Clendinnen, "The Cost of Courage in Aztec Society"
... the higher the rank the more strenuous the punishment. Public rhetoric insisted on the virtues of humility, modesty, frugality, and self-control.... These recommendations were made in a society which rewarded its warriors with the opportunity to bask in public adulation.... On the one hand we have h ...
... the higher the rank the more strenuous the punishment. Public rhetoric insisted on the virtues of humility, modesty, frugality, and self-control.... These recommendations were made in a society which rewarded its warriors with the opportunity to bask in public adulation.... On the one hand we have h ...
Guided Notes- Mesoamerica Conquistadors
... • Cortes immediately decided to put a _____________________________________________ __________________________________ The Campaign against the Aztec- part 3 • Cortes takes Montezuma prisoner in his own palace. • After several months, the Aztec people riot • Cortes __________________________________ ...
... • Cortes immediately decided to put a _____________________________________________ __________________________________ The Campaign against the Aztec- part 3 • Cortes takes Montezuma prisoner in his own palace. • After several months, the Aztec people riot • Cortes __________________________________ ...
Appendix 4 - Souls of Distortion
... Aztlán. It is generally thought that Aztlán was somewhere to the north of the Valley of Mexico; some experts have placed it as far north as Southwestern United States. Others however suggest it is a mythical place, since Aztlán can be translated as "the place of the origin". The mythical story of th ...
... Aztlán. It is generally thought that Aztlán was somewhere to the north of the Valley of Mexico; some experts have placed it as far north as Southwestern United States. Others however suggest it is a mythical place, since Aztlán can be translated as "the place of the origin". The mythical story of th ...
Francisco Pizarro First Spanish Conquests: The
... at first. Cortez was afraid the Aztecs would eventually push him out, so he took Montezuma as a hostage before he was forced out of city. May 1521 : After a series of negotiations, bloody battles & retreats, Cortez leads a final assault on the Capital City. 3 months later, Cortez destroys the Aztec ...
... at first. Cortez was afraid the Aztecs would eventually push him out, so he took Montezuma as a hostage before he was forced out of city. May 1521 : After a series of negotiations, bloody battles & retreats, Cortez leads a final assault on the Capital City. 3 months later, Cortez destroys the Aztec ...
Aztec Calendar - COSMICSOLUTIONS
... number of other predictions. More importantly, these names duplicated the names of the gods. The name formed a powerful bond between the children, the Calendar, and the gods. They became somewhat godlike, perhaps taking on some of the characteristics of the god. Since the gods also took the names of ...
... number of other predictions. More importantly, these names duplicated the names of the gods. The name formed a powerful bond between the children, the Calendar, and the gods. They became somewhat godlike, perhaps taking on some of the characteristics of the god. Since the gods also took the names of ...
aztec entertainment
... fashionable for women to make their facial complexion yellow. To do this they rubbed their cheeks with yellow earth or earth mixed with a cream containing axin, a waxy-yellowish substance obtained by crushing and cooking the bodies of certain insects. Aztec women enjoyed using cosmetics and perfumes ...
... fashionable for women to make their facial complexion yellow. To do this they rubbed their cheeks with yellow earth or earth mixed with a cream containing axin, a waxy-yellowish substance obtained by crushing and cooking the bodies of certain insects. Aztec women enjoyed using cosmetics and perfumes ...
The Aztecs- Part 1 - Melillo Middle School
... It was Montezuma II who was leading the Aztecs when Hernan Cortez landed on the southeastern shore of Mexico in 1519. The city of Tenochtitlan was several hundred miles away. Cortez had heard about cities of gold. He was determined to become a rich man by conquering these cities of gold. When he lan ...
... It was Montezuma II who was leading the Aztecs when Hernan Cortez landed on the southeastern shore of Mexico in 1519. The city of Tenochtitlan was several hundred miles away. Cortez had heard about cities of gold. He was determined to become a rich man by conquering these cities of gold. When he lan ...
Unit 4, Lesson 24 Civilization in Mesoamerica and Andean
... Tlatelolco, Tenochtitlan, Tlacopan, and Texcoco governed more than 12 million people throughout the Mesoamerican region. The Aztecs would hold this region until Spanish explorers entered and took the land from them during the sixteenth century C.E. (At approximately the same time, another important ...
... Tlatelolco, Tenochtitlan, Tlacopan, and Texcoco governed more than 12 million people throughout the Mesoamerican region. The Aztecs would hold this region until Spanish explorers entered and took the land from them during the sixteenth century C.E. (At approximately the same time, another important ...
Focus on Inquiry - How Did Geography Influence the Pre
... The Mexica (or Aztec) legendary search for a new homeland ended in the part of MesoAmerica known as the Valley of Mexico. This high central Mexican plateau provided all the essentials of life: water; rich, deep soil; all kinds of plant and animal life; and a comfortable climate. Surrounded by forest ...
