unit 7 – history and organization of biological diversity
... evolution states that all organisms on Earth have descended from a common ancestor. There is evidence that supports the theory of evolution by natural selection: 1. Variations do exist in populations 2. Fossils 3. Traits that allow organisms to thrive in particular environments. Since the time of Da ...
... evolution states that all organisms on Earth have descended from a common ancestor. There is evidence that supports the theory of evolution by natural selection: 1. Variations do exist in populations 2. Fossils 3. Traits that allow organisms to thrive in particular environments. Since the time of Da ...
Notes Chapter 18 Classification
... philosopher Aristotle. He classified everything as either a plant or an animal and then grouped them into land dwellers, water dwellers, and air dwellers. This system worked very well for a period of time but eventually, new species were discovered that didn’t fit into his categories. Also, using th ...
... philosopher Aristotle. He classified everything as either a plant or an animal and then grouped them into land dwellers, water dwellers, and air dwellers. This system worked very well for a period of time but eventually, new species were discovered that didn’t fit into his categories. Also, using th ...
Chapter 14 Darwin
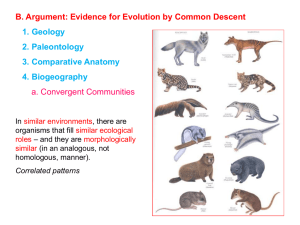
... Analogous Structures Analogous structures are a contrast to homologous structures. They serve the same function between organisms but are different in internal anatomy. Such as the wings of birds and butterflies. These structures are of no use in classifying organisms or in working out thei ...
... Analogous Structures Analogous structures are a contrast to homologous structures. They serve the same function between organisms but are different in internal anatomy. Such as the wings of birds and butterflies. These structures are of no use in classifying organisms or in working out thei ...
CHAPTER 9: THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION
... These “native” taxonomies characteristically break down the classification of animal life forms into one or more of the following categories:6 (1) Fish (aquatic animals, mostly fish but even whales); (2) Bird (animals that can fly, usually birds but occasionally bats); (3) Snake (creeping animals su ...
... These “native” taxonomies characteristically break down the classification of animal life forms into one or more of the following categories:6 (1) Fish (aquatic animals, mostly fish but even whales); (2) Bird (animals that can fly, usually birds but occasionally bats); (3) Snake (creeping animals su ...
Psychology 4000 - U of L Class Index
... that could have made such a mating preference adaptive during our species evolutionary history ...
... that could have made such a mating preference adaptive during our species evolutionary history ...
Blueprint of Life
... 1. Define the term natural selection and list three environmental pressures that may lead to selection in nature. 2. List three physical changes and three chemical changes in the environment which may place pressure on a species and lead to evolutionary change. 3. The emergence of the peppered moth ...
... 1. Define the term natural selection and list three environmental pressures that may lead to selection in nature. 2. List three physical changes and three chemical changes in the environment which may place pressure on a species and lead to evolutionary change. 3. The emergence of the peppered moth ...
Evolution and Taxonomy Outline
... 12. Why are fossils of hard - bodied organisms more common than soft-bodied organisms? (DOK 2) a. The fossils of soft-bodied organisms preserve better than hard structures. b. The fossils of hard-bodied organisms preserve better than soft structures. c. There are more organisms with hard structures ...
... 12. Why are fossils of hard - bodied organisms more common than soft-bodied organisms? (DOK 2) a. The fossils of soft-bodied organisms preserve better than hard structures. b. The fossils of hard-bodied organisms preserve better than soft structures. c. There are more organisms with hard structures ...
JEOPARDY!
... Genetic Variation 400 • Which fact provides the best evidence for the biological theory of evolution? – A. Most fossils are found in sedimentary rock – B. Most species of life on Earth have become extinct – C. Characteristics of simpler life-forms can be found in more complex life-forms. – D. Only ...
... Genetic Variation 400 • Which fact provides the best evidence for the biological theory of evolution? – A. Most fossils are found in sedimentary rock – B. Most species of life on Earth have become extinct – C. Characteristics of simpler life-forms can be found in more complex life-forms. – D. Only ...
