432EX2W7
... 3. A. Diagram a class I MHC antigen and state the cells on which the class I MHC antigen is expressed (10 pts) 3.B. Diagram a class II MHC antigen and state the cells on which the class II MHC antigen is expressed (10 pts) I am answering question 3_____. ...
... 3. A. Diagram a class I MHC antigen and state the cells on which the class I MHC antigen is expressed (10 pts) 3.B. Diagram a class II MHC antigen and state the cells on which the class II MHC antigen is expressed (10 pts) I am answering question 3_____. ...
Lecture 4: codominance and complementation
... Class III MHC genes: encode secreted proteins that have immune functions e.g. components of the complement system and molecules involved in inflammation, and other proteins Class I MHC genes: encode glycoproteins expressed on the surface of nearly all nucleated cells; present peptide antigens to ...
... Class III MHC genes: encode secreted proteins that have immune functions e.g. components of the complement system and molecules involved in inflammation, and other proteins Class I MHC genes: encode glycoproteins expressed on the surface of nearly all nucleated cells; present peptide antigens to ...
1.8mb ppt - UCLA.edu
... Processing is internalization, digestion, and presentation of Ag on surface Processing occurs in lysosomes, can eliminate by neutralizing pH ...
... Processing is internalization, digestion, and presentation of Ag on surface Processing occurs in lysosomes, can eliminate by neutralizing pH ...
Chapter 9
... ○ Associate with MHC – αβ TCR ○ Do not associate with MHC – γδ TCR - Much remains to be learned of function of γδ TCR ...
... ○ Associate with MHC – αβ TCR ○ Do not associate with MHC – γδ TCR - Much remains to be learned of function of γδ TCR ...
Presentation slides - Yale School of Medicine
... • most efficient of all APCs • high MHC class I, II & costimulators • efficient cross presentation • stimulate naïve T cells (CD4, CD8) initiate Ag-specific immune responses ...
... • most efficient of all APCs • high MHC class I, II & costimulators • efficient cross presentation • stimulate naïve T cells (CD4, CD8) initiate Ag-specific immune responses ...
Freeman 1e: How we got there
... cells and present cytosol-derived antigenic peptides to TCRs on TC cells. • Class II MHC proteins are expressed only on antigen-presenting cells (APCs). They present exogenously derived peptide antigens to TCRs on TH cells. • The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) spans about 4 million base pair ...
... cells and present cytosol-derived antigenic peptides to TCRs on TC cells. • Class II MHC proteins are expressed only on antigen-presenting cells (APCs). They present exogenously derived peptide antigens to TCRs on TH cells. • The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) spans about 4 million base pair ...
Cloning of the TCR b-chain gene by subtractive hybridization
... common to B and T cells. TCR should be in the 2% genes expressed specifically in T cells. (DNA subtractive ...
... common to B and T cells. TCR should be in the 2% genes expressed specifically in T cells. (DNA subtractive ...
TCR
... Step 2. Naïve lymphocytes circulate in the blood and lymph Step 3. The primary immune response occurs in the lymph nodes and spleen Step 4. Lymphocytes exit the lymph nodes and spleen and become effector lymphocytes--they produce antibody (B cells) or become competent to kill (CD8+ T cells) ...
... Step 2. Naïve lymphocytes circulate in the blood and lymph Step 3. The primary immune response occurs in the lymph nodes and spleen Step 4. Lymphocytes exit the lymph nodes and spleen and become effector lymphocytes--they produce antibody (B cells) or become competent to kill (CD8+ T cells) ...
... Dendritic Cell B-cell 2. Antigen processed by enzymes in primary & secondary granules, lysosome. 3. Peptides from antigen presented on class II MHC (DC can also present on class I, this is crosspresentation) 4. Specific interaction with Tcell receptor (TCR) on THcells. 5. Activation of TH- cells, fo ...
Major Histocompatibility Complex 02/28/06
... MHC II Molecules Antigen presenting features Alpha 1 and beta 1 domains form peptide-binding pocket 13-18 amino acid peptides can bind to MHC II molecule Alpha 2 and beta 2 interact with CD 4 on T helper cells ...