... The Mexica (or Aztec) legendary search for a new homeland ended in the part of MesoAmerica known as the Valley of Mexico. This high central Mexican plateau provided all the essentials of life: water; rich, deep soil; all kinds of plant and animal life; and a comfortable climate. Surrounded by forest ...
Cortés in Tenochtitlán Hernando Cortés was a Spanish explorer and
... but the rest and all the smaller ones are half on land, half canals where they paddle their canoes. All the streets have openings in places so that the water may pass from one canal to another. Over all these openings, and some of them are very wide, there are bridges. . . . There are, in all distri ...
... but the rest and all the smaller ones are half on land, half canals where they paddle their canoes. All the streets have openings in places so that the water may pass from one canal to another. Over all these openings, and some of them are very wide, there are bridges. . . . There are, in all distri ...
Mayan Social Structure
... of the Sun". They worshiped gods of nature - the sun god, the god of thunder, Moon, rainbows, mountain tops, stars, planets, and many more. Like the ancient Greeks, the Incas believed the gods could intervene to help you or hinder you. To avoid problems, they worshiped all the gods every day. Dreams ...
... of the Sun". They worshiped gods of nature - the sun god, the god of thunder, Moon, rainbows, mountain tops, stars, planets, and many more. Like the ancient Greeks, the Incas believed the gods could intervene to help you or hinder you. To avoid problems, they worshiped all the gods every day. Dreams ...
Maya, Aztec, Inca
... – Sophisticated mathematics— including zero, base 20 numeric system, numeric symbols so they could count into the billions ...
... – Sophisticated mathematics— including zero, base 20 numeric system, numeric symbols so they could count into the billions ...
Aztec gods2 - taughtbygoldin
... The snake represents the earth and vegetation, but it was in Teotihuacan (around 150 BC) where the snake got the precious feathers of the quetzal, as seen in the Murals of the city. The most ...
... The snake represents the earth and vegetation, but it was in Teotihuacan (around 150 BC) where the snake got the precious feathers of the quetzal, as seen in the Murals of the city. The most ...
Trade and Tribute: Empires in the Americas
... Like the Aztec rulers, who claimed descent from the god Huizilopochtli, the Sapa Inca, or “Sole Ruler,” was believed to be a descendant of the sun god and his representative on earth. Incorporating the Andean traditions of ancestor worship, the mummified bodies of dead kings became the tangible link ...
... Like the Aztec rulers, who claimed descent from the god Huizilopochtli, the Sapa Inca, or “Sole Ruler,” was believed to be a descendant of the sun god and his representative on earth. Incorporating the Andean traditions of ancestor worship, the mummified bodies of dead kings became the tangible link ...
REG. 3.2.3-3 ECOMUNDO CENTRO DE ESTUDIOS ACADEMIC
... _________________ fought battles; __________________ carried goods; ____________ created works of art. Most people were ________________. 1. Where and when did the incas create their empire? 2. What types of jobs did the Mayas have? Are they similar to or different from jobs that people have today? ...
... _________________ fought battles; __________________ carried goods; ____________ created works of art. Most people were ________________. 1. Where and when did the incas create their empire? 2. What types of jobs did the Mayas have? Are they similar to or different from jobs that people have today? ...
5 pt
... What is false? Incan civilization was famous for their roads and aqueducts, which allowed them to bring water to villages hundreds of miles away . ...
... What is false? Incan civilization was famous for their roads and aqueducts, which allowed them to bring water to villages hundreds of miles away . ...
CHAPTER SUMMARY
... THE INCAS CREATE AN EMPIRE While the Aztecs were ruling Mexico, the Incas were building an empire in South America. The Incas began as a small tribe high in the Andes. They built their capital, Cuzco, in modern-day Peru. In the mid-1400s, the ruler Pachacuti (pah-chah-KOO-tee) led the Incas to expan ...
... THE INCAS CREATE AN EMPIRE While the Aztecs were ruling Mexico, the Incas were building an empire in South America. The Incas began as a small tribe high in the Andes. They built their capital, Cuzco, in modern-day Peru. In the mid-1400s, the ruler Pachacuti (pah-chah-KOO-tee) led the Incas to expan ...
The Aztec Empire
... built a massive capital city that at its height had more than 200,000 inhabitants. This city was expertly laid out, with wide streets, town squares, markets and plazas. This massive city had over 600 pyramids, which were believed to be used for religious purposes. It also had well over 2000 apartmen ...
... built a massive capital city that at its height had more than 200,000 inhabitants. This city was expertly laid out, with wide streets, town squares, markets and plazas. This massive city had over 600 pyramids, which were believed to be used for religious purposes. It also had well over 2000 apartmen ...
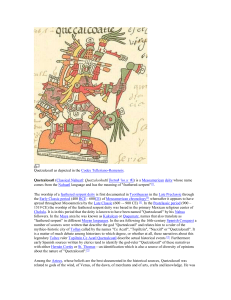
Quetzalcoatl as depicted in the Codex Telleriano
... Cholula. It is in this period that the deity is known to have been named "Quetzalcoatl" by his Nahua followers. In the Maya area he was known as Kukulcan or Ququmatz, names that also translate as "feathered serpent" in different Mayan languages. In the era following the 16th-century Spanish Conquest ...
