Physiology 2008
... Our objective for this unit - is to discuss how the structure of specific tissues, (and the cells that comprise the tissue) relate to the tissue’s function as well as the growth, aging and trauma of tissues and the changes that occur. The four basic tissue types are: ...
... Our objective for this unit - is to discuss how the structure of specific tissues, (and the cells that comprise the tissue) relate to the tissue’s function as well as the growth, aging and trauma of tissues and the changes that occur. The four basic tissue types are: ...
Test Review Mrs. Benham
... 1. What does your body need to stay alive? Oxygen, Nutrients (food), Water 2. How does your body get what it needs to stay alive? Eating (nutrients, sugar, fats, proteins: all of these things are needed to make energy at the cellular level and to keep our body functioning properly). Breathing (your ...
... 1. What does your body need to stay alive? Oxygen, Nutrients (food), Water 2. How does your body get what it needs to stay alive? Eating (nutrients, sugar, fats, proteins: all of these things are needed to make energy at the cellular level and to keep our body functioning properly). Breathing (your ...
connective tissue
... and relays commands for response • Consists of excitable neurons and supporting neuroglial cells ...
... and relays commands for response • Consists of excitable neurons and supporting neuroglial cells ...
1500Name: Period: Date: Practice | SWBAT relate parts of the
... 5. A person affected by arthritis has pains in the joints, because bones have worn grinded against each other over time, wearing them down. Which tissue in the skeletal system is most likely damaged in this person? A. Cartilage B. Bone marrow C. Ligaments D. Tendons 6. Match each part of the skeleta ...
... 5. A person affected by arthritis has pains in the joints, because bones have worn grinded against each other over time, wearing them down. Which tissue in the skeletal system is most likely damaged in this person? A. Cartilage B. Bone marrow C. Ligaments D. Tendons 6. Match each part of the skeleta ...
Skeletal System HW
... 5. A person affected by arthritis has pains in the joints, because bones have worn grinded against each other over time, wearing them down. Which tissue in the skeletal system is most likely damaged in this person? A. Cartilage B. Bone marrow C. Ligaments D. Tendons 6. Match each part of the skeleta ...
... 5. A person affected by arthritis has pains in the joints, because bones have worn grinded against each other over time, wearing them down. Which tissue in the skeletal system is most likely damaged in this person? A. Cartilage B. Bone marrow C. Ligaments D. Tendons 6. Match each part of the skeleta ...
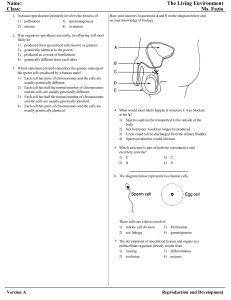
Reproduction and Development
... also form many other different kinds of cells. Stem cells in bone marrow offer a dramatic example. They can give rise to all of the structures in the blood: red blood cells, platelets, and various types of white blood cells. Other stem cells may produce the various components of the skin, liver, or ...
... also form many other different kinds of cells. Stem cells in bone marrow offer a dramatic example. They can give rise to all of the structures in the blood: red blood cells, platelets, and various types of white blood cells. Other stem cells may produce the various components of the skin, liver, or ...
Biology Summary
... so can see how a particular treatment is working newly discovered that some cancer cells don’t produce an important cell membrane receptor that allows the killer cells of the immune system to signal a damaged cell to begin apoptosis ...
... so can see how a particular treatment is working newly discovered that some cancer cells don’t produce an important cell membrane receptor that allows the killer cells of the immune system to signal a damaged cell to begin apoptosis ...
Tissues, Organs, Systems Review Answers
... The stomach lining tissue secretes mucous to protect the cells from the acid. As food enters the duodenum (first section of the small intestine), the pancreas secretes an alkaline solution to raise the pH in the small intestine. 23. Describe the passage of blood through the heart. Blood enters throu ...
... The stomach lining tissue secretes mucous to protect the cells from the acid. As food enters the duodenum (first section of the small intestine), the pancreas secretes an alkaline solution to raise the pH in the small intestine. 23. Describe the passage of blood through the heart. Blood enters throu ...
Laboratory 4: Cell Structure and Function
... Bio 120 Laboratory 4: Cells and Tissues Cells are the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Cells differ enormously in size, shape, and function; some are free living, independent organisms, while others are immovably fixed as part of tissues of multicellular organisms. All cells ex ...
... Bio 120 Laboratory 4: Cells and Tissues Cells are the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Cells differ enormously in size, shape, and function; some are free living, independent organisms, while others are immovably fixed as part of tissues of multicellular organisms. All cells ex ...
Lab on chip for rapid diagnosis of infectious diseases
... and microbiological tests, the future areas of application also comprise environmental analyses or civil protection measures. ...
... and microbiological tests, the future areas of application also comprise environmental analyses or civil protection measures. ...
Lesson 7A Specialized Cells
... •Do embryonic stem cells represent a human life? When does life begin – at fertilization, in the womb, or at birth? •Is a human embryo the same as a human child? •Does a human embryo have any rights? •Might the killing of a single embryo be justified if it provides a cure for a countless number of p ...
... •Do embryonic stem cells represent a human life? When does life begin – at fertilization, in the womb, or at birth? •Is a human embryo the same as a human child? •Does a human embryo have any rights? •Might the killing of a single embryo be justified if it provides a cure for a countless number of p ...
F212 2.6 Cell Division and Diversity
... Potential uses of stem cells Stem cells from bone marrow are extensively used in bone marrow transplants to treat diseases of the blood such as sickle cell anaemia Patients bone marrow cells can be extracted and reinserted after treatment Can be used in chemical testing as opposed to using ani ...
