5echap24guidedreading
... 3. Which innate defense actually help prevent infection and which come into play only after infection has occurred? ...
... 3. Which innate defense actually help prevent infection and which come into play only after infection has occurred? ...
Concept Analysis Diagram
... Concept-Based Transition to Professional Nursing Practice Concept – IMMUNITY Concept Definition Immunity is a physiologic process that provides an individual with protection or defense from disease. Exemplars Vaccines Otitis media Urinary Tract Infection Cellulitis Osteomyelitis Pneumonia Appendicit ...
... Concept-Based Transition to Professional Nursing Practice Concept – IMMUNITY Concept Definition Immunity is a physiologic process that provides an individual with protection or defense from disease. Exemplars Vaccines Otitis media Urinary Tract Infection Cellulitis Osteomyelitis Pneumonia Appendicit ...
31.4 Immunity and Technology KEY CONCEPT help keep a person healthy.
... 31.4 Immunity and Technology • Antiseptics kill pathogens outside of the body. – do not target specific pathogens – examples include vinegar and soap • Antibiotics kill pathogens inside the body. – target one specific bacterium or fungus – not effective against viruses ...
... 31.4 Immunity and Technology • Antiseptics kill pathogens outside of the body. – do not target specific pathogens – examples include vinegar and soap • Antibiotics kill pathogens inside the body. – target one specific bacterium or fungus – not effective against viruses ...
Chapter 1
... that lyse bacteria. Describe those molecules. Say which do you think is the most important for host defense? 2. The complement system is a cascade of enzymes capable of producing powerful deleterious effects. How is complement harnessed to protect us rather than creating harm? 3. During their develo ...
... that lyse bacteria. Describe those molecules. Say which do you think is the most important for host defense? 2. The complement system is a cascade of enzymes capable of producing powerful deleterious effects. How is complement harnessed to protect us rather than creating harm? 3. During their develo ...
Immune System Reading Guide
... What is the difference between innate immunity and acquired (adaptive) immunity? What does it mean to say one is non-specific and the other is specific? Which one is which? What are two types of innate immunity and give examples of both types? How does the skin and mucous membranes provide a hostile ...
... What is the difference between innate immunity and acquired (adaptive) immunity? What does it mean to say one is non-specific and the other is specific? Which one is which? What are two types of innate immunity and give examples of both types? How does the skin and mucous membranes provide a hostile ...
Immunology and Immunity of mucosal surfaces
... In this module, the fundamental aspects of innate and adaptive immunity will be taught. These two topics are central to understanding the host's interaction with an environment containing a wide range of potentially pathogenic microorganisms. The major role played by the dendritic cells at the inter ...
... In this module, the fundamental aspects of innate and adaptive immunity will be taught. These two topics are central to understanding the host's interaction with an environment containing a wide range of potentially pathogenic microorganisms. The major role played by the dendritic cells at the inter ...
The Immune System
... from producing more virus. It is called interferon because it interferes with the spread of the virus Interferons are now being produced for ...
... from producing more virus. It is called interferon because it interferes with the spread of the virus Interferons are now being produced for ...
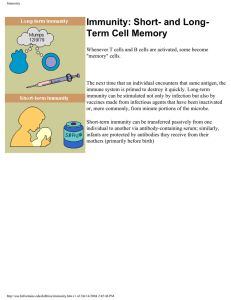
Immunity: Short- and Long
... Immunity: Short- and LongTerm Cell Memory Whenever T cells and B cells are activated, some become "memory" cells. ...
... Immunity: Short- and LongTerm Cell Memory Whenever T cells and B cells are activated, some become "memory" cells. ...
Office hours
... Office hours: M 10-12; T 3:30-5; W 10-11:30 Lecture and Discussion: T R 10:00-11:40am, Sci II 180 ...
... Office hours: M 10-12; T 3:30-5; W 10-11:30 Lecture and Discussion: T R 10:00-11:40am, Sci II 180 ...
Slide 1
... - mechanisms of recognition of “danger” signal - mechanisms of activation and regulation of defense - effector mechanisms of destruction and elimination of pathogens and neutralization of their harmful products ...
... - mechanisms of recognition of “danger” signal - mechanisms of activation and regulation of defense - effector mechanisms of destruction and elimination of pathogens and neutralization of their harmful products ...
EN90027_Imunology
... Students must acquire the basic and up-to-date concepts of immunology, in order to understand the importance of the various functions of the immune system as fundamental component of balance and maintenance of health. Students must recognize the relevance changes to such balance in the etiology of s ...
... Students must acquire the basic and up-to-date concepts of immunology, in order to understand the importance of the various functions of the immune system as fundamental component of balance and maintenance of health. Students must recognize the relevance changes to such balance in the etiology of s ...
Reading Guide - Belle Vernon Area School District
... 11. What is the role of cytotoxic T cells and describe their mechanism of action? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 12. What are some of the actions of helper T cells? ________________ ...
... 11. What is the role of cytotoxic T cells and describe their mechanism of action? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 12. What are some of the actions of helper T cells? ________________ ...
Chapter 43 – Immune System
... 11. What is the role of cytotoxic T cells and describe their mechanism of action? ...
... 11. What is the role of cytotoxic T cells and describe their mechanism of action? ...
Acquired immunity
... white blood cells) to prevent entrance by an antigen or microbe. Acquired immunity mounts a response after an invader has entered the body by producing specialized cells. ...
... white blood cells) to prevent entrance by an antigen or microbe. Acquired immunity mounts a response after an invader has entered the body by producing specialized cells. ...
Current Opinion in Immunology 2009, 21:440–445 Biomarkers of
... Age-associated failing immunity, or “immunosenescence”, contributes to the increased incidence and severity of infectious disease in old people. Which of the multitude of ageassociated alterations thus far reported are causally-related to a person´s health and longevity is not known. If we could ide ...
... Age-associated failing immunity, or “immunosenescence”, contributes to the increased incidence and severity of infectious disease in old people. Which of the multitude of ageassociated alterations thus far reported are causally-related to a person´s health and longevity is not known. If we could ide ...