Common Gov Final
... “The vast majority of local parties are essentially voluntary organizations. . . . They have the least influence and the fewest resources. The combination of . . . reliance on volunteers in an era when volunteers are hard to find, complex campaign finance regulations, and the general low regard in w ...
... “The vast majority of local parties are essentially voluntary organizations. . . . They have the least influence and the fewest resources. The combination of . . . reliance on volunteers in an era when volunteers are hard to find, complex campaign finance regulations, and the general low regard in w ...
Review for EOCT
... • The framers of the United States Constitution included the concepts of federalism, checks and balances, and separation of powers in the document because they – (1) feared a government with unlimited power – (2) favored the poor over the rich – (3) wanted to increase the powers of the states – ...
... • The framers of the United States Constitution included the concepts of federalism, checks and balances, and separation of powers in the document because they – (1) feared a government with unlimited power – (2) favored the poor over the rich – (3) wanted to increase the powers of the states – ...
The 535 Who Make the Nation`s Laws
... The legislative branch is the arm of the national government that makes the nation's laws. It is made up of two houses called the Senate and the House of Representatives. The legislative branch not only makes the country's laws but also serves as a check on the office of the presidency and the judic ...
... The legislative branch is the arm of the national government that makes the nation's laws. It is made up of two houses called the Senate and the House of Representatives. The legislative branch not only makes the country's laws but also serves as a check on the office of the presidency and the judic ...
Chapter 6 A Fledgling State in a New Nation
... gathered in the courthouse in New Bern to take part in this landmark case. • Among them were – William R. Davie – James Iredell ...
... gathered in the courthouse in New Bern to take part in this landmark case. • Among them were – William R. Davie – James Iredell ...
100 Essential Facts - b
... 31. Meriwether Lewis and William Clark were commissioned by President Thomas Jefferson to explore the Louisiana Territory. Their journey lasted from 1804-1806. 32. The War of 1812 against England lasted two years. An American victory increased nationalism and economic independence. 33. In 1819 the U ...
... 31. Meriwether Lewis and William Clark were commissioned by President Thomas Jefferson to explore the Louisiana Territory. Their journey lasted from 1804-1806. 32. The War of 1812 against England lasted two years. An American victory increased nationalism and economic independence. 33. In 1819 the U ...
Chapter 11 Jefferson Era-notes
... 1. The election resulted in a tie between Jefferson and Burr, which then went to a vote in the House of Representatives. 2. With the persuasion of Alexander Hamilton, the tie was broken in the ________________________________ and Jefferson became President. 3. After this election, in 1803, the Twelf ...
... 1. The election resulted in a tie between Jefferson and Burr, which then went to a vote in the House of Representatives. 2. With the persuasion of Alexander Hamilton, the tie was broken in the ________________________________ and Jefferson became President. 3. After this election, in 1803, the Twelf ...
PPT
... Federalist 81: “The arguments, or rather suggestions, upon which this charge is founded, are to this effect: "The authority of the proposed Supreme Court of the United States, which is to be a separate and independent body, will be superior to that of the legislature. The power of construing the law ...
... Federalist 81: “The arguments, or rather suggestions, upon which this charge is founded, are to this effect: "The authority of the proposed Supreme Court of the United States, which is to be a separate and independent body, will be superior to that of the legislature. The power of construing the law ...
SIX BASIC PRINCIPLES OF THE UNITED STATES CONSTITUTION
... Executive Branch – President appoints Supreme Court justices, President can veto Congressional legislation ...
... Executive Branch – President appoints Supreme Court justices, President can veto Congressional legislation ...
list - SCOTUSblog
... Holding: Affirmed in part, reversed in part, and remanded in a 6-3 decision with an opinion written by Chief Justice Roberts ...
... Holding: Affirmed in part, reversed in part, and remanded in a 6-3 decision with an opinion written by Chief Justice Roberts ...
Tic Tac Toe Branches of Government
... a formal agreement between the governments of two or more countries ambassador an official representative of a country's government chief justice the judge who presides over a supreme court Judiciary Act The Act set the number of Supreme Court justices of 1789 at six: one Chief Justice and five Asso ...
... a formal agreement between the governments of two or more countries ambassador an official representative of a country's government chief justice the judge who presides over a supreme court Judiciary Act The Act set the number of Supreme Court justices of 1789 at six: one Chief Justice and five Asso ...
Name
... 13. The __________________________________________ replaced the Embargo Act and banned trade with only Britain and France. 14. During the War of 1812 ___________________________________________ served as president and commander in chief. 15. ______________________________________ were members of Co ...
