Fact Sheet on Three American Societies
... They fought wars to gain prisoners for human sacrifice and cannibalism They were great borrowers and through this avenue obtained their faming methods, construction of buildings and the calendar. Tenochtitlan was built on an island in Late Texcoco, surrounded by high mountains. In Aztec society, the ...
... They fought wars to gain prisoners for human sacrifice and cannibalism They were great borrowers and through this avenue obtained their faming methods, construction of buildings and the calendar. Tenochtitlan was built on an island in Late Texcoco, surrounded by high mountains. In Aztec society, the ...
The Aztec – Mexico`s Great Empire
... site of present-day Mexico City. The Aztecs built temples, public buildings, and houses on an island in the center of Lake Texcoco. They connected the city to the mainland using causeways, or large bridges. The Aztecs developed a huge empire that lasted for 300 years. ...
... site of present-day Mexico City. The Aztecs built temples, public buildings, and houses on an island in the center of Lake Texcoco. They connected the city to the mainland using causeways, or large bridges. The Aztecs developed a huge empire that lasted for 300 years. ...
The Aztec
... school. There were different types of school options. Teenagers from noble families learned about their future responsibilities. Some Aztecs went to schools where they learned how to become a warrior. ...
... school. There were different types of school options. Teenagers from noble families learned about their future responsibilities. Some Aztecs went to schools where they learned how to become a warrior. ...
Cultures of Middle America
... artisans and merchants. Then came the farmers. They made up the largest class of people. • The lowest position in Aztec society was held by slaves, most of them were prisoners captured in battle. ...
... artisans and merchants. Then came the farmers. They made up the largest class of people. • The lowest position in Aztec society was held by slaves, most of them were prisoners captured in battle. ...
Rise and Fall of Tenochtitlan Evidence Analysis Exercise
... engage in trade. A specialized class of long-distance traders functioned as “advance men,” or merchant-spies, on behalf of the state. They would be followed by warriors whose military success ensured a steady flow of goods. The successful maintenance of the relationship between the urban center and ...
... engage in trade. A specialized class of long-distance traders functioned as “advance men,” or merchant-spies, on behalf of the state. They would be followed by warriors whose military success ensured a steady flow of goods. The successful maintenance of the relationship between the urban center and ...
Aztec Human Sacrifice
... Bernardino de Sahagun, Florentine Codex, II, circa 1555, in Carrasco, Daily Life of the Aztecs, People of the Sun and Earth, Greenwood Press, 1998. ...
... Bernardino de Sahagun, Florentine Codex, II, circa 1555, in Carrasco, Daily Life of the Aztecs, People of the Sun and Earth, Greenwood Press, 1998. ...
Aztec Civilization
... the Toltecs returned to worshiping the war-god After exile, he traveled across the sea on a raft made of snakes Promised to return and overthrow the king *Later, Aztecs thought the Spanish conquistadors were Quetzalcoatl ...
... the Toltecs returned to worshiping the war-god After exile, he traveled across the sea on a raft made of snakes Promised to return and overthrow the king *Later, Aztecs thought the Spanish conquistadors were Quetzalcoatl ...
Wilson Primary School Homework Grid ol Homework Grid Year: Six
... an Aztec warrior in an interview. Ask a friend or family mily member to ask you the questions whilst you pretend to be the warrior, and video yourself answering the questions! Draw a map of Tenochtitlan and write directions to get from one of the entrances to the temple. ...
... an Aztec warrior in an interview. Ask a friend or family mily member to ask you the questions whilst you pretend to be the warrior, and video yourself answering the questions! Draw a map of Tenochtitlan and write directions to get from one of the entrances to the temple. ...
Who Were the Aztec People? Reading
... the central portion of present-day Mexico in search of a new home for two hundred years. Finally, when they reached the Valley of Mexico, their god gave them a sign. This sign, an eagle devouring a snake while sitting on a cactus, is shown on the Mexican flag of today. Around 1325 CE the Mexica buil ...
... the central portion of present-day Mexico in search of a new home for two hundred years. Finally, when they reached the Valley of Mexico, their god gave them a sign. This sign, an eagle devouring a snake while sitting on a cactus, is shown on the Mexican flag of today. Around 1325 CE the Mexica buil ...
Assessment: Achievements of the Maya, Aztecs, and Incas
... 3. What was one way the Mayan system of numbers differs from ours? A. It lacked a way to show zero. B. It was based on 20 rather than 10. C. It could not be used to do subtraction. D. It used symbols to represent different amounts. 4. Which picture shows a Mayan stele? ...
