UTI 2014 - UMF IASI 2015
... Method for collecting urine is dependent the age : - Older children, teens - from medium urinary jet, after rigorous local toilet. This is the method most frequently used, but the chance of bacterial contamination of the urine sample is great. - Infants and toddlers - by peripheral collecting vessel ...
... Method for collecting urine is dependent the age : - Older children, teens - from medium urinary jet, after rigorous local toilet. This is the method most frequently used, but the chance of bacterial contamination of the urine sample is great. - Infants and toddlers - by peripheral collecting vessel ...
Urinary Incontinence in women
... • Psychological problems: depression, feelings of shame, loss of self confidence, poor self-rated health, low self esteem, guilt, social isolation. • Sexual problems: incontinence during sex may cause embarrassment • Loss of sleep: nocturia and fear of leakage. • Constipation: due to limiting fluid ...
... • Psychological problems: depression, feelings of shame, loss of self confidence, poor self-rated health, low self esteem, guilt, social isolation. • Sexual problems: incontinence during sex may cause embarrassment • Loss of sleep: nocturia and fear of leakage. • Constipation: due to limiting fluid ...
Nurse Practitioner Clinical Protocol
... Epidemiologically, UTIs be subdivided into catheter associated and non-catheter associated infections. Whether acquired in hospital (nosocomial) or in the community, infections the can be asymptomatic or non-symptomatic.2 A sudden deterioration of mental state in the elderly may be an indication of ...
... Epidemiologically, UTIs be subdivided into catheter associated and non-catheter associated infections. Whether acquired in hospital (nosocomial) or in the community, infections the can be asymptomatic or non-symptomatic.2 A sudden deterioration of mental state in the elderly may be an indication of ...
Urinary notes Lecture Notes Page
... 2. Physiologic failure of the cells of the tubules. The urinary system includes: ...
... 2. Physiologic failure of the cells of the tubules. The urinary system includes: ...
Flesh Eating Bacteria
... from these bacteria. Usually occurs in hospitals after surgery/trauma. 3. Vibrio vulnificus – Seawater 4. Type IV – Fungal infections ...
... from these bacteria. Usually occurs in hospitals after surgery/trauma. 3. Vibrio vulnificus – Seawater 4. Type IV – Fungal infections ...
Print PDF - The Urology Group
... which occurs once the previous one has been treated. Several recognized initiating events can trigger infection. Two of the most common are sexual intercourse and vaginal douching. It appears that the pressure in the vaginal area which occurs at intercourse may facilitate ascent of bacteria up the u ...
... which occurs once the previous one has been treated. Several recognized initiating events can trigger infection. Two of the most common are sexual intercourse and vaginal douching. It appears that the pressure in the vaginal area which occurs at intercourse may facilitate ascent of bacteria up the u ...
Urinary Tract Infections | Overview -
... push against the urethra and make it harder to completely empty the bladder. The urine that stays in the bladder is more likely to grow bacteria and cause infections. Frequent urinary tract infections may be caused by changes in the bacteria in the vagina. Antibacterial vaginal douches, spermicides ...
... push against the urethra and make it harder to completely empty the bladder. The urine that stays in the bladder is more likely to grow bacteria and cause infections. Frequent urinary tract infections may be caused by changes in the bacteria in the vagina. Antibacterial vaginal douches, spermicides ...
A Day in Nicaragua
... - Caused by: overexposure to UV light, aging, hypertension, eye trauma - Treatment: surgically remove lens and replace with artificial, preventative measures like sunglasses UTI (Urinary Tract Infection): infection of the urinary tract, specifically the bladder - Symptoms: painful and frequent urina ...
... - Caused by: overexposure to UV light, aging, hypertension, eye trauma - Treatment: surgically remove lens and replace with artificial, preventative measures like sunglasses UTI (Urinary Tract Infection): infection of the urinary tract, specifically the bladder - Symptoms: painful and frequent urina ...
Production of b-lactamase by pathogens causing urinary tract
... (Whitchurch et al.,2002) A typical high-affinity iron uptake system consists of a low-molecular-mass Fe (III)chelating compound, known as a siderophore, combined with its cognate membrane-located receptor. Such iron acquisition systems are generally regarded as important virulence or fitness factors ...
