* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download US RECESSION
Nouriel Roubini wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Great Recession in Russia wikipedia , lookup
Phillips curve wikipedia , lookup
Great Recession in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
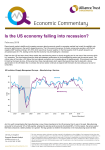
A Presentation by Gholam Syedain Khan nd (2 M.Com Sem.) Roll No. 36 St. Xavier’s College, Calcutta WHAT IS RECESSION??? The standard way of defining a recession looks at the value of economic output adjusted for inflation. This measure is known as Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Two consecutive quarters of decline in Real GDP is generally considered to be a recession. THE US RECESSION 2001 The Us economy shrank in three quarters in the early 2000s (the 3rd quarter of 2000), the first quarter of 2001, and the third quarter of 2001. The US economy was in recession from March 2001 to November 2001, a period of eight months. US RECESSION - 2001 U.S. had a recession in the first three quarters of 2001. US RECESSION - 2001 The 2001 recession saw a 0.6 percent decline from the peak in the fourth quarter of 2000. The U.S. economy took a year to exceed its prior peak in the 1990-91 business cycle. What Happened During 2001… •2.1 million people lost their jobs, as unemployment rose from 3.9% to 5.8%. •GDP growth slowed to 0.8% (compared to 3.9% average annual growth during 19942000). Causes of the U.S. recession of 2001 Index (1942 = 100) 1) Stock market decline C 1500 1200 Standard & Poor’s 500 900 600 300 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 Causes of the U.S. recession 2) 9/11 Terrorist Attack on US – increased uncertainty – fall in consumer & business confidence – result: lower spending, IS curve shifted left – reduced stock prices, discouraged investment Response of Fiscal Policy in The U.S. recession Fiscal policy response: shifted IS curve right tax cuts in 2001 and 2003 spending increases airline industry bailout Afghanistan war Respone of Monetary Policy in The U.S. recession of 2001 Monetary policy response: shifted LM curve downward (right) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Three-month T-Bill Rate The U.S. Growth Rate, 1999:1-2002:4 The Federal Funds Rate, 1999:12002:4 US RECESSION 2001 IN IS-LM MODEL WHAT IS SHOCKS IN THE IS CURVE? • Shocks to the IS curve are exogenous changes in the demand for goods and services. • Reduction in the demand for investment • This leads to the shift of IS curve left, reducing income and expenditure. • Sudden increase in consumption shifts the IS curve right, C and this raises income. WHAT IS LM SHOCKS? exogenous changes in the demand for money. Examples: more ATMs or the Internet reduce money demand. Thus increase in Money demand shifts the LM curve upward Rise in Interest rate & depress income. Summary of IS-LM model Several kinds of events can cause economic fluctuations by shifting the IS curve or the LM curve. The U.S. Recession in IS-LM MODEL • What happened in 2001 was the following: The decrease in investment demand led to a sharp shift of the IS curve to the left, from IS to IS”. The increase in the money supply led to a downward shift of the LM curve, from LM to LM’. The decrease in tax rates and the increase in spending both led to a shift of the IS curve to the right, from IS’’ to IS’. How does the IS-LM Model Fit the Facts? Introducing dynamics formally would be difficult, but we can describe the basic mechanisms in words. Consumers are likely to take some time to adjust their consumption following a change in disposable income. Firms are likely to take some time to adjust investment spending following a change in their sales. Firms are likely to take some time to adjust investment spending following a change in the interest rate. Firms are likely to take some time to adjust production following a change in their sales. How does the IS-LM Model Fit the Facts? The Empirical Effects of an Increase in the Federal Funds Rate In the short run, an increase in the federal funds rate leads to a decrease in output and to an increase in unemployment, but has little effect on the price level. Panel (a) shows the effects of an increase in the federal funds rate of 1% on retail sales over time. Panel (b) shows how lower sales lead to lower output. Panel (c) shows how lower output leads to lower employment. Panel (d) shows the increase in unemloyment Panel (e) looks at the behavior of the price level.