Document
... contain toxins and most species of Australian snake die after eating the toad. The cane toad toxin does not affect all snakes the same way. Longer snakes are less affected by toad toxin. Scientists investigated how redbellied black snakes had changed in the 70 years since cane toads were introduced ...
... contain toxins and most species of Australian snake die after eating the toad. The cane toad toxin does not affect all snakes the same way. Longer snakes are less affected by toad toxin. Scientists investigated how redbellied black snakes had changed in the 70 years since cane toads were introduced ...
Evolution and alleles
... Apart from organisms such as certain types of sharks, cockroaches or ferns, many living organisms today have no identical form in the fossil record. ...
... Apart from organisms such as certain types of sharks, cockroaches or ferns, many living organisms today have no identical form in the fossil record. ...
Document
... What did Darwin mean by descent? What is a descendant? What is an ancestor? What did he mean by modification? What does it mean to modify something? What did he mean by natural selection? What is nature? What does it mean to select something? ...
... What did Darwin mean by descent? What is a descendant? What is an ancestor? What did he mean by modification? What does it mean to modify something? What did he mean by natural selection? What is nature? What does it mean to select something? ...
Educational Standards
... well, some survive less well, and some cannot survive at all. Use evidence to construct an explanation for how the variations in characteristics among individuals of the same species may provide advantages in surviving, finding mates, and reproducing. Analyze and interpret data from fossils to provi ...
... well, some survive less well, and some cannot survive at all. Use evidence to construct an explanation for how the variations in characteristics among individuals of the same species may provide advantages in surviving, finding mates, and reproducing. Analyze and interpret data from fossils to provi ...
Biology Ch. 15 Notes Tracing Evolutionary History Opening Essay
... that benefited their owners at each stage. Gradual adaptation of existing parts to new functions (wings). Exaptations: Structures that evolve in one context but become co-opted for another function. A structure can become adapted to alternative functions. Novel features can arise gradually via a ser ...
... that benefited their owners at each stage. Gradual adaptation of existing parts to new functions (wings). Exaptations: Structures that evolve in one context but become co-opted for another function. A structure can become adapted to alternative functions. Novel features can arise gradually via a ser ...
Reviewing Biology: The Living Environment
... adaptations or variations are helpful and which are harmful. For example, in an environment that is undergoing a particularly cold period, animals that have thicker fur than most other members of their population are more likely to survive. In this case, their variation—thicker fur—is helpful in ter ...
... adaptations or variations are helpful and which are harmful. For example, in an environment that is undergoing a particularly cold period, animals that have thicker fur than most other members of their population are more likely to survive. In this case, their variation—thicker fur—is helpful in ter ...
Evolution - George Mason University
... • perceived a unity among species – all organisms related through descent from unknown organisms that lived in the past – as descendants spread into various habitats over millions of years » accumulated adaptations » adapted to various environments ...
... • perceived a unity among species – all organisms related through descent from unknown organisms that lived in the past – as descendants spread into various habitats over millions of years » accumulated adaptations » adapted to various environments ...
slides - Botany
... • Obscures evidence of paleopolyploidy • Return to a diploid genetic system – Restoration of full bivalent pairing – Gene and chromosome loss – Chromosomal rearrangements • Proceeds at different rates in different lineages ...
... • Obscures evidence of paleopolyploidy • Return to a diploid genetic system – Restoration of full bivalent pairing – Gene and chromosome loss – Chromosomal rearrangements • Proceeds at different rates in different lineages ...
Pre-AP Biology - Evolution Review
... Molecular Biology (DNA and amino acid sequences - proteins) – Note: This is the most important type of evidence proving evolution. The closer 2 different species DNA is to one another, then the closer those 2 are related. All living things use DNA and RNA. ...
... Molecular Biology (DNA and amino acid sequences - proteins) – Note: This is the most important type of evidence proving evolution. The closer 2 different species DNA is to one another, then the closer those 2 are related. All living things use DNA and RNA. ...