... (Whitchurch et al.,2002) A typical high-affinity iron uptake system consists of a low-molecular-mass Fe (III)chelating compound, known as a siderophore, combined with its cognate membrane-located receptor. Such iron acquisition systems are generally regarded as important virulence or fitness factors ...
123 bacteria in the bladder wall of women with lower urinary tract
... 10 CFU/ml is employed for diagnosis but has also been found in women with no symptoms in a lower proportion. This makes it controversial about whether the cultured organisms are contamination present in the urine. However by culturing bladder biopsies obtained during cystoscopy in sterile conditions ...
... 10 CFU/ml is employed for diagnosis but has also been found in women with no symptoms in a lower proportion. This makes it controversial about whether the cultured organisms are contamination present in the urine. However by culturing bladder biopsies obtained during cystoscopy in sterile conditions ...
Anatomy and Function of the Urinary System
... bladder. Muscles in the ureter walls continually tighten and relax forcing urine downward, away from the kidneys. If urine backs up, or is allowed to stand still, a kidney infection can develop. About every 10 to 15 sec onds, small amounts of urine are em ptied into the bladder from the ureters. ...
... bladder. Muscles in the ureter walls continually tighten and relax forcing urine downward, away from the kidneys. If urine backs up, or is allowed to stand still, a kidney infection can develop. About every 10 to 15 sec onds, small amounts of urine are em ptied into the bladder from the ureters. ...
Urinary System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 17
... – Some from anatomical malformations of the urinary tract or may have a genetic predisposition, or due to diet. • Treatment: – Drink lots of water: May be able to move a stone through your urinary tract simply by drinking plenty of water — as much as 2 to 3 quarts (1.9 to 2.8 liters) a day — and by ...
... – Some from anatomical malformations of the urinary tract or may have a genetic predisposition, or due to diet. • Treatment: – Drink lots of water: May be able to move a stone through your urinary tract simply by drinking plenty of water — as much as 2 to 3 quarts (1.9 to 2.8 liters) a day — and by ...
Treating Bacterial Infections: Ear Infections, Sinus Infections, Strep
... the infection with the fewest side effects. What antibiotic is the right choice for my child? Antibiotics can treat illnesses caused by bacteria. When antibiotics are necessary, it is important that your child receives an antibiotic that targets her specific bacterial infection. Amoxicillin is the r ...
... the infection with the fewest side effects. What antibiotic is the right choice for my child? Antibiotics can treat illnesses caused by bacteria. When antibiotics are necessary, it is important that your child receives an antibiotic that targets her specific bacterial infection. Amoxicillin is the r ...
When your pet doesn`t urinate normally
... specialized tests may be needed to reach a diagnosis. Treatment varies based on what’s causing the urination problem. Urinary tract infections are treated with antibiotics. If your pet has urinary incontinence associated with urethral weakness, your veterinarian may prescribe estrogen supplementatio ...
... specialized tests may be needed to reach a diagnosis. Treatment varies based on what’s causing the urination problem. Urinary tract infections are treated with antibiotics. If your pet has urinary incontinence associated with urethral weakness, your veterinarian may prescribe estrogen supplementatio ...
View Full Text-PDF
... presence of microbial pathogens within the urinary tract and it is usually classified by the site of infection as bladder (cystitis), kidney (pyelonephritis) (Gonzalez and Schaeffer, 1999). It has been estimated that globally symptomatic UTIs result in as many as 7 million visits to outpatient clini ...
... presence of microbial pathogens within the urinary tract and it is usually classified by the site of infection as bladder (cystitis), kidney (pyelonephritis) (Gonzalez and Schaeffer, 1999). It has been estimated that globally symptomatic UTIs result in as many as 7 million visits to outpatient clini ...
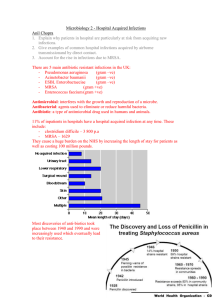
Microbiology 2 – Hospital Acquired Infections
... Antibacterial: agents used to eliminate or reduce harmful bacteria. Antibiotic: a type of antimicrobial drug used in humans and animals. 11% of inpatients in hospitals have a hospital acquired infection at any time. These include: - clostridium difficile – 3 800 p.a - MRSA – 1629 They cause a huge b ...