... Cholula. It is in this period that the deity is known to have been named "Quetzalcoatl" by his Nahua followers. In the Maya area he was known as Kukulcan or Ququmatz, names that also translate as "feathered serpent" in different Mayan languages. In the era following the 16th-century Spanish Conquest ...
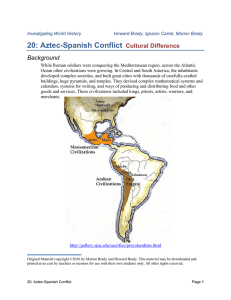
20: Aztec-Spanish Conflict Cultural Difference
... News reached the Aztec ruler, Montezuma1 in the city of Tenochtitlán, (now Mexico City) about the arrival on the east coast of strange people traveling on “floating mountains” [large ships]. He sent messengers to investigate, with gifts for the arriving “gods.” Years later, a native observer descri ...
... News reached the Aztec ruler, Montezuma1 in the city of Tenochtitlán, (now Mexico City) about the arrival on the east coast of strange people traveling on “floating mountains” [large ships]. He sent messengers to investigate, with gifts for the arriving “gods.” Years later, a native observer descri ...
8.2 Africa Americas Geo Readings
... While the Maya were developing their civilization to the south, other high cultures were evolving in central Mexico. Some of the most important developments took place in and around the Valley of Mexico. This valley, where modern Mexico City is located, eventually became the site of the greatest emp ...
... While the Maya were developing their civilization to the south, other high cultures were evolving in central Mexico. Some of the most important developments took place in and around the Valley of Mexico. This valley, where modern Mexico City is located, eventually became the site of the greatest emp ...
Maya, Aztec, and Inca Civilizations
... • Quetzalcoatl was a god worshipped by the Aztec peoples. • Was believed that Quetzalcoatl had traveled east across the sea and would one day return, bringing peace • When Hernan Cortes arrived in 1519 Moctezuma believed that it might be the return of Quetzalcoatl and allowed the Spanish easy entry ...
... • Quetzalcoatl was a god worshipped by the Aztec peoples. • Was believed that Quetzalcoatl had traveled east across the sea and would one day return, bringing peace • When Hernan Cortes arrived in 1519 Moctezuma believed that it might be the return of Quetzalcoatl and allowed the Spanish easy entry ...
SS6H1 History Notes - Henry County Schools
... Fighting broke out & Montezuma was killed. The Spanish were outnumbered, so they fled the city. Before they could prepare a 2nd attack, smallpox broke out in Tenochtitlan & greatly weakened the large Aztec empire. In 1521, the Spanish destroyed the Aztec capital. Cortes took part in one mo ...
... Fighting broke out & Montezuma was killed. The Spanish were outnumbered, so they fled the city. Before they could prepare a 2nd attack, smallpox broke out in Tenochtitlan & greatly weakened the large Aztec empire. In 1521, the Spanish destroyed the Aztec capital. Cortes took part in one mo ...
Westhill Institute
... Population (late 15th Century) o Ahuitzotl: how far did the Aztec empire grow during his time? (north and south) o What building was built during the time of Ahuitzotl? o What Gods were honored at the most important pyramid in city of Tenochtitlan? o What is the name of the stone used for building l ...
... Population (late 15th Century) o Ahuitzotl: how far did the Aztec empire grow during his time? (north and south) o What building was built during the time of Ahuitzotl? o What Gods were honored at the most important pyramid in city of Tenochtitlan? o What is the name of the stone used for building l ...
Human sacrifice in Aztec culture
.jpg?width=300)
Human sacrifice was a religious practice characteristic of pre-Columbian Aztec civilization, as well as of other Mesoamerican civilizations like the Maya and the Zapotec. The extent of the practice is debated by modern scholars.Spanish explorers, soldiers and clergy who had contact with the Aztecs between 1517, when an expedition from Cuba first explored the Yucatan, and 1521, when Hernán Cortés conquered the Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan, made observations of and wrote reports about the practice of human sacrifice. For example, Bernal Díaz's The Conquest of New Spain includes eyewitness accounts of human sacrifices as well as descriptions of the remains of sacrificial victims. In addition, there are a number of second-hand accounts of human sacrifices written by Spanish friars that relate the testimony of native eyewitnesses. The literary accounts have been supported by archeological research. Since the late 1970s, excavations of the offerings in the Great Pyramid of Tenochtitlan, Teotihuacán's Pyramid of the Moon, and other archaeological sites, have provided physical evidence of human sacrifice among the Mesoamerican peoples.A wide variety of explanations and interpretations of the Aztec practice of human sacrifice have been proposed by modern scholars. Most scholars of Pre-Columbian civilization see human sacrifice among the Aztecs as a part of the long cultural tradition of human sacrifice in Mesoamerica.