... 13. The __________________________________________ replaced the Embargo Act and banned trade with only Britain and France. 14. During the War of 1812 ___________________________________________ served as president and commander in chief. 15. ______________________________________ were members of Co ...
Citizenship Test
... 4. Who becomes president should the president and vice president die? ________________________ 5. What did the Emancipation Proclamation do? __________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 6. Who has the power to declare war? ...
... 4. Who becomes president should the president and vice president die? ________________________ 5. What did the Emancipation Proclamation do? __________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 6. Who has the power to declare war? ...
supreme court cases
... BURGER COURT (1969-1986): New York Times v. The United Sates (1971) 1st Amendment - Freedom of the Press; Pentagon Papers; Prior Restraint – Censorship; Government cannot stop publication unless “justification for the imposition of such restraint” is conclusively proven – e.g. national security – “c ...
... BURGER COURT (1969-1986): New York Times v. The United Sates (1971) 1st Amendment - Freedom of the Press; Pentagon Papers; Prior Restraint – Censorship; Government cannot stop publication unless “justification for the imposition of such restraint” is conclusively proven – e.g. national security – “c ...
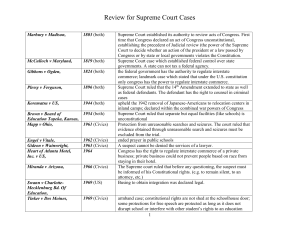
Review for Supreme Court Cases
... establishing the precedent of Judicial review (the power of the Supreme Court to decide whether an action of the president or a law passed by Congress or by state or local governments violates the Constitution. Supreme Court case which established federal control over state governments. A state can ...
... establishing the precedent of Judicial review (the power of the Supreme Court to decide whether an action of the president or a law passed by Congress or by state or local governments violates the Constitution. Supreme Court case which established federal control over state governments. A state can ...
Federalism
... The Supreme Court may: •Declare President’s actions unconstitutional •Declare laws unconstitutional The President may: •Veto laws passed by Congress •Call a special session of Congress ...
... The Supreme Court may: •Declare President’s actions unconstitutional •Declare laws unconstitutional The President may: •Veto laws passed by Congress •Call a special session of Congress ...
Document
... infringed on the rights of the people to govern themselves under their particular State Constitution’s. (6) In 1973, the Supreme Court of the United States infringed on the principles of federalism elucidated in the Tenth Amendment to the United States Constitution by ruling that abortion was a ...
... infringed on the rights of the people to govern themselves under their particular State Constitution’s. (6) In 1973, the Supreme Court of the United States infringed on the principles of federalism elucidated in the Tenth Amendment to the United States Constitution by ruling that abortion was a ...
Harish Salve SA on Judicial Activism in India
... Following the lifting of the Emergency, the Supreme Court worked hard to regain lost ground. Locus standi was considerably widened to enable ‘well-meaning citizens’ to bring cases even if they were not directly affected, and for judges themselves to refer possible breaches of rights for investigatio ...
... Following the lifting of the Emergency, the Supreme Court worked hard to regain lost ground. Locus standi was considerably widened to enable ‘well-meaning citizens’ to bring cases even if they were not directly affected, and for judges themselves to refer possible breaches of rights for investigatio ...
One major reason that Alexander Hamilton proposed a national
... the United States needed time to gain economic and military strength treaties were prohibited by the Constitution the United States should not expand by force alliances should be established with both France and England ...
... the United States needed time to gain economic and military strength treaties were prohibited by the Constitution the United States should not expand by force alliances should be established with both France and England ...
Marbury v. Madison

Marbury v. Madison, 5 U.S. 137 (1803), was a landmark United States Supreme Court case in which the Court formed the basis for the exercise of judicial review in the United States under Article III of the Constitution. The landmark decision helped define the boundary between the constitutionally separate executive and judicial branches of the American form of government.The case resulted from a petition to the Supreme Court by William Marbury, who had been appointed Justice of the Peace in the District of Columbia by President John Adams but whose commission was not subsequently delivered. Marbury petitioned the Supreme Court to force the new Secretary of State James Madison to deliver the documents. The Court, with John Marshall as Chief Justice, found firstly that Madison's refusal to deliver the commission was both illegal and correctible. Nonetheless, the Court stopped short of ordering Madison (by writ of mandamus) to hand over Marbury's commission, instead holding that the provision of the Judiciary Act of 1789 that enabled Marbury to bring his claim to the Supreme Court was itself unconstitutional, since it purported to extend the Court's original jurisdiction beyond that which Article III established. The petition was therefore denied.