... 3. What was one way the Mayan system of numbers differs from ours? A. It lacked a way to show zero. B. It was based on 20 rather than 10. C. It could not be used to do subtraction. D. It used symbols to represent different amounts. 4. Which picture shows a Mayan stele? ...
chapter 6 - Lone Star College
... c. mountainous areas of Nicaragua and Honduras. d. Yucatan Peninsula. 12. The sacred ball court a. had life or death implications for those who played upon it. b. could only be played on by Mayan priests. c. was a large, open, circular playing area that employed the use of straw baskets into which l ...
... c. mountainous areas of Nicaragua and Honduras. d. Yucatan Peninsula. 12. The sacred ball court a. had life or death implications for those who played upon it. b. could only be played on by Mayan priests. c. was a large, open, circular playing area that employed the use of straw baskets into which l ...
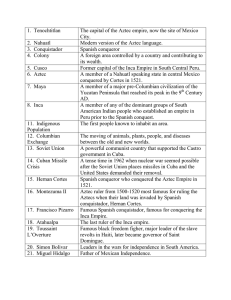
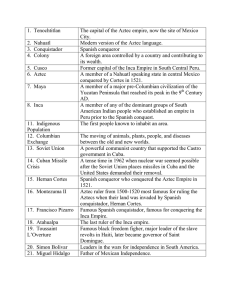
1. Tenochtitlan The capital of the Aztec empire, now the site of
... Yucatan Peninsula that reached its peak in the 9th Century AD. A member of any of the dominant groups of South American Indian people who established an empire in Peru prior to the Spanish conquest. The first people known to inhabit an area. The moving of animals, plants, people, and diseases betwee ...
... Yucatan Peninsula that reached its peak in the 9th Century AD. A member of any of the dominant groups of South American Indian people who established an empire in Peru prior to the Spanish conquest. The first people known to inhabit an area. The moving of animals, plants, people, and diseases betwee ...
1. Tenochtitlan The capital of the Aztec empire, now the site of
... Yucatan Peninsula that reached its peak in the 9th Century AD. A member of any of the dominant groups of South American Indian people who established an empire in Peru prior to the Spanish conquest. The first people known to inhabit an area. The moving of animals, plants, people, and diseases betwee ...
... Yucatan Peninsula that reached its peak in the 9th Century AD. A member of any of the dominant groups of South American Indian people who established an empire in Peru prior to the Spanish conquest. The first people known to inhabit an area. The moving of animals, plants, people, and diseases betwee ...
Maya, Aztec, and Inca Study Guide
... 3. Which of the following did the Maya have: a system of writing, a system of numbers, a calendar, or scientific tools? (circle all that apply) 4. What were the most important buildings in the Maya civilization? 5. The Aztecs built their civilization in the location of modern-day ___________________ ...
... 3. Which of the following did the Maya have: a system of writing, a system of numbers, a calendar, or scientific tools? (circle all that apply) 4. What were the most important buildings in the Maya civilization? 5. The Aztecs built their civilization in the location of modern-day ___________________ ...
The Americas
... The Aztecs were located in the middle of the Mexico Valley in the middle of Lake Texcoco. The valley was very marshy and scattered with islands. The islands were unwanted and solid ground was needed so the Aztecs began sinking large trees and then covering them with mud and boulders creating a solid ...
... The Aztecs were located in the middle of the Mexico Valley in the middle of Lake Texcoco. The valley was very marshy and scattered with islands. The islands were unwanted and solid ground was needed so the Aztecs began sinking large trees and then covering them with mud and boulders creating a solid ...
AZTEC GODS
... captured by Aztec warriors. Victims’ heads were strung as trophies on a great rack. He is always shown as a warrior. He wears a warrior’s cotton oversuit and carries a shield and a snake of fire. His body and clothes are painted blue. ...
... captured by Aztec warriors. Victims’ heads were strung as trophies on a great rack. He is always shown as a warrior. He wears a warrior’s cotton oversuit and carries a shield and a snake of fire. His body and clothes are painted blue. ...
the aztec empire - Ms. Wilcox`s Classroom
... Every member of the household, including children, helped in the household. Many also created goods that could be used by the empire in trade for goods that were highly valued in the Aztec culture, such as Jaguar skins. Education was important to the Aztec people. Fathers were responsible for educat ...