... MHC II Molecules Antigen presenting features Alpha 1 and beta 1 domains form peptide-binding pocket 13-18 amino acid peptides can bind to MHC II molecule Alpha 2 and beta 2 interact with CD 4 on T helper cells ...
Quiz 2 Practice with Answers
... 1. Which of the MHC receptors are found on the surface of most nucleated cells? a. MHC Class I b. MHC Class II c. MHC Class III d. CD4 e. CD8 2. Positive and negative selection occurs in the thymus in order to: a. Delete autoreactive T cells that bind too tightly to self MHC plus self peptide b. Act ...
... 1. Which of the MHC receptors are found on the surface of most nucleated cells? a. MHC Class I b. MHC Class II c. MHC Class III d. CD4 e. CD8 2. Positive and negative selection occurs in the thymus in order to: a. Delete autoreactive T cells that bind too tightly to self MHC plus self peptide b. Act ...
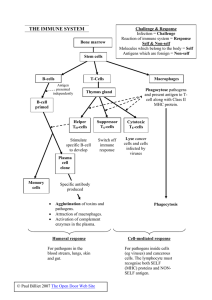
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
... Reaction of immune system = Response Self & Non-self Molecules which belong to the body = Self Antigens which are foreign = Non-self ...
... Reaction of immune system = Response Self & Non-self Molecules which belong to the body = Self Antigens which are foreign = Non-self ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 11. _______ is added in the HAT medium to block dihydrofolate reductase. 12. Immunoproteasomes generate peptides that can bind with MHC class _____ molecules. 13. ________ graft rejection occurs months or years after transplantation. 14. ________ bind to antibodies but do not induce an immune respon ...
... 11. _______ is added in the HAT medium to block dihydrofolate reductase. 12. Immunoproteasomes generate peptides that can bind with MHC class _____ molecules. 13. ________ graft rejection occurs months or years after transplantation. 14. ________ bind to antibodies but do not induce an immune respon ...
ImmunLec21-2010 - 81-493
... human infant the thymus weighs 70 gms by age 40-50 it is only 3 gms. ...
... human infant the thymus weighs 70 gms by age 40-50 it is only 3 gms. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 5. Immuno suppression is not induced by a) anti histamines b) removal of lymphoid tissue c)use of anti lymphocyte antibodies d) cytotoxic drugs II. State True or False.If false Give reasons ...
... 5. Immuno suppression is not induced by a) anti histamines b) removal of lymphoid tissue c)use of anti lymphocyte antibodies d) cytotoxic drugs II. State True or False.If false Give reasons ...
Regulatory T
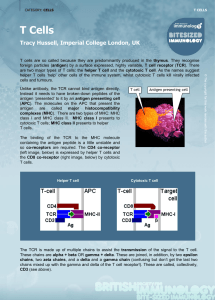
... Unlike antibody, the TCR cannot bind antigen directly. Instead it needs to have broken-down peptides of the antigen ‘presented’ to it by an antigen presenting cell (APC). The molecules on the APC that present the antigen are called major histocompatibility complexes (MHC). There are two types of MHC ...
... Unlike antibody, the TCR cannot bind antigen directly. Instead it needs to have broken-down peptides of the antigen ‘presented’ to it by an antigen presenting cell (APC). The molecules on the APC that present the antigen are called major histocompatibility complexes (MHC). There are two types of MHC ...
ANTIGEN Molecule that is recognized by specific antibody or T cells
... • Determines success of tissue and organ transplants ...
... • Determines success of tissue and organ transplants ...
Quiz 2 Answers
... d. The antigens bound by classical class I and class II molecules are different in their fundamental biochemistry. e. None of the above are true. 9. The MHC is one of the most polymorphic genetic regions known in mammals. This is partly due to the multiple MHC class I genes that are found in that re ...
... d. The antigens bound by classical class I and class II molecules are different in their fundamental biochemistry. e. None of the above are true. 9. The MHC is one of the most polymorphic genetic regions known in mammals. This is partly due to the multiple MHC class I genes that are found in that re ...
