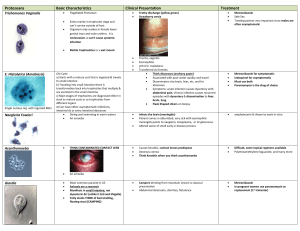
List the ways that diseases are transmitted from
... How quickly do infectious diseases spread? Procedures Suppose a single bacterium is placed on an agar plate and the number of bacteria in the population doubles every 30 minutes. How long do you think it would take before there would be 1000 bacteria? To calculate how long it would actually take for ...
... How quickly do infectious diseases spread? Procedures Suppose a single bacterium is placed on an agar plate and the number of bacteria in the population doubles every 30 minutes. How long do you think it would take before there would be 1000 bacteria? To calculate how long it would actually take for ...
PPT Version - OMICS International
... Each infectious disease has its own specific signs and symptoms. General signs and symptoms common to a number of infectious diseases include: • Fever • Diarrhea • Fatigue • Muscle aches ...
... Each infectious disease has its own specific signs and symptoms. General signs and symptoms common to a number of infectious diseases include: • Fever • Diarrhea • Fatigue • Muscle aches ...
Oral antibiotics for ear infections
... antibiotics for middle-ear infections, especially when they have severe ear pain or high fever. • Children with ear tubes should take oral antibiotics if: They are very ill. They have another reason to be on an antibiotic. The infection doesn’t go away with eardr ...
... antibiotics for middle-ear infections, especially when they have severe ear pain or high fever. • Children with ear tubes should take oral antibiotics if: They are very ill. They have another reason to be on an antibiotic. The infection doesn’t go away with eardr ...
HSII 2.02 Classes of Microorganisms
... Fungi – organisms that usually enjoy a symbiotic, but sometimes parasitic relationship with their host – provide numerous drugs and foods – provide bubbles in bread, champagne, and beer – cause a number of plant and animal diseases – fungal diseases are very difficult to treat ...
... Fungi – organisms that usually enjoy a symbiotic, but sometimes parasitic relationship with their host – provide numerous drugs and foods – provide bubbles in bread, champagne, and beer – cause a number of plant and animal diseases – fungal diseases are very difficult to treat ...
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
... duration and have fewer systemic manifestations. Except for the greater tendency of HSV-2 to recur, the clinical manifestations of HSV-2 and genital HSV-1 are similar. Recurrent HSV infection results from reactivation of the virus stored in the dorsal root ganglia of the infected dermatomes. An outb ...
... duration and have fewer systemic manifestations. Except for the greater tendency of HSV-2 to recur, the clinical manifestations of HSV-2 and genital HSV-1 are similar. Recurrent HSV infection results from reactivation of the virus stored in the dorsal root ganglia of the infected dermatomes. An outb ...
Diabetic foot Infection: Microbiological Causes with
... Diabetic patients often have chronic non-healing foot ulcers due to several underlying factors such as neuropathy, high plantar pressures and peripheral arterial disease; such chronic long-standing ulcers are more prone for infection which further delays the wound healing process. A wide range of ba ...
... Diabetic patients often have chronic non-healing foot ulcers due to several underlying factors such as neuropathy, high plantar pressures and peripheral arterial disease; such chronic long-standing ulcers are more prone for infection which further delays the wound healing process. A wide range of ba ...
Infectious-Diseases
... • It is a slowly progressive mycobacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium leprae which is an obligate intracellular acid fast bacteria. Mode of infection: • Human-to-human transmission is the usual cause of transimission, but requiring “prolonged and intimate contact.” • The organisms enter throu ...
... • It is a slowly progressive mycobacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium leprae which is an obligate intracellular acid fast bacteria. Mode of infection: • Human-to-human transmission is the usual cause of transimission, but requiring “prolonged and intimate contact.” • The organisms enter throu ...
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)
... MRSA stands for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus, which is a bacteria. ...
... MRSA stands for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus, which is a bacteria. ...
Manuscript type: Review article Title: Maxillary third molar and
... Scanning and clinical presentation The orbital abscess is usually caused by extension of the infection to the pterygopalatine and infratemporal regions progressing next to the inferior orbital fissure. Proptosis and extraocular muscle dysfunction are marked but no decrease in visual acuity is obser ...
... Scanning and clinical presentation The orbital abscess is usually caused by extension of the infection to the pterygopalatine and infratemporal regions progressing next to the inferior orbital fissure. Proptosis and extraocular muscle dysfunction are marked but no decrease in visual acuity is obser ...
microbio 62 [4-20
... Haemophilus influenzae i. just HATES children (osteomyelitis, pneumonia in infants, meningitis too??) ...
... Haemophilus influenzae i. just HATES children (osteomyelitis, pneumonia in infants, meningitis too??) ...
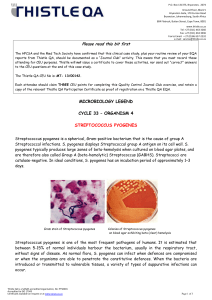
Cycle 33 Organism 4 - Streptococcus pyogenes
... S. pyogenes is the leading cause of uncomplicated bacterial pharyngitis and tonsillitis commonly referred to as strep throat. Other respiratory infections include sinusitis, otitis, and pneumonia. Infections of the skin can be superficial (impetigo) or deep (cellulitis). Invasive streptococci cause ...
