Start Smart, Then Focus
... - Within 1 hour for severe sepsis or neutropenic sepsis When deciding on the most appropriate antibiotic(s) to prescribe, consider the following factors: - History of drug allergy (document allergy type: minor (rash only) or major (anaphylaxis, angioedema)) - Recent culture results (e.g. is patient ...
... - Within 1 hour for severe sepsis or neutropenic sepsis When deciding on the most appropriate antibiotic(s) to prescribe, consider the following factors: - History of drug allergy (document allergy type: minor (rash only) or major (anaphylaxis, angioedema)) - Recent culture results (e.g. is patient ...
Infection Control - Expert Ease International
... Infection which was neither present nor incubating at the time of admission Includes infection which only becomes apparent after discharge from hospital but which was acquired during hospitalisation (Rcn, 1995) Also called nosocomial infection ...
... Infection which was neither present nor incubating at the time of admission Includes infection which only becomes apparent after discharge from hospital but which was acquired during hospitalisation (Rcn, 1995) Also called nosocomial infection ...
emergence of major international high
... determined by logistic regression model of SAS. E. coli (43.4%, n=419/966) was the most frequently isolated bacteria followed by Proteus mirabilis (16.0%, n=155/966), Staphylococcus spp. (13.2%, n=128/966) and Enterococcus spp. (6.8%, n=66/966). Gram negative resistance to amoxicillin/clavulanate, 3 ...
... determined by logistic regression model of SAS. E. coli (43.4%, n=419/966) was the most frequently isolated bacteria followed by Proteus mirabilis (16.0%, n=155/966), Staphylococcus spp. (13.2%, n=128/966) and Enterococcus spp. (6.8%, n=66/966). Gram negative resistance to amoxicillin/clavulanate, 3 ...
Microbial infection
... UTI, are common, but most are not spread via urine. Urine can contaminate food, drink and living space. Transmission from the oropharynx Saliva is often the vehicle of transmission. M.O such as streptococci and tubercle bacilli reach saliva during upper and lower respiratory tract infections. Ce ...
... UTI, are common, but most are not spread via urine. Urine can contaminate food, drink and living space. Transmission from the oropharynx Saliva is often the vehicle of transmission. M.O such as streptococci and tubercle bacilli reach saliva during upper and lower respiratory tract infections. Ce ...
Surgical Management of MRSA Soft Tissue Infections
... Nonpurulent Cellulitis: Cellulitis with no purulent drainage or exudate and no associated abscess. β-hemolytic hemolytic Empirical therapy for infection due to β streptococci is recommended. The role of CA-MRSA is unknown. Empirical E i i l coverage for f CA-MRSA CA MRSA iis recommended d d ...
... Nonpurulent Cellulitis: Cellulitis with no purulent drainage or exudate and no associated abscess. β-hemolytic hemolytic Empirical therapy for infection due to β streptococci is recommended. The role of CA-MRSA is unknown. Empirical E i i l coverage for f CA-MRSA CA MRSA iis recommended d d ...
Acute Viral Encephalitis and Brain abscess
... Microorganisms that cause brain abscess reach the brain by: • Direct extension from a contiguous focus of infection: (otitis media, sinusitis or mastoiditis; veins that bridge the surrounding bony structures and cerebral cortex can become infected (septic thrombophlebitis). • Hematogenous disseminat ...
... Microorganisms that cause brain abscess reach the brain by: • Direct extension from a contiguous focus of infection: (otitis media, sinusitis or mastoiditis; veins that bridge the surrounding bony structures and cerebral cortex can become infected (septic thrombophlebitis). • Hematogenous disseminat ...
Microbiology-1-Syllabus
... 9. Serology (antigen-antibody reactions in microbiology, agglutination, precipitation, complement fixation, ELISA, IF, immunoblotting) 10. Resident oral microflora ( gram-positive cocci, gram-positive rods, gram-negative cocci, gram-negative rods, mycoplasma, fungi, viruses, distribution of the resi ...
... 9. Serology (antigen-antibody reactions in microbiology, agglutination, precipitation, complement fixation, ELISA, IF, immunoblotting) 10. Resident oral microflora ( gram-positive cocci, gram-positive rods, gram-negative cocci, gram-negative rods, mycoplasma, fungi, viruses, distribution of the resi ...