Watching Class II MHC molecules move Hidde L. Ploegh
... Antigen presentation requires the coordination of assembly, intracellular trafficking and display of MHC molecules. Class II MHC products sample endocytic compartments and there acquire peptides to be presented to CD4 T cells. The details of these pathways have been worked out mostly in established ...
... Antigen presentation requires the coordination of assembly, intracellular trafficking and display of MHC molecules. Class II MHC products sample endocytic compartments and there acquire peptides to be presented to CD4 T cells. The details of these pathways have been worked out mostly in established ...
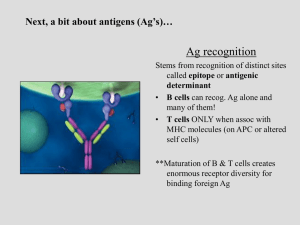
Next, a bit about antigens (Ag`s)…
... Next encounter with same Ag = Secondary (2° ) immune response; lags 1-2 days, Ab response is greater and sustained longer *more memory cells present more plasma cells produced (100-1,000X more Ab’s produced) ...
... Next encounter with same Ag = Secondary (2° ) immune response; lags 1-2 days, Ab response is greater and sustained longer *more memory cells present more plasma cells produced (100-1,000X more Ab’s produced) ...
Name Student ID Oct 29,2015 Choose the BEST alternative. What
... c. Determine if cells can recognize self MHC at a low level as part of dual recognition d. Determine if cells can recognize foreign MHC e. Both a and c 4. What is one of the major roles of the complement cascade in the body's defense against infection? a. It interferes with intracellular viral repli ...
... c. Determine if cells can recognize self MHC at a low level as part of dual recognition d. Determine if cells can recognize foreign MHC e. Both a and c 4. What is one of the major roles of the complement cascade in the body's defense against infection? a. It interferes with intracellular viral repli ...
antigen recognition by b-cell and t
... Antibodies bind to conformational shapes on the surface of antigens. ...
... Antibodies bind to conformational shapes on the surface of antigens. ...
Exam 2
... T cells – what does it mean to be double negative? Double positive? Is CD4 found on Tc or TH cells? Is CD8 found on Tc or TH cells? What is the function of a cytotoxic T cell? T helper cell? ...
... T cells – what does it mean to be double negative? Double positive? Is CD4 found on Tc or TH cells? Is CD8 found on Tc or TH cells? What is the function of a cytotoxic T cell? T helper cell? ...
Major histocompatibility complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a set of cell surface molecules encoded by a large gene family which controls a major part of the immune system in all vertebrates. The major function of major histocompatibility complexes is to bind to peptide fragments derived from pathogens and display them on the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T-cells. MHC molecules mediate interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), which are immune cells, with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines compatibility of donors for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to an autoimmune disease via crossreacting immunization. In humans, the MHC is also called the human leukocyte antigen (HLA).In a cell, protein molecules of the host's own phenotype or of other biologic entities are continually synthesized and degraded. Each MHC molecule on the cell surface displays a molecular fraction of a protein, called epitope. The presented antigen can be either 'self' or 'nonself', thus preventing an organism`s immune system targeting its own cells. In its entirety, the MHC population is like a meter indicating the balance of proteins within the cell.The MHC gene family is divided into three subgroups: class I, class II, and class III. Class I MHC molecules have β2 subunits so can only be recognised by CD8 co-receptors. Class II MHC molecules have no β2 subunits so can be recognised by CD4 co-receptors. In this way MHC molecules chaperones which type of lymphocytes may bind to the given antigen with high affinity, since different lymphocytes express different TCR co-receptors. Diversity of antigen presentation, mediated by MHC classes I and II, is attained in at least three ways: (1) an organism's MHC repertoire is polygenic (via multiple, interacting genes); (2) MHC expression is codominant (from both sets of inherited alleles); (3) MHC gene variants are highly polymorphic (diversely varying from organism to organism within a species). Major histocompatibility complex and sexual selection has been observed in male mice making mate choices of females with different MHCs and thus demonstrating sexual selection.