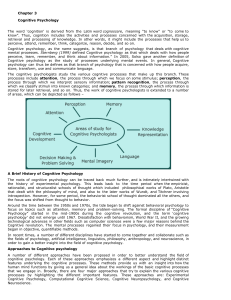
Chapter 3 Cognitive Psychology The word `cognition` is derived from
... A Brief History of Cognitive Psychology The roots of cognitive psychology can be traced back much further, and is intimately intertwined with the history of experimental psychology. This leads back to the time period when the empiricist, rationalist, and structuralist schools of thought which includ ...
... A Brief History of Cognitive Psychology The roots of cognitive psychology can be traced back much further, and is intimately intertwined with the history of experimental psychology. This leads back to the time period when the empiricist, rationalist, and structuralist schools of thought which includ ...
Limbic system – Emotional Experience
... When we lose a battle, a match, or a job, the hippocampus is stimulated making sure we would remember the loss forever. The center of our emotions, the amygdala, fuses this sense of memory into a profound notion of misery. This all creates a powerful reminder of failure to put us off making the same ...
... When we lose a battle, a match, or a job, the hippocampus is stimulated making sure we would remember the loss forever. The center of our emotions, the amygdala, fuses this sense of memory into a profound notion of misery. This all creates a powerful reminder of failure to put us off making the same ...
Topographic Mapping with fMRI
... Neurons in the brain form a continuous map of the sensory surface. Nearby neurons on the map represent nearby locations in sensory space. In vision, the sensory surface is the retina with a spatial map called retinotopy. In hearing, the sensory surface is the cochlea with a map of sound frequencies ...
... Neurons in the brain form a continuous map of the sensory surface. Nearby neurons on the map represent nearby locations in sensory space. In vision, the sensory surface is the retina with a spatial map called retinotopy. In hearing, the sensory surface is the cochlea with a map of sound frequencies ...
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS
... other organs in the body, such as the desire to use the toilet. The brain therefore plays a part in everything we do, including interpreting images, sounds and smells. The brain is made up of 100 billion nerve cells called neurons. Neurons are connected to the rest of the body via the spinal cord. T ...
... other organs in the body, such as the desire to use the toilet. The brain therefore plays a part in everything we do, including interpreting images, sounds and smells. The brain is made up of 100 billion nerve cells called neurons. Neurons are connected to the rest of the body via the spinal cord. T ...
Temporal Aspects of Visual Extinction
... Responsible for manipulating discrete and skilled voluntary movements through planning and innervation of muscles Refers to highly conscious planning and sequencing Site of reasoning, thinking, planning ...
... Responsible for manipulating discrete and skilled voluntary movements through planning and innervation of muscles Refers to highly conscious planning and sequencing Site of reasoning, thinking, planning ...
L7- Brainstem Studen..
... • (1) coordinates motor control signals sent from the brain to the body. • (2) The brainstem also controls life supporting autonomic functions of the peripheral nervous system. • (3) It sis essential to note that the cranial nerves 3 – 12 emerge from the brainstem. • (4) The main role of brainstem h ...
... • (1) coordinates motor control signals sent from the brain to the body. • (2) The brainstem also controls life supporting autonomic functions of the peripheral nervous system. • (3) It sis essential to note that the cranial nerves 3 – 12 emerge from the brainstem. • (4) The main role of brainstem h ...
Chapter 2 Functional Neuroanatomy
... and axon terminals. The cell body, or soma, is the trophic or life center of the neuron (see Fig. 2.1). Cell bodies vary in size and shape and contain the ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of the neuron. RNA, the site of protein synthesis, transmits instructions from DNA directi ...
... and axon terminals. The cell body, or soma, is the trophic or life center of the neuron (see Fig. 2.1). Cell bodies vary in size and shape and contain the ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of the neuron. RNA, the site of protein synthesis, transmits instructions from DNA directi ...
Motor Cortex
... General area integrates multiple stimuli into a single cogent “understanding of the situation.” ...
... General area integrates multiple stimuli into a single cogent “understanding of the situation.” ...
Motor Systems I Cortex
... Learning changes the nature and locus of sensorimotor control (e.g., conscious to automatic) ...
... Learning changes the nature and locus of sensorimotor control (e.g., conscious to automatic) ...
A1984TF19600002
... Medical School in London, leaving Tom with the unenviable task of making the relevant chapters of my thesis into a paper. At that time, Ted Jones arrived in Oxford from Otago and together they worked through the material, and added some; and so the paper was written. It gave anatomical support to co ...
... Medical School in London, leaving Tom with the unenviable task of making the relevant chapters of my thesis into a paper. At that time, Ted Jones arrived in Oxford from Otago and together they worked through the material, and added some; and so the paper was written. It gave anatomical support to co ...
Cerebellar system and diseases
... Motor coordination Cerebellum does not initiate movement It contributes to coordination, precision, and accurate timing. It receives input from sensory systems and from other parts of the brain and spinal cord, It integrates these inputs to tune fine motor activity. Because of this fine-tun ...
... Motor coordination Cerebellum does not initiate movement It contributes to coordination, precision, and accurate timing. It receives input from sensory systems and from other parts of the brain and spinal cord, It integrates these inputs to tune fine motor activity. Because of this fine-tun ...