INFECTION AND INFECTIOUS PROCESS
... bacteria circulate and multiply in the blood, form toxic products and cause swinging type of fever. • Pyemia is a condition where pyogenic bacteria produce septicemia with multiple abscesses in the internal organs such as the spleen, liver and kidney. ...
... bacteria circulate and multiply in the blood, form toxic products and cause swinging type of fever. • Pyemia is a condition where pyogenic bacteria produce septicemia with multiple abscesses in the internal organs such as the spleen, liver and kidney. ...
Nonspecific Infections of the Genitourinary Tract
... abscess into the perinephric space. Gerota’s fascia usually confines the abscess formation to the perinephritic space, it can extend widely throughout the retroperitoneum to affect surrounding structures. ...
... abscess into the perinephric space. Gerota’s fascia usually confines the abscess formation to the perinephritic space, it can extend widely throughout the retroperitoneum to affect surrounding structures. ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... Late onset disease (acquired at or soon after birth): meningitis or meningoencephalitis with septicemia, similar to that caused by group B streptococci. ...
... Late onset disease (acquired at or soon after birth): meningitis or meningoencephalitis with septicemia, similar to that caused by group B streptococci. ...
C difficile - Carolinas College of Health Sciences
... • 1. Aerotolerant: ability of an anaerobic microorganism to grow in air; usually poorly, especially after initial anaerobic isolation. • 2. Glove/Gloveless Box: a device with flexible, semi-rigid or complete rigid plastic walls used for the cultivation of anaerobic bacteria. The bacteriologist must ...
... • 1. Aerotolerant: ability of an anaerobic microorganism to grow in air; usually poorly, especially after initial anaerobic isolation. • 2. Glove/Gloveless Box: a device with flexible, semi-rigid or complete rigid plastic walls used for the cultivation of anaerobic bacteria. The bacteriologist must ...
Infection Control for Obstetrics and Gynecology: Ware
... In recent years, the healthcare industry has placed a stronger emphasis on reducing medical errors, monitoring everything from how long doctors sleep to whether or not their handwriting is legible. Now one organization is not only recognizing the hospitals that follow patient safety and clinical gui ...
... In recent years, the healthcare industry has placed a stronger emphasis on reducing medical errors, monitoring everything from how long doctors sleep to whether or not their handwriting is legible. Now one organization is not only recognizing the hospitals that follow patient safety and clinical gui ...
The global crisis of multidrug resistance: how to face healthcare
... the larger is the proportion of its health-care budget being absorbed by the cost of antibacterial drugs: indeed, antibacterial drug resistance forces healthcare to turn from cheaper, but previously largely administered drugs, to more expensive alternatives (3). Unfortunately, a synergistic combinat ...
... the larger is the proportion of its health-care budget being absorbed by the cost of antibacterial drugs: indeed, antibacterial drug resistance forces healthcare to turn from cheaper, but previously largely administered drugs, to more expensive alternatives (3). Unfortunately, a synergistic combinat ...
Chapter 14 Study Guide Microbiology (Bauman 2007)
... As you work through the activities and practice quizzes for this chapter, keep the following learning objectives in mind. Once you have mastered this chapter, you should be able to: * Distinguish among the types of symbiosis, listing them in order from most beneficial to most harmful for the host. * ...
... As you work through the activities and practice quizzes for this chapter, keep the following learning objectives in mind. Once you have mastered this chapter, you should be able to: * Distinguish among the types of symbiosis, listing them in order from most beneficial to most harmful for the host. * ...
Helpful and Harmful Bacteria Graphic Organizer PP
... • Nitrogen-fixing bacteria help plants get the nitrogen they need to grow • Foods contain bacteria like yogurt, pickles, cheese, and sauerkraut • Bacteria in our stomachs help to break down foods • Some medicines are made from bacteria • Bacteria are used in tanning leather for belts, shoes, wallets ...
... • Nitrogen-fixing bacteria help plants get the nitrogen they need to grow • Foods contain bacteria like yogurt, pickles, cheese, and sauerkraut • Bacteria in our stomachs help to break down foods • Some medicines are made from bacteria • Bacteria are used in tanning leather for belts, shoes, wallets ...
感染致病性
... normal flora正常菌群:Nonpathogen: A microorganism that does not cause disease; may be part of the normal flora. Opportunistic pathogen机会病原体: An agent capable of causing disease only when the host’s resistance is impaired (ie, when the patient is “immunocompromised”). ...