Ch. 15 Darwin`s Theory of Evolution
... • Over 20 years later, Darwin published all his findings in a book called, On the Origin of Species. • He didn’t publish it earlier because it went against the common beliefs about organisms. ...
... • Over 20 years later, Darwin published all his findings in a book called, On the Origin of Species. • He didn’t publish it earlier because it went against the common beliefs about organisms. ...
classification
... 1. vultures american, african and asian a. american habit of urinating on legs to cool themselves, same as storks. African and asian vultures do not. ii. Evolutionary classification Overhead of humans and apes 1. guided by evolutionary theory, biologists new group organisms into categories that repr ...
... 1. vultures american, african and asian a. american habit of urinating on legs to cool themselves, same as storks. African and asian vultures do not. ii. Evolutionary classification Overhead of humans and apes 1. guided by evolutionary theory, biologists new group organisms into categories that repr ...
Slides
... they? It seems like quite a coincidence that of all the intermediate species that must have existed between the mesonychid and whale, only species that are very similar to the end species have been found.”! ...
... they? It seems like quite a coincidence that of all the intermediate species that must have existed between the mesonychid and whale, only species that are very similar to the end species have been found.”! ...
Darwin and the Theory of Evolution
... • He dug up fossils of gigantic extinct mammals, such as the ground sloth. This was hard evidence that organisms looked very different in the past. It suggested that living things — like Earth’s surface — change over time. The Galápagos Islands Darwin’s most important observations were made on the G ...
... • He dug up fossils of gigantic extinct mammals, such as the ground sloth. This was hard evidence that organisms looked very different in the past. It suggested that living things — like Earth’s surface — change over time. The Galápagos Islands Darwin’s most important observations were made on the G ...
Comp 6b – 6e
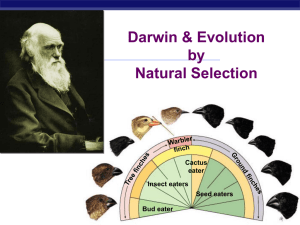
... 9. What is a theory? How are theories developed? Can theories be disproven? 10. Who established the Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection? What was the name of the book he published? What island is famous for its relationship to the theory? 11. How are finches on the Galapagos Islands similar? Ho ...
... 9. What is a theory? How are theories developed? Can theories be disproven? 10. Who established the Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection? What was the name of the book he published? What island is famous for its relationship to the theory? 11. How are finches on the Galapagos Islands similar? Ho ...
Transitional fossil

A transitional fossil is any fossilized remains of a life form that exhibits traits common to both an ancestral group and its derived descendant group. This is especially important where the descendant group is sharply differentiated by gross anatomy and mode of living from the ancestral group. These fossils serve as a reminder that taxonomic divisions are human constructs that have been imposed in hindsight on a continuum of variation. Because of the incompleteness of the fossil record, there is usually no way to know exactly how close a transitional fossil is to the point of divergence. Therefore, it cannot be assumed that transitional fossils are direct ancestors of more recent groups, though they are frequently used as models for such ancestors.In 1859, when Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species was first published, the fossil record was poorly known. Darwin described the perceived lack of transitional fossils as, ""...the most obvious and gravest objection which can be urged against my theory,"" but explained it by relating it to the extreme imperfection of the geological record. He noted the limited collections available at that time, but described the available information as showing patterns that followed from his theory of descent with modification through natural selection. Indeed, Archaeopteryx was discovered just two years later, in 1861, and represents a classic transitional form between dinosaurs and birds. Many more transitional fossils have been discovered since then, and there is now abundant evidence of how all classes of vertebrates are related, much of it in the form of transitional fossils. Specific examples include humans and other primates, tetrapods and fish, and birds and dinosaurs.The term ""missing link"" has been used extensively in popular writings on human evolution to refer to a perceived gap in the hominid evolutionary record. It is most commonly used to refer to any new transitional fossil finds. Scientists, however, do not use the term, as it refers to a pre-evolutionary view of nature.