Transistors
... • If the “input” current is IB and the “output” current is IC, then we have a current amplification or gain – Happens because base–emitter junction is forward-biased – Forward bias ensures that the base–emitter junction conducts (transistor is turned on) – Reverse bias ensures that most of the large ...
... • If the “input” current is IB and the “output” current is IC, then we have a current amplification or gain – Happens because base–emitter junction is forward-biased – Forward bias ensures that the base–emitter junction conducts (transistor is turned on) – Reverse bias ensures that most of the large ...
Resistance - Purdue Physics
... An understanding of how much current flows through a conductor for a given applied voltage resulted from Georg Ohm’s thorough work in 1827. The empirical relationship known as Ohm’s Law has remained valid over the years and is still widely used today. Although Ohm’s work focussed primarily on metals ...
... An understanding of how much current flows through a conductor for a given applied voltage resulted from Georg Ohm’s thorough work in 1827. The empirical relationship known as Ohm’s Law has remained valid over the years and is still widely used today. Although Ohm’s work focussed primarily on metals ...
CISC-340 Digital Systems Everything You Need to Know
... Let's start with the basics. Matter is composed of molecules. Molecules are composed of atoms. Atoms are composed of a centre mass called the nucleus, containing positively charged particles called protons and neutral particles called neutrons. Orbiting around the nucleus at different but well defin ...
... Let's start with the basics. Matter is composed of molecules. Molecules are composed of atoms. Atoms are composed of a centre mass called the nucleus, containing positively charged particles called protons and neutral particles called neutrons. Orbiting around the nucleus at different but well defin ...
Handout
... of measuring the planetary motion were found, it was discovered that the orbits deviated from the predictions made from Newton’s laws by very small amounts that couldn’t be attributed to experimental error. Hence it had to be concluded that Newton’s laws were only approximately correct, and a more c ...
... of measuring the planetary motion were found, it was discovered that the orbits deviated from the predictions made from Newton’s laws by very small amounts that couldn’t be attributed to experimental error. Hence it had to be concluded that Newton’s laws were only approximately correct, and a more c ...
How to check the electric components in the IMRC of the Cougar V6
... Information about the built-in power transistor The built-in transistor is a so-called NPN Darlington Transistor. These specific Transistors have a very high current gain. This means for example: they can switch with an input current of 10 mA (0,01 A) a 1000 times or bigger current, so ~ 10 A. This ...
... Information about the built-in power transistor The built-in transistor is a so-called NPN Darlington Transistor. These specific Transistors have a very high current gain. This means for example: they can switch with an input current of 10 mA (0,01 A) a 1000 times or bigger current, so ~ 10 A. This ...
SS3LA EDA
... The SS3LA transducer connects to a single MP3X/45 input channel to record electrodermal activity (changes in skin conductance) or, with modified setup, skin resistance*. The SS3LA operates by applying a fixed voltage (0.5 Volts DC) across the two electrodes and then detects the minute current flowin ...
... The SS3LA transducer connects to a single MP3X/45 input channel to record electrodermal activity (changes in skin conductance) or, with modified setup, skin resistance*. The SS3LA operates by applying a fixed voltage (0.5 Volts DC) across the two electrodes and then detects the minute current flowin ...
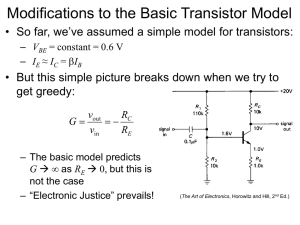
Modifications to the Basic Transistor Model
... – However the feedback is quite small (< 0.1%) at signal frequencies, so signal gain is essentially undisturbed ...
... – However the feedback is quite small (< 0.1%) at signal frequencies, so signal gain is essentially undisturbed ...
5 Dynamic Characteristics I
... 5.1 Switching Times In practice, changes in the state of conduction of the transistor take time to occur. These cause delays in the response of the output to changes at the input. Consider the circuit in Fig. 5.1. ...
... 5.1 Switching Times In practice, changes in the state of conduction of the transistor take time to occur. These cause delays in the response of the output to changes at the input. Consider the circuit in Fig. 5.1. ...
Capacitor Self
... b. Measure and record the actual value of the 10-kΩ and 820-kΩ resistors that will be used in your circuit. ...
... b. Measure and record the actual value of the 10-kΩ and 820-kΩ resistors that will be used in your circuit. ...