3. Ocean Geography Notes
... Since it is the only accessible layer, we know the most about it. Consists of layered rocks located on 12 plates The MOHO separates the crust from the mantle Crust slides around on liquid mantle 5 km to 70 km in depth ...
... Since it is the only accessible layer, we know the most about it. Consists of layered rocks located on 12 plates The MOHO separates the crust from the mantle Crust slides around on liquid mantle 5 km to 70 km in depth ...
Plate Boundaries
... Age of the rocks increase as distance from the ridge increases Extreme Ecosystems – Hydrothermal Vents ...
... Age of the rocks increase as distance from the ridge increases Extreme Ecosystems – Hydrothermal Vents ...
Lesson 10 - Rift Volcanism
... 1) Beneath Oceans The greatest volume of volcanic rock is produced within oceanic ridges where seafloor spreading is active. Example; along the Mid Atlantic Ridge. Shield volcanoes are formed along ridges when basaltic lava flows on the ocean floor. In some case these volcanoes can rise above se ...
... 1) Beneath Oceans The greatest volume of volcanic rock is produced within oceanic ridges where seafloor spreading is active. Example; along the Mid Atlantic Ridge. Shield volcanoes are formed along ridges when basaltic lava flows on the ocean floor. In some case these volcanoes can rise above se ...
Stop the Continent, I Want to Get Off! - PLC-METS
... • Melting decreases the density, so it rises, forming a row of volcanic mountains parallel to the convergent boundary, therefore parallel to the continental coast. • This chain of volcanoes is known as a “Volcanic Arc”. ...
... • Melting decreases the density, so it rises, forming a row of volcanic mountains parallel to the convergent boundary, therefore parallel to the continental coast. • This chain of volcanoes is known as a “Volcanic Arc”. ...
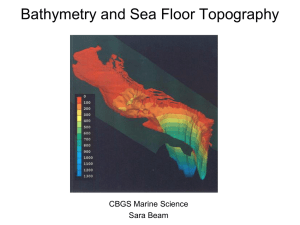
Bathymetry
... terrigenous sediment from land out to sea • Hatteras Canyon may be a drowned river valley from lower sea level **Note the narrow vs. wide continental shelves Active coast- narrow shelf Passive coast- wide shelf ...
... terrigenous sediment from land out to sea • Hatteras Canyon may be a drowned river valley from lower sea level **Note the narrow vs. wide continental shelves Active coast- narrow shelf Passive coast- wide shelf ...
Karenia Brevis
... 10-12 F rise in temperature Most severe marine extinction in the last 90 million years Humans will add as much carbon to the atmosphere in 500 years (1800 to 2300) as the PETM did over 10,000 years ...
... 10-12 F rise in temperature Most severe marine extinction in the last 90 million years Humans will add as much carbon to the atmosphere in 500 years (1800 to 2300) as the PETM did over 10,000 years ...
Rio+20 Policy Ocean Governance 23 April 2012 Oceans are critical
... Strategic Environmental Assessments (SEAs); and access and benefit sharing for marine Page 1 of 2 ...
... Strategic Environmental Assessments (SEAs); and access and benefit sharing for marine Page 1 of 2 ...
Global Concerns Vocabulary
... Deposits of organic matter that have been altered over geologic time (since the Earth's formation) and can be burned for energy; for example, coal, crude oil and natural gas. ...
... Deposits of organic matter that have been altered over geologic time (since the Earth's formation) and can be burned for energy; for example, coal, crude oil and natural gas. ...
The Ocean Floor
... http://www.log.furg.br/WEBens/ocean/wormuth/marineprovinces/natlanticseafloor.gif ...
... http://www.log.furg.br/WEBens/ocean/wormuth/marineprovinces/natlanticseafloor.gif ...
Chapter 14
... Ocean density Density is mass per unit volume - how heavy something is for its size Determines the water’s vertical position in the ocean Factors affecting seawater density • Salinity • Temperature - the greatest influence ...
... Ocean density Density is mass per unit volume - how heavy something is for its size Determines the water’s vertical position in the ocean Factors affecting seawater density • Salinity • Temperature - the greatest influence ...
The Ocean-Atmosphere Hydrothermohaline Conveyor Belt
... The ocean thermohaline circulation is linked to the hydrothermal circulation of the atmosphere. The ocean thermohaline circulation is expressed in potential temperature-salinity space and comprises a tropical upper-ocean circulation, a global conveyor belt cell and an Antarctic Bottom Water cell. Th ...
... The ocean thermohaline circulation is linked to the hydrothermal circulation of the atmosphere. The ocean thermohaline circulation is expressed in potential temperature-salinity space and comprises a tropical upper-ocean circulation, a global conveyor belt cell and an Antarctic Bottom Water cell. Th ...
Chapter 22 Reading Guide
... 2. Middle Zone: bottom of mixed layer to about 1000 meters deep; temperature falls rapidly with depth to low of about 5C. 3. Deep water: below 1000 meters deep; around 2C everywhere except for isolated waters. 1. Define salinity and explain how its composition and strength can vary. Salinity is th ...
