
16 EXPERIMENT Equipotential Lines and Electric Fields
... In this experiment we will measure the electric potential in the vicinity of two different charge distributions. Each charge distribution will consist of two metal objects mounted on conductive paper. We consider metals to be ideal conductors (same electric potential everywhere on the metal). Wherea ...
... In this experiment we will measure the electric potential in the vicinity of two different charge distributions. Each charge distribution will consist of two metal objects mounted on conductive paper. We consider metals to be ideal conductors (same electric potential everywhere on the metal). Wherea ...
The AdS 3/CFT2 correspondence in black hole physics
... included, the requirement of preservation of T-duality leads to the presence of the so-called Dbranes, spatially extended objects of any dimension on which open strings can end. It turned out that in any given string theory D-branes can only be stable if their dimensionality is the one dictated by t ...
... included, the requirement of preservation of T-duality leads to the presence of the so-called Dbranes, spatially extended objects of any dimension on which open strings can end. It turned out that in any given string theory D-branes can only be stable if their dimensionality is the one dictated by t ...
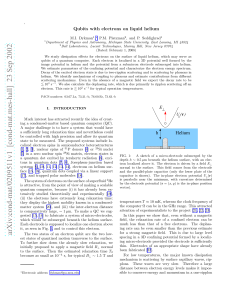
Qubits with electrons on liquid helium
... ∼ 6 × 10 s . This shows that singlequbit operations should not limit ΩQC at least at the level of 107 − 108 Hz. Because the wave functions of different electrons do not overlap, the interaction between the qubits that we consider is dipolar, as in liquid-state NMR quantum computers [28]. An importan ...
... ∼ 6 × 10 s . This shows that singlequbit operations should not limit ΩQC at least at the level of 107 − 108 Hz. Because the wave functions of different electrons do not overlap, the interaction between the qubits that we consider is dipolar, as in liquid-state NMR quantum computers [28]. An importan ...
DOUGLAS C. GIANCOLI
... where 6 and V are shown in Fig. 25-16. We can write! length by noting that 9 = h/N (Fig. 25-16b) and (f where A it the height of the object and we assume the .' 6' equal their sines and tangents. If the eye is relaxed image will be at infinity and the object will be precr Fig. 25-17. Then d, - / and ...
... where 6 and V are shown in Fig. 25-16. We can write! length by noting that 9 = h/N (Fig. 25-16b) and (f where A it the height of the object and we assume the .' 6' equal their sines and tangents. If the eye is relaxed image will be at infinity and the object will be precr Fig. 25-17. Then d, - / and ...
http://ncatlab.org/schreiber/files/QFTinCohesiveHoTT.pdf
... The value of cohesive homotopy theory for physics lies in the observation that the QFTs observed to govern our world at the fundamental level — namely, Yang-Mills theory (for electromagnetism and the weak and strong nuclear forces) and Einstein general relativity (for gravity) — are not random insta ...
... The value of cohesive homotopy theory for physics lies in the observation that the QFTs observed to govern our world at the fundamental level — namely, Yang-Mills theory (for electromagnetism and the weak and strong nuclear forces) and Einstein general relativity (for gravity) — are not random insta ...
Introduction to Subatomic
... briefly introduce subatomic particles and their detection before treating particle detectors in more detail. We conclude with three examples that illustrate how a variety of detectors often work together in typical high-energy-physics experiments. The experimental study of subatomic particles and th ...
... briefly introduce subatomic particles and their detection before treating particle detectors in more detail. We conclude with three examples that illustrate how a variety of detectors often work together in typical high-energy-physics experiments. The experimental study of subatomic particles and th ...
DYNAMIC PROPERTIES OF THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD
... considered body is in vacuo. An analysis of the expressions of the mentioned type is not given in literature, but it could be carried out starting from references: [3, p. 192–193, 490–491], [7, p. 258], [17, p. 30, 92, 101, 107], [12], [14]. It is worth noting that Maxwell introduced certain express ...
... considered body is in vacuo. An analysis of the expressions of the mentioned type is not given in literature, but it could be carried out starting from references: [3, p. 192–193, 490–491], [7, p. 258], [17, p. 30, 92, 101, 107], [12], [14]. It is worth noting that Maxwell introduced certain express ...
