049539193X_177844
... 14. The most rapid recycling occurs in the daily feeding, death, and decay of surface organisms. A slower loop occurs as the bodies of organisms fall below the pycnocline, and phosphorus escapes downward into deep ocean circulation. The longest loop begins with the phosphorus or silicon locked into ...
... 14. The most rapid recycling occurs in the daily feeding, death, and decay of surface organisms. A slower loop occurs as the bodies of organisms fall below the pycnocline, and phosphorus escapes downward into deep ocean circulation. The longest loop begins with the phosphorus or silicon locked into ...
OCR ASA Level Geography Exploring Oceans Learner Resource 1
... Guyots were seamounts that extended above sea level, wave erosion flattened the ridge. As the mount moved long the plate away from the ridge, through the process of sea floor spreading, the mount subsided below the level of the sea. ...
... Guyots were seamounts that extended above sea level, wave erosion flattened the ridge. As the mount moved long the plate away from the ridge, through the process of sea floor spreading, the mount subsided below the level of the sea. ...
chapter 5 ecosystems and the physical environment
... Pacific – 2. ocean currents which normally flow westward in this area, slow down, stop altogether, or even reverse and go eastward – 3. devastating effects on the fisheries off South America – normally, the colder, nutrient-rich deep water below the surface upwells along the coast in response to tra ...
... Pacific – 2. ocean currents which normally flow westward in this area, slow down, stop altogether, or even reverse and go eastward – 3. devastating effects on the fisheries off South America – normally, the colder, nutrient-rich deep water below the surface upwells along the coast in response to tra ...
Marine Biome
... From 200 m down to around 1,000 m (3,281 ft) Also known as the middle pelagic or twilight zone • some light penetrates this deep but it is insufficient for photosynthesis • at about 500 m the water becomes depleted of oxygen • some creatures living in the mesopelagic zone will rise to the epipelagic ...
... From 200 m down to around 1,000 m (3,281 ft) Also known as the middle pelagic or twilight zone • some light penetrates this deep but it is insufficient for photosynthesis • at about 500 m the water becomes depleted of oxygen • some creatures living in the mesopelagic zone will rise to the epipelagic ...
Layers of the Earth (Notes 1/5)
... 2. Atmosphere: Sunlight broke up water molecules into oxygen, & volcanoes released gases. a.) green plants also add Oxygen through photosynthesis. ...
... 2. Atmosphere: Sunlight broke up water molecules into oxygen, & volcanoes released gases. a.) green plants also add Oxygen through photosynthesis. ...
01A-2 - Etudes
... but are not “good” swimmers ○ most of the biomass in the ocean consists of tiny pelagic organisms (pelagic = planktonic) ○ many animals grab / strain / filter the tiny plankton from the water (this is called “suspension” or “filter” feeding) ...
... but are not “good” swimmers ○ most of the biomass in the ocean consists of tiny pelagic organisms (pelagic = planktonic) ○ many animals grab / strain / filter the tiny plankton from the water (this is called “suspension” or “filter” feeding) ...
Chapter 3 The Origin of Ocean Basins LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1
... volcanism in terms of the concept of global plate tectonics. 5. Calculate spreading rates of ocean basins. CHAPTER OUTLINE A. Ocean basin is defined as that part of the sea floor deeper than 2000 m (6000 ft). 3-1. Continental Drift B. Based upon the fit of continental outlines and fossil and geologi ...
... volcanism in terms of the concept of global plate tectonics. 5. Calculate spreading rates of ocean basins. CHAPTER OUTLINE A. Ocean basin is defined as that part of the sea floor deeper than 2000 m (6000 ft). 3-1. Continental Drift B. Based upon the fit of continental outlines and fossil and geologi ...
Extinction Hypothesis B – Continental Drift
... of their ultimate extinction. Conversely, a sudden "now you see them, now you don't" end to the dinosaurs implies a catastrophic cause. Depending on location and interpretation, the fossil record seems to say different things. According to some scientists, fossil evidence clearly shows a decline in ...
... of their ultimate extinction. Conversely, a sudden "now you see them, now you don't" end to the dinosaurs implies a catastrophic cause. Depending on location and interpretation, the fossil record seems to say different things. According to some scientists, fossil evidence clearly shows a decline in ...