... normal flora正常菌群:Nonpathogen: A microorganism that does not cause disease; may be part of the normal flora. Opportunistic pathogen机会病原体: An agent capable of causing disease only when the host’s resistance is impaired (ie, when the patient is “immunocompromised”). ...
Bacteria - GEOCITIES.ws
... • asexual binary fission (binary=2, fission=split), means to split in two; no meiosis or mitosis because no nucleus • sexual conjugation: 2 bacteria share genetic information Bacteria live in environments both with oxygen (aerobic) and w/out oxygen (anaerobic); some can live in both • Archaebacter ...
... • asexual binary fission (binary=2, fission=split), means to split in two; no meiosis or mitosis because no nucleus • sexual conjugation: 2 bacteria share genetic information Bacteria live in environments both with oxygen (aerobic) and w/out oxygen (anaerobic); some can live in both • Archaebacter ...
Knowing the Process Understanding Infection
... NZDA ACCREDITED. AAPM Sterilising, Disinfecting and Infection Control Certification, Continuing Education in Dentistry Sydney University, Certificate in Contemporary Infection Control, HBDI Certified Practitioner ...
... NZDA ACCREDITED. AAPM Sterilising, Disinfecting and Infection Control Certification, Continuing Education in Dentistry Sydney University, Certificate in Contemporary Infection Control, HBDI Certified Practitioner ...
Infection and Disease
... Human body maintains a symbiosis with microbes Infection refers to: relationship between the host and microbe competition for supremacy between them If the host loses the competition, disease occurs ...
... Human body maintains a symbiosis with microbes Infection refers to: relationship between the host and microbe competition for supremacy between them If the host loses the competition, disease occurs ...
Respiratory tract infections
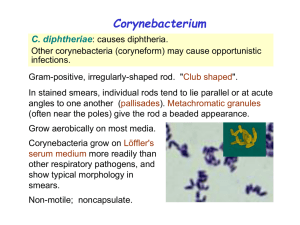
... • Diphtheria is managed by immediate treatment with antitoxin and antibiotic • Diphtheria is a life-threatening disease, and clinical diagnosis is a matter of urgency. As soon as the diagnosis is suspected clinically, the patient is isolated to reduce the risk of the toxigenic strain spreading to ot ...
... • Diphtheria is managed by immediate treatment with antitoxin and antibiotic • Diphtheria is a life-threatening disease, and clinical diagnosis is a matter of urgency. As soon as the diagnosis is suspected clinically, the patient is isolated to reduce the risk of the toxigenic strain spreading to ot ...
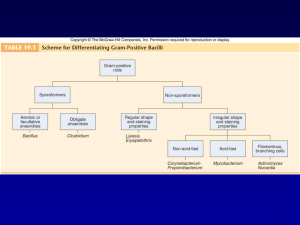
Chapter 19 - eacfaculty.org
... rifampin, pyrazinamide) • Drug resistance is growing! • Clavulanate + meropenem (experimental) • vaccine based on attenuated bacilli Calmet-Guerin strain of M. bovis used in other countries (low effectiveness for adults) ...
... rifampin, pyrazinamide) • Drug resistance is growing! • Clavulanate + meropenem (experimental) • vaccine based on attenuated bacilli Calmet-Guerin strain of M. bovis used in other countries (low effectiveness for adults) ...
Lecture 15 and 16 Microbiology: Gram Positive Bacteria infections
... − Coagulase differentiates more virulent S. aureus from other species − Microdilution / Disk Diffusion susceptibility tests should be done (this will come up later!) ...
... − Coagulase differentiates more virulent S. aureus from other species − Microdilution / Disk Diffusion susceptibility tests should be done (this will come up later!) ...
Microorganisms and Disease
... • indigenous flora: “synonymous with normal flora, indicates the microbial population that lives with the host in a healthy condition” • opportunists: “an organism that exists as part of the normal flora but may become pathogenic under certain conditions” • drug-fast: “resistant, as in bacteria, to ...
... • indigenous flora: “synonymous with normal flora, indicates the microbial population that lives with the host in a healthy condition” • opportunists: “an organism that exists as part of the normal flora but may become pathogenic under certain conditions” • drug-fast: “resistant, as in bacteria, to ...