Memory
... change (e.g., shape of terminal button, number of receptors) • This causes memories to be now be stored in the long term ...
... change (e.g., shape of terminal button, number of receptors) • This causes memories to be now be stored in the long term ...
CHAPTER SIX Memory The experience of pain cannot be separated
... reserves of cells for this purpose) and they undergo a transformation. The arrangement of their neurotransmitters and receptors is altered in response to a new and previously unlearned experience. This process takes time, perhaps as long as a few minutes. As we all know, the act of rote memorization ...
... reserves of cells for this purpose) and they undergo a transformation. The arrangement of their neurotransmitters and receptors is altered in response to a new and previously unlearned experience. This process takes time, perhaps as long as a few minutes. As we all know, the act of rote memorization ...
LO: Explain how biological factors may affect one cognitive process.
... in synaptic changes in the neural network. His research showed that learning (forming memories) means growing new connections or strengthening connections between neurons. Kandel went on to study synaptic changes due to memory in the hippocampus. In other words, what changes occur in the hippocampus ...
... in synaptic changes in the neural network. His research showed that learning (forming memories) means growing new connections or strengthening connections between neurons. Kandel went on to study synaptic changes due to memory in the hippocampus. In other words, what changes occur in the hippocampus ...
Memory Systems
... cortex in temporal lobe of monkeys and found that they could no longer perform in recognition memory tests • Later showed that perirhinal cortex is most important for new memory; temporary storage? Memory consolidation? ...
... cortex in temporal lobe of monkeys and found that they could no longer perform in recognition memory tests • Later showed that perirhinal cortex is most important for new memory; temporary storage? Memory consolidation? ...
Can You Remember My Name? Part 2
... – Facilitation (paired pulse facilitation): 100-200 ms; increased Ca++ increased p(NT release) – Post-tetanic potentiation: 5-10 sec – Depression: hundreds of ms – few minutes; caused by repetitive stimulation causing a decrease in p(NT release). ...
... – Facilitation (paired pulse facilitation): 100-200 ms; increased Ca++ increased p(NT release) – Post-tetanic potentiation: 5-10 sec – Depression: hundreds of ms – few minutes; caused by repetitive stimulation causing a decrease in p(NT release). ...
Behavioural and electrophysiological studies of learning, memory and long-term potentiation.
... Long‐term potentiation (LTP) is a form of synaptic plasticity widely assumed to be involved in learning and memory. However, LTP is a phenomenon generated by electrical stimulation of brain pathways and learning and memory result from physiological activation of ...
... Long‐term potentiation (LTP) is a form of synaptic plasticity widely assumed to be involved in learning and memory. However, LTP is a phenomenon generated by electrical stimulation of brain pathways and learning and memory result from physiological activation of ...
Week 14 The Memory Function of Sleep
... Explain “there is a fine-tuned temporal relationship between the occurrence of slow oscillations, spindles, and sharp wave-ripples during SWS that coordinate the bidirectional information flow between the neocortex and the hippocampus.” Explain how “up-states” play a role here, and the excitatory p ...
... Explain “there is a fine-tuned temporal relationship between the occurrence of slow oscillations, spindles, and sharp wave-ripples during SWS that coordinate the bidirectional information flow between the neocortex and the hippocampus.” Explain how “up-states” play a role here, and the excitatory p ...
Brain Jeopardy Game
... “Immediate memory” and “working memory”are the two components of this type of memory. ...
... “Immediate memory” and “working memory”are the two components of this type of memory. ...
11/10/16 Memory Part 2 Reinforcement learning (12.2) • Involves a
... Memories can be “manipulated” by manipulating (consciously or not) their relationship to other memories – false memories. Eye witness testimony. Implanted memories ...
... Memories can be “manipulated” by manipulating (consciously or not) their relationship to other memories – false memories. Eye witness testimony. Implanted memories ...
Memory notes Explaining memory Learning required memorisation
... Kandel has identified changes in the structure and functioning of neurons in the brain when forming the memory of a newly learned experience. He was recognised with a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2000. He studied Aplysia californica, a very large seaweed munching sea slug found along the ...
... Kandel has identified changes in the structure and functioning of neurons in the brain when forming the memory of a newly learned experience. He was recognised with a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2000. He studied Aplysia californica, a very large seaweed munching sea slug found along the ...
a PowerPoint Presentation of Module 24
... Karl Lashley (18901958) showed that rats who had learned a maze retained parts of that memory, even when various small parts of their brain were removed. ...
... Karl Lashley (18901958) showed that rats who had learned a maze retained parts of that memory, even when various small parts of their brain were removed. ...
Stages of Memory
... To retrieve a specific memory from the web of associations, you must first activate one of the strands that leads to it. This process is called ...
