
Non-Intrusive Parameter Estimation for Single-Phase Induction Motors Using Transient Data
... [2] Y. Liu, V. Vittal, J. Undrill, and J.H. Eto, “Transient Model of AirConditioner Compressor Single Phase Induction Motor,” IEEE Trans. ...
... [2] Y. Liu, V. Vittal, J. Undrill, and J.H. Eto, “Transient Model of AirConditioner Compressor Single Phase Induction Motor,” IEEE Trans. ...
Linear IC Applications UNIT -1 DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER
... which is usually connected to the ground node.) In a linear amplifier, the output signal = A input signal, where A is the amplification factor or “gain.” Depending on the nature of the input and output signals, we can have four types of amplifier gain: voltage gain (voltage out / voltage in), curr ...
... which is usually connected to the ground node.) In a linear amplifier, the output signal = A input signal, where A is the amplification factor or “gain.” Depending on the nature of the input and output signals, we can have four types of amplifier gain: voltage gain (voltage out / voltage in), curr ...
Document
... (A) is designed to be the principal heating source for the living space of one or more residences; (B) is not contained within the same cabinet with a central air conditioner whose rated cooling capacity is above 65,000 Btus per hour; and (C) has a heat input rate of less than 225,000 Btus per hour. ...
... (A) is designed to be the principal heating source for the living space of one or more residences; (B) is not contained within the same cabinet with a central air conditioner whose rated cooling capacity is above 65,000 Btus per hour; and (C) has a heat input rate of less than 225,000 Btus per hour. ...
Technical Description
... Negative active energy in second tariff (T2) Negative active energy in third tariff (T3) Negative active energy in forth tariff (T4) A+ max. billing demand in first tariff (T1) A+ max. billing demand in second tariff (T2) A+ max. billing demand in third tariff (T3) A+ max. billing demand in forth ta ...
... Negative active energy in second tariff (T2) Negative active energy in third tariff (T3) Negative active energy in forth tariff (T4) A+ max. billing demand in first tariff (T1) A+ max. billing demand in second tariff (T2) A+ max. billing demand in third tariff (T3) A+ max. billing demand in forth ta ...
SMJE 2103
... Synchronous Generator -testing (short circuit)Procedures of short circuit test: 1) Generator is rotated at rated speed 2) Adjust field current to 0 3) Short circuit the terminals 4) Measure armature current or line current as the field current is increased. ...
... Synchronous Generator -testing (short circuit)Procedures of short circuit test: 1) Generator is rotated at rated speed 2) Adjust field current to 0 3) Short circuit the terminals 4) Measure armature current or line current as the field current is increased. ...
Evaluate: MAX9987/MAX9988 MAX9987/MAX9988 Evaluation Kits General Description Features
... MAX9987, or at 1800MHz for the MAX9988. Important: Use a power sensor rated to at least 0dBm. Measure the loss in the 20dB attenuator (pad) that will be connected to OUT1; account for this loss as an offset in the power meter. 2) Connect the 20dB pad to OUT1. The 20dB pad maintains a reasonable load ...
... MAX9987, or at 1800MHz for the MAX9988. Important: Use a power sensor rated to at least 0dBm. Measure the loss in the 20dB attenuator (pad) that will be connected to OUT1; account for this loss as an offset in the power meter. 2) Connect the 20dB pad to OUT1. The 20dB pad maintains a reasonable load ...
smart voltage reduction
... This may cause circuits to be leading when in reduction When leaving reduction, some of the capacitors need to be switched off to get back to unity power factor ...
... This may cause circuits to be leading when in reduction When leaving reduction, some of the capacitors need to be switched off to get back to unity power factor ...
LT5503
... significant bit of the four-step modulator gain control. MODIN (Pin 4): Modulator Carrier Input Pin. This pin is internally biased and should be AC-coupled. An external matching network is required for a 50Ω source. VCCMOD (Pin 5): Power Supply Pin for the I/Q Modulator. This pin should be externall ...
... significant bit of the four-step modulator gain control. MODIN (Pin 4): Modulator Carrier Input Pin. This pin is internally biased and should be AC-coupled. An external matching network is required for a 50Ω source. VCCMOD (Pin 5): Power Supply Pin for the I/Q Modulator. This pin should be externall ...
FET Dream User`s Guide
... During normal operation, the bright blue LED is off when bypassed and on when the pedal is active. Of course, if there’s no power, the LED will be off regardless and if there’s no power in active mode, there won’t be any signal output. Power Jack This is a standard 2.1mm, center negative power jack. ...
... During normal operation, the bright blue LED is off when bypassed and on when the pedal is active. Of course, if there’s no power, the LED will be off regardless and if there’s no power in active mode, there won’t be any signal output. Power Jack This is a standard 2.1mm, center negative power jack. ...