Marine Sediment Proxy Records
... bridge towards terrestrial proxy records (such as lake sediments and ice cores) at comparable time resolution. Temporal Resolution of Marine Sediments Work on decadal to centennial timescales demands a very tight age control and precise correlation between proxy records if robust conclusions are to ...
... bridge towards terrestrial proxy records (such as lake sediments and ice cores) at comparable time resolution. Temporal Resolution of Marine Sediments Work on decadal to centennial timescales demands a very tight age control and precise correlation between proxy records if robust conclusions are to ...
Chap7Sect2 -Cont Drift and Sea-floor
... 1. What is continental drift? 2. How do landforms, fossils, and climate changes show evidence of the changing surface of the Earth? 3. Explain how sea-floor spreading provides a way for continents to move. ...
... 1. What is continental drift? 2. How do landforms, fossils, and climate changes show evidence of the changing surface of the Earth? 3. Explain how sea-floor spreading provides a way for continents to move. ...
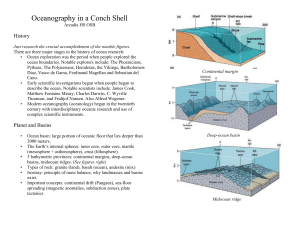
InAConchShell - some tryout study material
... Upwelling: rising of bottom water; downwelling: sinking of surface water. Langmuir circulation is a complex horizontal helical (spiral) motion that extends parallel to the wind. ...
... Upwelling: rising of bottom water; downwelling: sinking of surface water. Langmuir circulation is a complex horizontal helical (spiral) motion that extends parallel to the wind. ...
Theory of plate tectonics - 8th Grade Social Studies
... Wegener was intrigued by the fossil species and unusual geologic structures found in both S. America and Africa Further evidence existed in the discovery of glacial deposits in Africa and tropical plant fossils in Antarctica At the time, Wegener could not explain what force would be strong enough to ...
... Wegener was intrigued by the fossil species and unusual geologic structures found in both S. America and Africa Further evidence existed in the discovery of glacial deposits in Africa and tropical plant fossils in Antarctica At the time, Wegener could not explain what force would be strong enough to ...
Plate Tectonics
... Earth’s lithosphere is divided into pieces called tectonic plates that move around on top of the asthensophere • Plates are either oceanic or continental ...
... Earth’s lithosphere is divided into pieces called tectonic plates that move around on top of the asthensophere • Plates are either oceanic or continental ...
Marine Biology Worksheet I
... surface water causing the density to increase. 3. When sea ice forms salt is left behind causing the density to increase 4. The cold salty dense surface water sinks bringing oxygen to the ocean depths. 5. The surface water has oxygen due to two things: • There is enough light at the surface for phot ...
... surface water causing the density to increase. 3. When sea ice forms salt is left behind causing the density to increase 4. The cold salty dense surface water sinks bringing oxygen to the ocean depths. 5. The surface water has oxygen due to two things: • There is enough light at the surface for phot ...
Continental Margins and Marginal Seas
... Significantly higher specific rates of organic productivity, for instance, occur in the coastal oceans than in the open oceans (see The Open Oceans) owing to a more rapid turnover rate and a higher nutrient supply from upwelling and riverine inputs. Another example is that 8 to 30 times more organic ...
... Significantly higher specific rates of organic productivity, for instance, occur in the coastal oceans than in the open oceans (see The Open Oceans) owing to a more rapid turnover rate and a higher nutrient supply from upwelling and riverine inputs. Another example is that 8 to 30 times more organic ...
Chapter 2
... less saline than deep waters, and thus less dense. The layers don’t mix. Where warm tropical currents reach polar areas, the water cools, ice forms, and the water becomes more saline and more dense. The water mass sinks in these regions, and moves back toward the equator. ...
... less saline than deep waters, and thus less dense. The layers don’t mix. Where warm tropical currents reach polar areas, the water cools, ice forms, and the water becomes more saline and more dense. The water mass sinks in these regions, and moves back toward the equator. ...
exam_1
... 32. Which of the following is NOT true about passive continental margins? A. They have little seismic or volcanic activity. B. They form after continents are rifted apart. C. They tend to be wider than active margins. D. They occur away from plate boundaries. E. They are commonly at subduction zones ...