... To retrieve a specific memory from the web of associations, you must first activate one of the strands that leads to it. This process is called ...
Notes-Brain and Memory
... As the main part of the central nervous system, the brain may be divided into many parts, but we will focus on the Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Cerebellum, and Brain Stem 1. Cerebrum is the largest area of the brain taking up almost two-thirds of the volume of the total brain. The outermost layer, cerebr ...
... As the main part of the central nervous system, the brain may be divided into many parts, but we will focus on the Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Cerebellum, and Brain Stem 1. Cerebrum is the largest area of the brain taking up almost two-thirds of the volume of the total brain. The outermost layer, cerebr ...
Biological Basis of Memory
... o Shows that must be used in the encoding of new memories and them from STM to LTM. o Implicit memories like memories do still occur showing that these may not involve the hippocampus but knowing they are there ( memory) does not work showing the hippocampus is involved in these. 3. Infantile Amnesi ...
... o Shows that must be used in the encoding of new memories and them from STM to LTM. o Implicit memories like memories do still occur showing that these may not involve the hippocampus but knowing they are there ( memory) does not work showing the hippocampus is involved in these. 3. Infantile Amnesi ...
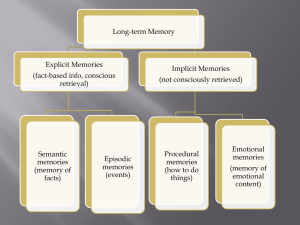
Long-term memory
... – Damages mammilary bodies and other nearby parts of the hypothalamus and thalamus – This damage produces an amnesia similar to the type of NA and HM (sever anterograde amnesia) ...
... – Damages mammilary bodies and other nearby parts of the hypothalamus and thalamus – This damage produces an amnesia similar to the type of NA and HM (sever anterograde amnesia) ...
INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONAL NEUROBIOLOGY Tamás
... consolidation, storage and retrieval are explained in details, with special attention paid to the role of hippocampus and sleep. One has gained sufficient knowledge, if understands and can explain the following: 1. Memory has developed under evolutionary pressure ensuring usage of previous experienc ...
... consolidation, storage and retrieval are explained in details, with special attention paid to the role of hippocampus and sleep. One has gained sufficient knowledge, if understands and can explain the following: 1. Memory has developed under evolutionary pressure ensuring usage of previous experienc ...
Storage and Retrieval
... sister home from school 6.The fact that the smell of eggs makes you sick and you don’t know why ...
... sister home from school 6.The fact that the smell of eggs makes you sick and you don’t know why ...
“Describe the neuroanatomy of and neural processes related to
... which new information and abilities are incorporated into one’s mind, whereas memory is the way in which that information or those abilities are stored. It is important to note from the outset that there are certainly different kinds of memory, such as procedural memory (remembering how to do someth ...
... which new information and abilities are incorporated into one’s mind, whereas memory is the way in which that information or those abilities are stored. It is important to note from the outset that there are certainly different kinds of memory, such as procedural memory (remembering how to do someth ...
Memory_Ch7_all - Arizona State University
... How did these particular memories come to be represented by these particular neurons firing in this ...
... How did these particular memories come to be represented by these particular neurons firing in this ...
3.10 notes
... stored in the cerebellum • PET scans suggest short-term memories are stored in the prefrontal cortex and temporal lobe • Consolidation – Changes in structure and functioning of neurons when a memory is formed ...
... stored in the cerebellum • PET scans suggest short-term memories are stored in the prefrontal cortex and temporal lobe • Consolidation – Changes in structure and functioning of neurons when a memory is formed ...
The Neural Basis Of Memory
... neurons can be seen by the naked eye, so can be observed, stimulated or removed . ...
... neurons can be seen by the naked eye, so can be observed, stimulated or removed . ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... Positron emission tomography (PET) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scans use changes in blood flow to measure brain activity ...
... Positron emission tomography (PET) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scans use changes in blood flow to measure brain activity ...
Chap2
... Memory consists of a change in the structure of neurons that leads to increased likelihood of firing. Review of neural structure: ...
... Memory consists of a change in the structure of neurons that leads to increased likelihood of firing. Review of neural structure: ...
Memory consolidation

Memory consolidation is a category of processes that stabilize a memory trace after its initial acquisition. Consolidation is distinguished into two specific processes, synaptic consolidation, which is synonymous with late-phase LTP and occurs within the first few hours after learning, and systems consolidation, where hippocampus-dependent memories become independent of the hippocampus over a period of weeks to years. Recently, a third process has become the focus of research, reconsolidation, in which previously-consolidated memories can be made labile again through reactivation of the memory trace.