A true Science Adventure - Wave Structure of Matter (WSM)
... There are no orbits. For many (too many) years people imagined atoms as point electrons orbiting around a nucleus. This myth, obviously imitating our planetary system, was shown wrong by quantum theory more than sixty years ago. For example in the hydrogen atom, quantum theory predicts the electron ...
... There are no orbits. For many (too many) years people imagined atoms as point electrons orbiting around a nucleus. This myth, obviously imitating our planetary system, was shown wrong by quantum theory more than sixty years ago. For example in the hydrogen atom, quantum theory predicts the electron ...
ppt
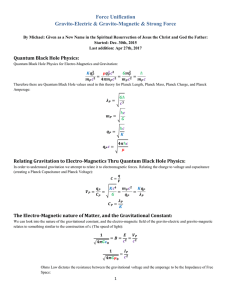
... Quantum gravity is widely recognized as one of the most difficult problems of modern theoretical physics. There is currently a vast body of knowledge which includes several different approaches to this area of research. Among the most popular are string theory and loop quantum gravity. There is, ho ...
... Quantum gravity is widely recognized as one of the most difficult problems of modern theoretical physics. There is currently a vast body of knowledge which includes several different approaches to this area of research. Among the most popular are string theory and loop quantum gravity. There is, ho ...
electric field
... We could therefore prove that the voltage V is proportional to the distance moved x, since the charge moving and the force depends on the the charges and the distance from it. So for a uniform field we end up with lines where the potential of that point and all points along it are equal. Just like ...
... We could therefore prove that the voltage V is proportional to the distance moved x, since the charge moving and the force depends on the the charges and the distance from it. So for a uniform field we end up with lines where the potential of that point and all points along it are equal. Just like ...
Single particle motion and trapped particles
... motion is three-dimensional and looks like a helix. The pitch angle of the helix or particle velocity with respect to the field depends on the ratio of perpendicular to parallel velocity components. ...
... motion is three-dimensional and looks like a helix. The pitch angle of the helix or particle velocity with respect to the field depends on the ratio of perpendicular to parallel velocity components. ...
Electric Field
... • But if you touch the inside of the neutral container, all of it will transfer! • Let’s draw to explain. ...
... • But if you touch the inside of the neutral container, all of it will transfer! • Let’s draw to explain. ...
Section B: CHEMICAL ENGINEERING – Answer ALL questions
... If the cube has sides of length 2 units, work out the (x, y, z) coordinates of each of the four hydrogen atoms with reference to the carbon atom at the origin ...
... If the cube has sides of length 2 units, work out the (x, y, z) coordinates of each of the four hydrogen atoms with reference to the carbon atom at the origin ...
Chap. 11 -- E-M wave..
... a) Consider the peak value in the pattern that you observe at t = 0.03 s. As time goes on, that peak value (with direction pointing upward) will reappear again at what value of t? b) The period of an e-m wave [symbol: T] is the elapsed time between two consecutive maxima in the magnitude of the elec ...
... a) Consider the peak value in the pattern that you observe at t = 0.03 s. As time goes on, that peak value (with direction pointing upward) will reappear again at what value of t? b) The period of an e-m wave [symbol: T] is the elapsed time between two consecutive maxima in the magnitude of the elec ...
E/M writeup
... After passing through a small hole in the anode, the electrons are in a region with no electric field but with a uniform magnetic field B oriented in a horizontal direction. The magnetic force Fm acting on a particle of charge q moving with velocity v in a magnetic field B is given by the equation F ...
... After passing through a small hole in the anode, the electrons are in a region with no electric field but with a uniform magnetic field B oriented in a horizontal direction. The magnetic force Fm acting on a particle of charge q moving with velocity v in a magnetic field B is given by the equation F ...
Induced Electric Fields.
... It is better to say that there is an electric field, as described by Maxwell’s equations. We saw in lecture 17 that what an observer measures for the magnetic field depends on the motion of the observer relative to the source of the field. We see here that the same is true for the electric field. Th ...
... It is better to say that there is an electric field, as described by Maxwell’s equations. We saw in lecture 17 that what an observer measures for the magnetic field depends on the motion of the observer relative to the source of the field. We see here that the same is true for the electric field. Th ...
Einstein memorial lecture.
... Important contributions to geodesy and geography were also made by al-Biruni. He introduced techniques to measure the earth and distances on it using triangulation. He found the radius of the earth to be 6339.6 km, a value not obtained in the West until the 16th century. His Masudic canon contains a ...
... Important contributions to geodesy and geography were also made by al-Biruni. He introduced techniques to measure the earth and distances on it using triangulation. He found the radius of the earth to be 6339.6 km, a value not obtained in the West until the 16th century. His Masudic canon contains a ...