply. 5. The lower cost of foreign goods means that the costs of production fall in the United States and the aggregate supply curve shifts outward. The strong dollar makes for ...
... has no effect on the aggregate demand curve and cannot offset the leftward shift stemming from the reduction in the money supply. 5. The lower cost of foreign goods means that the costs of production fall in the United States and the aggregate supply curve shifts outward. The strong dollar makes for ...
Phillips curve

In economics, the Phillips curve is a historical inverse relationship between rates of unemployment and corresponding rates of inflation that result in an economy. Stated simply, decreased unemployment, (i.e., increased levels of employment) in an economy will correlate with higher rates of inflation.While there is a short run tradeoff between unemployment and inflation, it has not been observed in the long run. In 1968, Milton Friedman asserted that the Phillips Curve was only applicable in the short-run and that in the long-run, inflationary policies will not decrease unemployment. Friedman then correctly predicted that, in the upcoming years after 1968, both inflation and unemployment would increase. The long-run Phillips Curve is now seen as a vertical line at the natural rate of unemployment, where the rate of inflation has no effect on unemployment. Accordingly, the Phillips curve is now seen as too simplistic, with the unemployment rate supplanted by more accurate predictors of inflation based on velocity of money supply measures such as the MZM (""money zero maturity"") velocity, which is affected by unemployment in the short but not the long term.