... S. pyogenes is the leading cause of uncomplicated bacterial pharyngitis and tonsillitis commonly referred to as strep throat. Other respiratory infections include sinusitis, otitis, and pneumonia. Infections of the skin can be superficial (impetigo) or deep (cellulitis). Invasive streptococci cause ...
Unexplained Benefits of Antibiotics in Childhood
... adding amoxicillin or cefdinir to readyto-use therapeutic food regimens for the outpatient treatment of acute severe malnutrition [5]. Why might the addition of azithromycin to chloroquine reduce gut and respiratory infections? It is possible that the illnesses averted in the azithromycin antibiotic ...
... adding amoxicillin or cefdinir to readyto-use therapeutic food regimens for the outpatient treatment of acute severe malnutrition [5]. Why might the addition of azithromycin to chloroquine reduce gut and respiratory infections? It is possible that the illnesses averted in the azithromycin antibiotic ...
Document
... • No growth in the environment • Survival/persistence that is longer than that of pathogens • Easily detected and quantified • Numbers associated to the risk of consumers of contracting enteric diseases ...
... • No growth in the environment • Survival/persistence that is longer than that of pathogens • Easily detected and quantified • Numbers associated to the risk of consumers of contracting enteric diseases ...
6-1-11 The Chronicle - Paterson Counseling Center
... pus (an abscess) forms, and major surgery may be necessary and even lifesaving. Gonorrhea infection in people with conditions causing serious abnormal immune function, such as AIDS, can also be more serious. Diagnosis of gonorrhea Testing for gonorrhea is done by swabbing the infected site (rectum, ...
... pus (an abscess) forms, and major surgery may be necessary and even lifesaving. Gonorrhea infection in people with conditions causing serious abnormal immune function, such as AIDS, can also be more serious. Diagnosis of gonorrhea Testing for gonorrhea is done by swabbing the infected site (rectum, ...
Infection Control
... Fungi – organisms that usually enjoy a symbiotic, but sometimes parasitic relationship with their host – provide numerous drugs and foods – provide bubbles in bread, champagne, and beer – cause a number of plant and animal diseases – fungal diseases are very difficult to treat ...
... Fungi – organisms that usually enjoy a symbiotic, but sometimes parasitic relationship with their host – provide numerous drugs and foods – provide bubbles in bread, champagne, and beer – cause a number of plant and animal diseases – fungal diseases are very difficult to treat ...
Bacteria WebQuest
... 21. What is decomposition and how do bacteria play a role in the environment? 22. What is nitrogen fixation and why are bacteria crucial to this cycle of life? 23. What is denitrifying bacteria and why are they harmful to crops? Please visit the following websites: http://www.cellsalive.com/pen.htm ...
... 21. What is decomposition and how do bacteria play a role in the environment? 22. What is nitrogen fixation and why are bacteria crucial to this cycle of life? 23. What is denitrifying bacteria and why are they harmful to crops? Please visit the following websites: http://www.cellsalive.com/pen.htm ...
Emerging infections – implications for dental care
... when the number of humans contracting an infection has increased in the past 20 years, or when there is threat of such increase in the near future.1 There are different reasons why a disease may emerge including: • New infections from changes or evolution of existing organisms • Infections affecti ...
... when the number of humans contracting an infection has increased in the past 20 years, or when there is threat of such increase in the near future.1 There are different reasons why a disease may emerge including: • New infections from changes or evolution of existing organisms • Infections affecti ...
When To Test When to Treat
... Negative urine analysis for WBCs and negative dipsticks tests for leukocyte esterase and nitrites do not support UTI BUT cannot completely rule it out ...
... Negative urine analysis for WBCs and negative dipsticks tests for leukocyte esterase and nitrites do not support UTI BUT cannot completely rule it out ...
- ATS Journals
... and so patient outcome is not confounded by this factor. Briefly, the MIST1 trial recruited 454 patients from 52 centers in the United Kingdom. Entry criteria were macroscopically purulent, or bacterial culture, or Gram stain–positive pleural fluid, or a pleural fluid of pH ⬍ 7.2, in the presence of cl ...
... and so patient outcome is not confounded by this factor. Briefly, the MIST1 trial recruited 454 patients from 52 centers in the United Kingdom. Entry criteria were macroscopically purulent, or bacterial culture, or Gram stain–positive pleural fluid, or a pleural fluid of pH ⬍ 7.2, in the presence of cl ...
The oral cavity is not a primary source for implantable pacemaker or
... medical treatment for decreasing the mortality in patients with arrhythmias or cardiomyopathy [11]. However, infection rates range from 1-12% and can involve the pacemaker/ICD pocket, electrodes, generator or endocardium [12]. Aside from difficulties to diagnose infections of cardiac devices the cla ...
... medical treatment for decreasing the mortality in patients with arrhythmias or cardiomyopathy [11]. However, infection rates range from 1-12% and can involve the pacemaker/ICD pocket, electrodes, generator or endocardium [12]. Aside from difficulties to diagnose infections of cardiac devices the cla ...