555 Timer
... •To switch on or off an output after a certain time delay i.e. Games timer, Porch light, Childs mobile, Exercise timer. ...
... •To switch on or off an output after a certain time delay i.e. Games timer, Porch light, Childs mobile, Exercise timer. ...
Protecting PV systems. Technical info
... Depending on the PV system capacity, there may be several PV output circuits (each output circuit consisting of multiple PV source circuits) connected in parallel to achieve higher ampacity and subsequently more power. A PV Overcurrent Protective Device (OCPD) on each PV output circuit will protect ...
... Depending on the PV system capacity, there may be several PV output circuits (each output circuit consisting of multiple PV source circuits) connected in parallel to achieve higher ampacity and subsequently more power. A PV Overcurrent Protective Device (OCPD) on each PV output circuit will protect ...
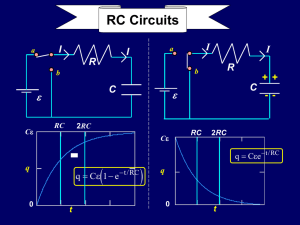
Lect11
... The two circuits shown below contain identical fully charged capacitors at t=0. Circuit 2 has twice as much resistance as circuit 1. ...
... The two circuits shown below contain identical fully charged capacitors at t=0. Circuit 2 has twice as much resistance as circuit 1. ...
YNV05T10-0 - Power-One
... Power-One’s point-of-load converters are recommended for use with regulated bus converters in an Intermediate Bus Architecture (IBA). The YNV05T10 non-isolated DC-DC converter delivers up to 10 A of output current in an industry-standard through-hole Single In-Line Package (SIP). Operating from a 3. ...
... Power-One’s point-of-load converters are recommended for use with regulated bus converters in an Intermediate Bus Architecture (IBA). The YNV05T10 non-isolated DC-DC converter delivers up to 10 A of output current in an industry-standard through-hole Single In-Line Package (SIP). Operating from a 3. ...
Neo900 Infrared Subsystem
... When the control signals from the CPU are in their reset state, the configuration of the IR system is determined by the state of the GPIO pin of the bq27200 battery fuel gauge. We call this pin “bq.GPIO” in the rest of the document. The fuel gauge chip is directly connected to the battery and retain ...
... When the control signals from the CPU are in their reset state, the configuration of the IR system is determined by the state of the GPIO pin of the bq27200 battery fuel gauge. We call this pin “bq.GPIO” in the rest of the document. The fuel gauge chip is directly connected to the battery and retain ...
Fundamental limits of energy dissipation in charge
... charge to physically represent information, and the manipulation and movement of this charge is used to perform computations. Digital transistors, however, dissipate energy as heat at a rate which currently limits scaling and packing density. Modern digital devices based on field-effect transistors ...
... charge to physically represent information, and the manipulation and movement of this charge is used to perform computations. Digital transistors, however, dissipate energy as heat at a rate which currently limits scaling and packing density. Modern digital devices based on field-effect transistors ...
New vacuum interrupters for contactors and switches
... quires less maintenance or is environmen- ...
... quires less maintenance or is environmen- ...
LT5519 - 0.7GHz to 1.4GHz High Linearity
... pins are internally biased and an external resistor must be connected from each IF pin to ground to set the current through the mixer core. The circuit has been optimized to work with 100Ω resistors, which will result in approximately 18mA of DC current per side. For best LO leakage performance, the ...
... pins are internally biased and an external resistor must be connected from each IF pin to ground to set the current through the mixer core. The circuit has been optimized to work with 100Ω resistors, which will result in approximately 18mA of DC current per side. For best LO leakage performance, the ...
LS7538-LS7539
... NOTE 2: A good PCB layout using through-hole components will provide protection for ESD introduced at the Touch Plate in the range of 25kV. Using surface mount components and/or a poor PCB layout can reduce the ESD protection. The OEM can increase the ESD protection provided by the product with any ...
... NOTE 2: A good PCB layout using through-hole components will provide protection for ESD introduced at the Touch Plate in the range of 25kV. Using surface mount components and/or a poor PCB layout can reduce the ESD protection. The OEM can increase the ESD protection provided by the product with any ...
Buck converter
A buck converter is a voltage step down and current step up converter.The simplest way to reduce the voltage of a DC supply is to use a linear regulator (such as a 7805), but linear regulators waste energy as they operate by dissipating excess power as heat. Buck converters, on the other hand, can be remarkably efficient (95% or higher for integrated circuits), making them useful for tasks such as converting the main voltage in a computer (12V in a desktop, 12-24V in a laptop) down to the 0.8-1.8V needed by the processor.

















![[PDF]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008779543_1-98fc070b36888fd6a5b6528db5e9697d-300x300.png)