... 2. Middle Zone: bottom of mixed layer to about 1000 meters deep; temperature falls rapidly with depth to low of about 5C. 3. Deep water: below 1000 meters deep; around 2C everywhere except for isolated waters. 1. Define salinity and explain how its composition and strength can vary. Salinity is th ...
How The Earth Works
... 35 minutes to birth of Christ 1 hour+ to pyramids 3 hours to retreat of glaciers from Wisconsin 12 days = 1 million years 2 years to extinction of dinosaurs 14 years to age of Niagara Escarpment 31 years = 1 billion years ...
... 35 minutes to birth of Christ 1 hour+ to pyramids 3 hours to retreat of glaciers from Wisconsin 12 days = 1 million years 2 years to extinction of dinosaurs 14 years to age of Niagara Escarpment 31 years = 1 billion years ...
Extreme Trapping O
... long-term (hundreds of millions of years) when, following a ments. For those who use sediments traps, two long trip to the deep seafloor, the carbon of their dead examples of difficult environments are bodies is absorbed into Earth’s crust the deepest oceans and the permaby the plate tectonic proces ...
... long-term (hundreds of millions of years) when, following a ments. For those who use sediments traps, two long trip to the deep seafloor, the carbon of their dead examples of difficult environments are bodies is absorbed into Earth’s crust the deepest oceans and the permaby the plate tectonic proces ...
Ocean life
... Ocean temperature Surface water temperature varies with the amount of solar radiation received • Lower surface temperatures are found in high-latitude regions • Higher temperatures found in low-latitude ...
... Ocean temperature Surface water temperature varies with the amount of solar radiation received • Lower surface temperatures are found in high-latitude regions • Higher temperatures found in low-latitude ...
Chapter 10 Biological Productivity in the Ocean
... It is possible to estimate plant and fish productivity in the ocean. • The size of the plankton biomass is a good indicator of the biomass of the remainder of the food web. • Annual primary production (APP) is equal to primary production rate (PPR) times the area for which the rate is applicable. – ...
... It is possible to estimate plant and fish productivity in the ocean. • The size of the plankton biomass is a good indicator of the biomass of the remainder of the food web. • Annual primary production (APP) is equal to primary production rate (PPR) times the area for which the rate is applicable. – ...
Section 4 Sea-Floor Spreading
... _sinks_ beneath a _deep_-_ocean_ trench and back into the _mantle_ at a _convergent_ plate boundary. ...
... _sinks_ beneath a _deep_-_ocean_ trench and back into the _mantle_ at a _convergent_ plate boundary. ...
ExamView Pro - oceanography review.tst
... 7. In the ocean, high salinities are found where evaporation is ____________________. 8. A thermocline is not present in high latitudes; instead, the water column is ____________________. 9. The ocean’s surface water temperature varies with the amount of solar radiation received, which is primarily ...
... 7. In the ocean, high salinities are found where evaporation is ____________________. 8. A thermocline is not present in high latitudes; instead, the water column is ____________________. 9. The ocean’s surface water temperature varies with the amount of solar radiation received, which is primarily ...
The Oldest Crust in Ocean Basins
... Scientists have been studying this area, in water depths of more than 6000m, through ocean drilling for more than three decades. The most recent penetration of the approximately 170 million-yearold crust by ODP occurred on Leg 185 as part of the "Subduction Factory Experiment". ...
... Scientists have been studying this area, in water depths of more than 6000m, through ocean drilling for more than three decades. The most recent penetration of the approximately 170 million-yearold crust by ODP occurred on Leg 185 as part of the "Subduction Factory Experiment". ...
Landforms and Oceans Class Notes
... 3. ___________________________ forces tear down or destroy landforms and other things on the earth’s surface. 4. _____________________ is the process through which rocks or other materials are broken down. This is a natural process that happens over a long period of time. 5. Weathering can be ______ ...
... 3. ___________________________ forces tear down or destroy landforms and other things on the earth’s surface. 4. _____________________ is the process through which rocks or other materials are broken down. This is a natural process that happens over a long period of time. 5. Weathering can be ______ ...
marine ecosystem
... sunlight – photosynthetic processes depend on how deep and turbid the water is nutrients – are transported by ocean currents to different marine habitats from land runoff, or by upwellings from the deep sea, or they sink though the sea as marine snow salinity – varies, particularly in estuaries or n ...
... sunlight – photosynthetic processes depend on how deep and turbid the water is nutrients – are transported by ocean currents to different marine habitats from land runoff, or by upwellings from the deep sea, or they sink though the sea as marine snow salinity – varies, particularly in estuaries or n ...
Anoxic event

Oceanic anoxic events or anoxic events (Anoxia conditions) refer to intervals in the Earth's past where portions of oceans become depleted in oxygen (O2) at depths over a large geographic area. During some of these events, euxinia develops - euxinia refers to anoxic waters that contain H2S hydrogen sulfide. Although anoxic events have not happened for millions of years, the geological record shows that they happened many times in the past. Anoxic events coincide with several mass extinctions and may contribute to these events. These mass extinctions include some that geobiologists use as time markers in biostratigraphic dating. It is believed oceanic anoxic events are strongly linked to slowing of ocean circulation, climatic warming and elevated levels of greenhouse gases. Enhanced volcanism (through the release of CO2 and other greenhouse gases) is the proposed central external trigger for the development of these events.