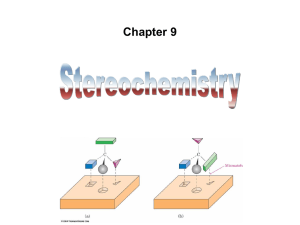
Theoretical Background
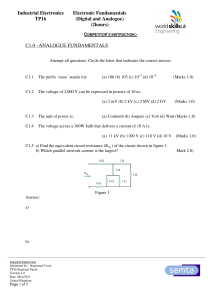
... The ideal Inverter model is important because it gives a metric by which we can judge the quality of actual implementation. Its VTC is shown in figure 1.1 and has the following properties: Infinite gain in the transition region, and gate threshold located in the middle of the logic swing, with high ...
... The ideal Inverter model is important because it gives a metric by which we can judge the quality of actual implementation. Its VTC is shown in figure 1.1 and has the following properties: Infinite gain in the transition region, and gate threshold located in the middle of the logic swing, with high ...
Lecture 5
... 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O The chemical substances on the left of the equation are the ‘reactants’. The chemical substances on the right of the equation are the ‘products’. The numbers in front of the formulas are the coefficients. ...
... 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O The chemical substances on the left of the equation are the ‘reactants’. The chemical substances on the right of the equation are the ‘products’. The numbers in front of the formulas are the coefficients. ...
6.2.6 Transistors
... Transistors Parts of the Transistor The First Transistor Transistors as Amplifiers Transistors as Switches Night Light Circuit ...
... Transistors Parts of the Transistor The First Transistor Transistors as Amplifiers Transistors as Switches Night Light Circuit ...
Chapter 3 Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations
... were called organic; compounds from the nonliving environment were called inorganic. • Organic compounds easily decomposed and could not be made in an 18th-century lab. • Inorganic compounds are very difficult to decompose, but can be synthesized. ...
... were called organic; compounds from the nonliving environment were called inorganic. • Organic compounds easily decomposed and could not be made in an 18th-century lab. • Inorganic compounds are very difficult to decompose, but can be synthesized. ...
File - electro science club
... Such materials are called “Insulators". Insulators are materials that have structural properties exactly opposite of Conductors. The electrons of Insulator material atoms are not easily "freed." These Electrons are said to be tightly bound to the "nucleus" and are very stable. Due to this high stabi ...
... Such materials are called “Insulators". Insulators are materials that have structural properties exactly opposite of Conductors. The electrons of Insulator material atoms are not easily "freed." These Electrons are said to be tightly bound to the "nucleus" and are very stable. Due to this high stabi ...
Electricity and Circuits
... Atoms sometimes gain or lose electrons to other atoms. When electrons move from atom to atom a current is produced. Electricity is the movement of electrons from one atom to another. Some atoms hold onto their electrons very tightly. Materials composed of such atoms tend not to let electricity move ...
... Atoms sometimes gain or lose electrons to other atoms. When electrons move from atom to atom a current is produced. Electricity is the movement of electrons from one atom to another. Some atoms hold onto their electrons very tightly. Materials composed of such atoms tend not to let electricity move ...
Chapter 3 Molecules Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical
... were called organic; compounds from the nonliving environment were called inorganic. Organic compounds easily decomposed and could not be made in an 18th-century lab. Inorganic compounds are very difficult to decompose, but can be synthesized. ...
... were called organic; compounds from the nonliving environment were called inorganic. Organic compounds easily decomposed and could not be made in an 18th-century lab. Inorganic compounds are very difficult to decompose, but can be synthesized. ...
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
... metallurgy, electrochemistry, and molecular biology Scanning Probe Microscopes (SPM): designed based on the scanning technology of STM ...
... metallurgy, electrochemistry, and molecular biology Scanning Probe Microscopes (SPM): designed based on the scanning technology of STM ...
Slide 1
... How to avoid shock. • Turn power off before working on equipment. • Don’t touch circuits that could have high voltage on them. • Do not allow electrons to flow through the heart. I don’t think the snake knew about this detail. ...
... How to avoid shock. • Turn power off before working on equipment. • Don’t touch circuits that could have high voltage on them. • Do not allow electrons to flow through the heart. I don’t think the snake knew about this detail. ...
Additional Notes (Class 7)
... technology; that is, if the device is properly constructed, we can drive electrons through external circuits (the reverse of formal current flow). So, if you believe that electronic devices can be powered with batteries (!) you basically have to accept that oxidationreduction chemistry takes place. ...
... technology; that is, if the device is properly constructed, we can drive electrons through external circuits (the reverse of formal current flow). So, if you believe that electronic devices can be powered with batteries (!) you basically have to accept that oxidationreduction chemistry takes place. ...