... Every member of the household, including children, helped in the household. Many also created goods that could be used by the empire in trade for goods that were highly valued in the Aztec culture, such as Jaguar skins. Education was important to the Aztec people. Fathers were responsible for educat ...
Aztec Civilization - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Anyone who died in battle had honor of dying for Huitzilopochtli, the god of war Believed the way to appease the gods and make them happy was through human sacrifice Polytheistic—believed in many different gods “There is nothing like death in war” Only blood can nourish the Sun God 30,00 ...
... Anyone who died in battle had honor of dying for Huitzilopochtli, the god of war Believed the way to appease the gods and make them happy was through human sacrifice Polytheistic—believed in many different gods “There is nothing like death in war” Only blood can nourish the Sun God 30,00 ...
Engineering an Empire: The Aztecs
... 5. The Aztec capital, Tenochtitlan, does not exist today because this modern day city, Mexico City, was built on top of it. 6. The Aztec capital was modeled after Teotihuacan, the City of the Gods. 7. Since there was no foundation to build on the Aztecs drove wooden pylons deep into the ground to se ...
... 5. The Aztec capital, Tenochtitlan, does not exist today because this modern day city, Mexico City, was built on top of it. 6. The Aztec capital was modeled after Teotihuacan, the City of the Gods. 7. Since there was no foundation to build on the Aztecs drove wooden pylons deep into the ground to se ...
The Aztecs - ClearsHonorsLA
... of basketball and soccer. It was played during religious ceremonies. Sometimes the Aztecs sacrificed the losers Aztecs also played board games, like patolli. The exact rules are unknown, but it was similar to Parcheesi. It was a gambling game. ...
... of basketball and soccer. It was played during religious ceremonies. Sometimes the Aztecs sacrificed the losers Aztecs also played board games, like patolli. The exact rules are unknown, but it was similar to Parcheesi. It was a gambling game. ...
1. Compare and contrast characteristics of the Mayans
... Cities were the center of trade and religious ceremonies and included large palaces, temples and pyramids City-states were linked through trade, trading maize, beans and squash ...
... Cities were the center of trade and religious ceremonies and included large palaces, temples and pyramids City-states were linked through trade, trading maize, beans and squash ...
File
... The Maya built their great cities between A.D. 250 and A.D. 900. Their accomplishments included the development of complex writing and mathematical systems and impressive advances in astronomy. They used two calendars. One calendar was based on a solar year, while the other was a kind of sacred alma ...
... The Maya built their great cities between A.D. 250 and A.D. 900. Their accomplishments included the development of complex writing and mathematical systems and impressive advances in astronomy. They used two calendars. One calendar was based on a solar year, while the other was a kind of sacred alma ...
Primary Sources: The Spanish Conquest of the Aztecs
... The spots above the drawings represent the age of the children—starting with seven spots for seven years and so on. The round and semicircular objects drawn into each picture represent tortillas (maize pancakes); at seven years old a child is only allowed one and a half of these each day, to teach h ...
... The spots above the drawings represent the age of the children—starting with seven spots for seven years and so on. The round and semicircular objects drawn into each picture represent tortillas (maize pancakes); at seven years old a child is only allowed one and a half of these each day, to teach h ...
Aztec warfare

Aztec warfare concerns the aspects associated with the militaristic conventions, forces, weaponry and strategic expansions conducted by the Late Postclassic Aztec civilizations of Mesoamerica, including particularly the military history of the Aztec Triple Alliance involving the city-states of Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, Tlacopan and other allied polities of the central Mexican region.The Aztec armed forces were typically composed of a large number of commoners (yāōquīzqueh [jaː.oːˈkiːskeʔ], ""those who have gone to war"") who possessed only basic military training, and a smaller but still considerable number of professional warriors belonging to the nobility (pīpiltin [piːˈpiɬtin]) and who were organized into warrior societies and ranked according to their achievements. The Aztec state was centered on political expansion and dominance of and exaction of tribute from other city states, and warfare was the basic dynamic force in Aztec politics. Aztec society was also centered on warfare: every Aztec male received basic military training from an early age and the only possibility of upwards social mobility for commoners(mācehualtin [maːseˈwaɬtin]) was through military achievement — especially the taking of captives (māltin [ˈmaːɬtin], singular malli). The sacrifice of war captives was an important part of many of the Aztec religious festivals. Warfare was thus the main driving force of both the Aztec economy and religion.