Central Nervous System
... • General area integrates multiple stimuli into a single cogent “understanding of the situation.” – Found on only one hemisphere – typically left. – Contained by 3 lobes: temporal, occipital, and parietal. ...
... • General area integrates multiple stimuli into a single cogent “understanding of the situation.” – Found on only one hemisphere – typically left. – Contained by 3 lobes: temporal, occipital, and parietal. ...
Cortical Functions Reference
... in these cases the primary motor activation is found in addition to a more extensive pattern of activation, obviously including sensory areas; that is, area 4 may some times be included in a brain circuitry supporting sensory perception; area 4 activation may reflect in those cases the implicit repr ...
... in these cases the primary motor activation is found in addition to a more extensive pattern of activation, obviously including sensory areas; that is, area 4 may some times be included in a brain circuitry supporting sensory perception; area 4 activation may reflect in those cases the implicit repr ...
Editorial overview: Neurobiology of cognitive behavior: Complexity
... their precursors and creators – brains – acquire and use knowledge. For at least two centuries, psychologists and cognitive scientists have studied human and animal behavior in an effort to better understand the faculties that support natural cognition: multisensory integration, working memory, valu ...
... their precursors and creators – brains – acquire and use knowledge. For at least two centuries, psychologists and cognitive scientists have studied human and animal behavior in an effort to better understand the faculties that support natural cognition: multisensory integration, working memory, valu ...
From autism to ADHD: computational simulations
... • “Default brain network” involves a large-scale brain network (cingulate cortex, mPFC, lateral PC), shows low activity for goal-related actions; it is active in social and emotional processing, mindwandering, daydreaming. • Activity of the default network is negatively correlated with the “action n ...
... • “Default brain network” involves a large-scale brain network (cingulate cortex, mPFC, lateral PC), shows low activity for goal-related actions; it is active in social and emotional processing, mindwandering, daydreaming. • Activity of the default network is negatively correlated with the “action n ...
cerebral cortex
... districts, which represent the seats of the highest processing and integration of motor and sensory information (motor cortex, sensory, visual, auditory etc.) ...
... districts, which represent the seats of the highest processing and integration of motor and sensory information (motor cortex, sensory, visual, auditory etc.) ...
A.P. Psychology Rubric: Chapter 2 10 point question Question: You
... Recognize that the temporal lobes are associated with hearing. Example: The temporal lobes would allow the checker player to hear the sound of the pieces as she moves them across the board or hear her say, “KING,” triumphantly. 1 point: hippocampus Recognize that the hippocampus is involved in the f ...
... Recognize that the temporal lobes are associated with hearing. Example: The temporal lobes would allow the checker player to hear the sound of the pieces as she moves them across the board or hear her say, “KING,” triumphantly. 1 point: hippocampus Recognize that the hippocampus is involved in the f ...
Short-term memory
... paradigmatic test is the delayed response task, which requires a subject to memorize an instruction stimulus and to wait for a go signal before responding to it. This task is typically impaired after lesions of the prefrontal cortex (Fuster 1989). Prefrontal neurons recorded during delayed response ...
... paradigmatic test is the delayed response task, which requires a subject to memorize an instruction stimulus and to wait for a go signal before responding to it. This task is typically impaired after lesions of the prefrontal cortex (Fuster 1989). Prefrontal neurons recorded during delayed response ...
w - Fizyka UMK
... mathematics, proposing 23 major problems worth working at in future. 100 years later the impact of this talk is still strong: some problems have been solved, new problems have been added, but the direction once set - identify the most important problems and focus on them - is still important. It bec ...
... mathematics, proposing 23 major problems worth working at in future. 100 years later the impact of this talk is still strong: some problems have been solved, new problems have been added, but the direction once set - identify the most important problems and focus on them - is still important. It bec ...
differentiation of brain vesicles
... 14) What was most likely the most ancient ascending pathway from the secondary sensory neurons of the trigeminal system? 15) Describe the hypothesis for how the somatosensory and visual system pathways to the midbrain and forebrain evolved to become predominantly crossed. 16) What is the meaning of ...
... 14) What was most likely the most ancient ascending pathway from the secondary sensory neurons of the trigeminal system? 15) Describe the hypothesis for how the somatosensory and visual system pathways to the midbrain and forebrain evolved to become predominantly crossed. 16) What is the meaning of ...
Document
... mathematics, proposing 23 major problems worth working at in future. 100 years later the impact of this talk is still strong: some problems have been solved, new problems have been added, but the direction once set - identify the most important problems and focus on them - is still important. It bec ...
... mathematics, proposing 23 major problems worth working at in future. 100 years later the impact of this talk is still strong: some problems have been solved, new problems have been added, but the direction once set - identify the most important problems and focus on them - is still important. It bec ...
Executive functions

Executive functions (also known as cognitive control and supervisory attentional system) is an umbrella term for the management (regulation, control) of cognitive processes, including working memory, reasoning, task flexibility, and problem solving as well as planning and execution.The executive system is a theorized cognitive system in psychology that controls and manages other cognitive processes, such as executive functions. The prefrontal areas of the frontal lobe are necessary but not solely sufficient for carrying out these functions.