... 32. Which of the following is NOT true about passive continental margins? A. They have little seismic or volcanic activity. B. They form after continents are rifted apart. C. They tend to be wider than active margins. D. They occur away from plate boundaries. E. They are commonly at subduction zones ...
Divergent Plate Boundaries (plates move )
... A_________ is formed where it bends down. As the oceanic lithosphere descends, it triggers _________ due to the release of the salt _________ it contains. The _______ rises creating a chain of __________ called a continental _________ _____. An example is the ___________ mountains and Mt. St._______ ...
... A_________ is formed where it bends down. As the oceanic lithosphere descends, it triggers _________ due to the release of the salt _________ it contains. The _______ rises creating a chain of __________ called a continental _________ _____. An example is the ___________ mountains and Mt. St._______ ...
Continental-Drift-and-Seafloor-Spreading
... 4. Tropical plant fossils that were found on an island in Artic Ocean! (Scratches in rocks made by glaciers in South Africa) The continental drift theory was NOT accepted because Wegener could not explain HOW the continents were moving/drifted apart. ...
... 4. Tropical plant fossils that were found on an island in Artic Ocean! (Scratches in rocks made by glaciers in South Africa) The continental drift theory was NOT accepted because Wegener could not explain HOW the continents were moving/drifted apart. ...
Nova Scotia ingenuity sets sail
... Stickers” — creates a cohesive collection process. The “Bedford Stickers,” which use adhesive that withstand wet and dry conditions and variable temperatures, are distributed by Cabot Shipping Supplies of Dartmouth, NS. “OFI is an international hub for ocean science, bringing together researchers fr ...
... Stickers” — creates a cohesive collection process. The “Bedford Stickers,” which use adhesive that withstand wet and dry conditions and variable temperatures, are distributed by Cabot Shipping Supplies of Dartmouth, NS. “OFI is an international hub for ocean science, bringing together researchers fr ...
GEOL 1e Lecture Outlines
... • Common in Pacific Ocean basin • Earthquakes along Benioff zones • Volcano chain on overriding plate ...
... • Common in Pacific Ocean basin • Earthquakes along Benioff zones • Volcano chain on overriding plate ...
13.3 Ocean Water Chemistry
... ii. Sodium chloride, table salt, is the most common salt in ocean water—86% 1. When dissolved, it separates into sodium and chloride ions iii.Other ions include magnesium, calcium, sulfate, and potassium ...
... ii. Sodium chloride, table salt, is the most common salt in ocean water—86% 1. When dissolved, it separates into sodium and chloride ions iii.Other ions include magnesium, calcium, sulfate, and potassium ...
mitrie_sediment_marine
... bridge towards terrestrial proxy records (such as lake sediments and ice cores) at comparable time resolution. Temporal Resolution of Marine Sediments Work on decadal to centennial timescales demands a very tight age control and precise correlation between proxy records if robust conclusions are to ...
... bridge towards terrestrial proxy records (such as lake sediments and ice cores) at comparable time resolution. Temporal Resolution of Marine Sediments Work on decadal to centennial timescales demands a very tight age control and precise correlation between proxy records if robust conclusions are to ...
Anoxic event

Oceanic anoxic events or anoxic events (Anoxia conditions) refer to intervals in the Earth's past where portions of oceans become depleted in oxygen (O2) at depths over a large geographic area. During some of these events, euxinia develops - euxinia refers to anoxic waters that contain H2S hydrogen sulfide. Although anoxic events have not happened for millions of years, the geological record shows that they happened many times in the past. Anoxic events coincide with several mass extinctions and may contribute to these events. These mass extinctions include some that geobiologists use as time markers in biostratigraphic dating. It is believed oceanic anoxic events are strongly linked to slowing of ocean circulation, climatic warming and elevated levels of greenhouse gases. Enhanced volcanism (through the release of CO2 and other greenhouse gases) is the proposed central external trigger for the development of these events.