... Potential uses of stem cells Stem cells from bone marrow are extensively used in bone marrow transplants to treat diseases of the blood such as sickle cell anaemia Patients bone marrow cells can be extracted and reinserted after treatment Can be used in chemical testing as opposed to using ani ...
Hematology PowerPoint
... tasteless gas that is commonly produced by fire, automobiles exhaust, and space heaters. CO interferes with the delivery of O2 in the blood. O2 is crowded out of the hemoglobin, eventually depriving cells of their oxygen supply and can be fatal. ...
... tasteless gas that is commonly produced by fire, automobiles exhaust, and space heaters. CO interferes with the delivery of O2 in the blood. O2 is crowded out of the hemoglobin, eventually depriving cells of their oxygen supply and can be fatal. ...
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems Ch. 16
... Form of cancer in which any one of the different types of wbc’s is produced excessively and abnormally. ...
... Form of cancer in which any one of the different types of wbc’s is produced excessively and abnormally. ...
Levels of Organization Notes (pg 418-427)
... shown below on the left, prokaryotic cells also have fewer cell structures. A unicellular organism made of one prokaryotic cell is called a prokaryote. Some prokaryotes live in groups called colonies. Some can also live in extreme environments, as shown in Figure 2 in your text. The heat-loving bact ...
... shown below on the left, prokaryotic cells also have fewer cell structures. A unicellular organism made of one prokaryotic cell is called a prokaryote. Some prokaryotes live in groups called colonies. Some can also live in extreme environments, as shown in Figure 2 in your text. The heat-loving bact ...
Communicable Diseases
... The immune system is made up of many different kinds of white blood cells. White blood cells work together to protect us against disease-causing germs. ...
... The immune system is made up of many different kinds of white blood cells. White blood cells work together to protect us against disease-causing germs. ...
Body Systems Work Together
... electrical system, and a support system. If any system in a building breaks down, other systems can be affected. As one example, think about a building's electrical system. Suppose a mouse chewed through an electrical wire to a furnace. Without electricity, the heating system would not work. If this ...
... electrical system, and a support system. If any system in a building breaks down, other systems can be affected. As one example, think about a building's electrical system. Suppose a mouse chewed through an electrical wire to a furnace. Without electricity, the heating system would not work. If this ...
Cell - St. Pius X High School
... 1. What are the two main types of cells? 2. Which one is larger? 3. Which one does not have a membrane bound nucleus? 4. What are the three main parts of the cell (that all cells have)? 5. What are the 3 components of the cell theory? 6. What theory explains how eukaryotes evolved? 7. What limits th ...
... 1. What are the two main types of cells? 2. Which one is larger? 3. Which one does not have a membrane bound nucleus? 4. What are the three main parts of the cell (that all cells have)? 5. What are the 3 components of the cell theory? 6. What theory explains how eukaryotes evolved? 7. What limits th ...
The immortal Hydra
... indefinite self-renewal capacity of their stem cells, has long attracted attention from biologists as it promises insights into the mechanisms controlling longevity in more advanced animals, including humans. While in search of transcription factors that are strongly expressed and shared by all thre ...
... indefinite self-renewal capacity of their stem cells, has long attracted attention from biologists as it promises insights into the mechanisms controlling longevity in more advanced animals, including humans. While in search of transcription factors that are strongly expressed and shared by all thre ...
File
... • Blood vessels are the tube like structures through which the blood flows. There are three types of blood vessels: – Arteries – carry blood away from the heart – Veins – carry blood toward the heart – Capillaries – are tiny vessels that connect arteries to veins. They exchange substances such as ga ...
... • Blood vessels are the tube like structures through which the blood flows. There are three types of blood vessels: – Arteries – carry blood away from the heart – Veins – carry blood toward the heart – Capillaries – are tiny vessels that connect arteries to veins. They exchange substances such as ga ...
Chapter 20 – Pregnancy, Growth, and Development
... As the fetal head stretches the cervix, a positive feedback mechanism results in stronger and stronger uterine contractions and a greater release of oxytocin. ...
... As the fetal head stretches the cervix, a positive feedback mechanism results in stronger and stronger uterine contractions and a greater release of oxytocin. ...
Function of the blood
... oxygen, carbon dioxide, antibodies, anti-toxins and other nutrients. Carbon dioxide is a by-product which is produced through respiration and is dissolved in the plasma after the cells have respired aerobically. It is then transported to the lungs where it is exhaled, forming the 4% of exhaled carbo ...
... oxygen, carbon dioxide, antibodies, anti-toxins and other nutrients. Carbon dioxide is a by-product which is produced through respiration and is dissolved in the plasma after the cells have respired aerobically. It is then transported to the lungs where it is exhaled, forming the 4% of exhaled carbo ...
Hematopoietic stem cell
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the blood cells that give rise to all the other blood cells and are derived from mesoderm. They are located in the red bone marrow, which is contained in the core of most bones.They give rise to both the myeloid and lymphoid lineages of blood cells. (Myeloid cells include monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, erythrocytes, dendritic cells, and megakaryocytes or platelets. Lymphoid cells include T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells.) The definition of hematopoietic stem cells has changed in the last two decades. The hematopoietic tissue contains cells with long-term and short-term regeneration capacities and committed multipotent, oligopotent, and unipotent progenitors. HSCs constitute 1:10.000 of cells in myeloid tissue.HSCs are a heterogeneous population. The third category consists of the balanced (Bala) HSC, whose L/M ratio is between 3 and 10. Only the myeloid-biased and -balanced HSCs have durable self-renewal properties. In addition, serial transplantation experiments have shown that each subtype preferentially re-creates its blood cell type distribution, suggesting an inherited epigenetic program for each subtype.HSC studies through much of the past half century have led to a much deeper understanding. More recent advances have resulted in the use of HSC transplants in the treatment of cancers and other immune system disorders.