... Antibacterial: agents used to eliminate or reduce harmful bacteria. Antibiotic: a type of antimicrobial drug used in humans and animals. 11% of inpatients in hospitals have a hospital acquired infection at any time. These include: - clostridium difficile – 3 800 p.a - MRSA – 1629 They cause a huge b ...
prompt/encourage the patient to void at least every 3
... 5. In and out sterile catheterization, if the residual volume is greater than 250 cc on bladder scan. Measure the amount of urine and record. 6. If bladder scan is not available, do an in and out sterile catheterization to assess the post void residual volume 7. Continue to assess post void residual ...
... 5. In and out sterile catheterization, if the residual volume is greater than 250 cc on bladder scan. Measure the amount of urine and record. 6. If bladder scan is not available, do an in and out sterile catheterization to assess the post void residual volume 7. Continue to assess post void residual ...
Antibiotics!
... treated with 25 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours, 20 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours, 40 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours or 45 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours depending on infection. • Timentin (Ticarcillin): This medication is given intravenously.It is diluted i ...
... treated with 25 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours, 20 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours, 40 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours or 45 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours depending on infection. • Timentin (Ticarcillin): This medication is given intravenously.It is diluted i ...
Urinary System
... • The urinary bladder is the organ that collects urine excreted by the kidneys before disposal by urination. • A hollow, muscular and elastic organ ...
... • The urinary bladder is the organ that collects urine excreted by the kidneys before disposal by urination. • A hollow, muscular and elastic organ ...
Urinary reflux
... A child with urinary reflux is more likely to get urinary tract infections (UTIs), and these can cause kidney damage if they're not treated. This is called reflux nephropathy (nef-roh-path-y), and as a result their kidneys can't work as well as they should. ...
... A child with urinary reflux is more likely to get urinary tract infections (UTIs), and these can cause kidney damage if they're not treated. This is called reflux nephropathy (nef-roh-path-y), and as a result their kidneys can't work as well as they should. ...
cystitis (bladder infection) and urinary tract infection
... doctor or go to a hospital emergency room if these symptoms develop. If you’ve had more that 3 UTIs in a year you may have a problem that requires further evaluation by a specialist. ...
... doctor or go to a hospital emergency room if these symptoms develop. If you’ve had more that 3 UTIs in a year you may have a problem that requires further evaluation by a specialist. ...
Urinary tract infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI), also known as acute cystitis or bladder infection, is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a simple cystitis (a bladder infection) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as pyelonephritis (a kidney infection). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract include painful urination and either frequent urination or urge to urinate (or both); while the symptoms of pyelonephritis include fever and flank pain in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. In some cases, a painful burning sensation in the urethra may be present even when not urinating. In the elderly and the very young, symptoms may be vague or non-specific. The main causal agent of both types is Escherichia coli, though other bacteria, viruses or fungi may rarely be the cause.Urinary tract infections occur more commonly in women than men, with half of women having at least one infection at some point in their lives. Recurrences are common. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse and family history. Pyelonephritis, if it occurs, usually follows a bladder infection but may also result from a blood-borne infection. Diagnosis in young healthy women can be based on symptoms alone. In those with vague symptoms, diagnosis can be difficult because bacteria may be present without there being an infection. In complicated cases or if treatment has failed, a urine culture may be useful. In those with frequent infections, low dose antibiotics may be taken as a preventative measure.In uncomplicated cases, urinary tract infections are easily treated with a short course of antibiotics, although resistance to many of the antibiotics used to treat this condition is increasing. In complicated cases, a longer course or intravenous antibiotics may be needed, and if symptoms have not improved in two or three days, further diagnostic testing is needed. In women, urinary tract infections are the most common form of bacterial infection with 10% developing urinary tract infections yearly. In those who have bacteria or white blood cells in their urine but have no symptoms, antibiotics are generally not needed, although pregnant women are an exception to this recommendation.