The Higgs Boson - University of Toronto Physics
... defined at every point throughout some region of space and time, such as the surface of a frying pan. In physics the term "field" is usually reserved for such entities as the gravitational field and the electromagnetic field. Fields ...
... defined at every point throughout some region of space and time, such as the surface of a frying pan. In physics the term "field" is usually reserved for such entities as the gravitational field and the electromagnetic field. Fields ...
cavity design - lombarda.web.cern.ch
... for a given wave type and mode, there is a limited passband between o and ; at these points, vg = 0; the bigger the coupling between cells, the bigger the passband; for a given frequency, there is an infinite series of space harmonics, with the same vg, but with different vph; when the electromag ...
... for a given wave type and mode, there is a limited passband between o and ; at these points, vg = 0; the bigger the coupling between cells, the bigger the passband; for a given frequency, there is an infinite series of space harmonics, with the same vg, but with different vph; when the electromag ...
PSE4_Lecture_2_Ch21
... toner (ink) particles onto the drum. The toner particles temporarily stick to the pattern on the drum and are later transferred to paper and “melted” to produce the copy. Suppose each toner particle has a mass of 9.0 x 10-16 kg and carries an average of 20 extra electrons to provide an electric char ...
... toner (ink) particles onto the drum. The toner particles temporarily stick to the pattern on the drum and are later transferred to paper and “melted” to produce the copy. Suppose each toner particle has a mass of 9.0 x 10-16 kg and carries an average of 20 extra electrons to provide an electric char ...
Phenomenology Beyond the Standard Model
... Favoured values of gluino mass significantly above pre-LHC, > 2 TeV ...
... Favoured values of gluino mass significantly above pre-LHC, > 2 TeV ...
electric potential - DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska
... Potential as a Function of Position ...
... Potential as a Function of Position ...
CHAPTER 24: CAPACITANCE AND DIELECTRICS • Suppose you
... are connected in parallel if they share two common junctions. Or, another way of saying this – if two capacitors are connected at both ends, then they are connected in parallel We are treating the wires as ideal conductors so there is no potential difference across them. Therefore the potential di ...
... are connected in parallel if they share two common junctions. Or, another way of saying this – if two capacitors are connected at both ends, then they are connected in parallel We are treating the wires as ideal conductors so there is no potential difference across them. Therefore the potential di ...
Landau Theory of Phase Transitions
... committed suicide at age 53, after shooting his younger son who had Down’s syndrome. ...
... committed suicide at age 53, after shooting his younger son who had Down’s syndrome. ...
Temporal interferences driven by a single-cycle terahertz pulse in the... dynamics of negative ions
... the photodetachment process and the other later, indicated by the dotted lines in Figs. 1(a) and 1(b). The associated electron waves interfere with each other as a result of the different quantum phases accumulated by the electron moving along these two trajectories. Two examples of the interference ...
... the photodetachment process and the other later, indicated by the dotted lines in Figs. 1(a) and 1(b). The associated electron waves interfere with each other as a result of the different quantum phases accumulated by the electron moving along these two trajectories. Two examples of the interference ...
Contact and Space-Charge Effects in Quantum Well Infrared
... We present the results of a new self-consistent analytical model for the calculation of the dark current and the electric-field and space-charge distributions in quantum well infrared photodetectors (QWIPs). This model takes into account thermionic emission from the QWs, tunneling injection of elect ...
... We present the results of a new self-consistent analytical model for the calculation of the dark current and the electric-field and space-charge distributions in quantum well infrared photodetectors (QWIPs). This model takes into account thermionic emission from the QWs, tunneling injection of elect ...
A new extended model of the electron
... i / Runaway : the acceleration of the electron increases indefinitely with time , and even when there is no external field , the electron can exert a force on itself which accelerates it to infinite velocity . ii / Pre-acceleration : the electron is accelerated before the external field is turned on ...
... i / Runaway : the acceleration of the electron increases indefinitely with time , and even when there is no external field , the electron can exert a force on itself which accelerates it to infinite velocity . ii / Pre-acceleration : the electron is accelerated before the external field is turned on ...





![[ G69 ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014611684_1-e16c579c4f99cbecf32e42b89cdaa891-300x300.png)
















