Elise_Harais_annotated bib #3
... The ear has three sections (inner ear, middle ear, and outer ear) that each complete different jobs that help the brain understand different sounds. There are also three sections of the outer ear, the auricle, the external auditory meatus, and the tympanic membrane. It takes the brain a long process ...
... The ear has three sections (inner ear, middle ear, and outer ear) that each complete different jobs that help the brain understand different sounds. There are also three sections of the outer ear, the auricle, the external auditory meatus, and the tympanic membrane. It takes the brain a long process ...
Sensations vs. Perception
... colors combined in pairs of red-green, blueyellow, and black-white. ...
... colors combined in pairs of red-green, blueyellow, and black-white. ...
`Sound` PowerPoint
... Sound waves travel fastest through solids. The particles in a solid are closer together than in a gas or a liquid. This means vibrations are more easily passed from particle to particle and so sound travels faster. ...
... Sound waves travel fastest through solids. The particles in a solid are closer together than in a gas or a liquid. This means vibrations are more easily passed from particle to particle and so sound travels faster. ...
Systems Neuroscience Auditory system
... Sound stimuli pass through pinna and ext aud canal to strike TM, causing it to vibrate. The ossicular system conducts sound from the TM through the middle ear to the cochlea. The faceplate of the stapes pushes forward on the cochlear fluid ...
... Sound stimuli pass through pinna and ext aud canal to strike TM, causing it to vibrate. The ossicular system conducts sound from the TM through the middle ear to the cochlea. The faceplate of the stapes pushes forward on the cochlear fluid ...
The human ear and its function Wolfgang Kropp 3.1 The human ear
... tired and faint. However, even if we do not register such effects, disturbances of the sleep cycles affect our health. It has been shown that sleep disturbances may lead to higher production of stress hormones. The research in this field is still active. It is still not perfectly clear what time var ...
... tired and faint. However, even if we do not register such effects, disturbances of the sleep cycles affect our health. It has been shown that sleep disturbances may lead to higher production of stress hormones. The research in this field is still active. It is still not perfectly clear what time var ...
1 . If its wavelength is 1.5 cm, what is the frequency of the wave? Will
... Intensity of a sound wave is defined as the amount of sound energy passing through a unit area per second. Loudness is a measure of the response of the ear to the sound. The loudness of a sound is defined by its amplitude. The amplitude of a sound decides its intensity, which in turn is perceived by ...
... Intensity of a sound wave is defined as the amount of sound energy passing through a unit area per second. Loudness is a measure of the response of the ear to the sound. The loudness of a sound is defined by its amplitude. The amplitude of a sound decides its intensity, which in turn is perceived by ...
November 12, 2016 Spider Hearing and Robot
... sound waves, radio waves, visible light waves, earthquake waves, waves of the hand]. Have students define the different types of waves. Penn State’s site on Longitudinal and Transverse Wave Motion has animations for students to explore. Have students sort their examples of waves into the correct typ ...
... sound waves, radio waves, visible light waves, earthquake waves, waves of the hand]. Have students define the different types of waves. Penn State’s site on Longitudinal and Transverse Wave Motion has animations for students to explore. Have students sort their examples of waves into the correct typ ...
Ch11
... – Hair cells at this point are stimulated the most strongly leading to the nerve fibers firing the most strongly at this location. – Position of the peak is a function of frequency. ...
... – Hair cells at this point are stimulated the most strongly leading to the nerve fibers firing the most strongly at this location. – Position of the peak is a function of frequency. ...
Chapter 11: Hearing
... • Békésy determined this in two ways: – Direct observation of the basilar membrane in cadavers. – Building a model of the cochlea using the physical properties of the basilar ...
... • Békésy determined this in two ways: – Direct observation of the basilar membrane in cadavers. – Building a model of the cochlea using the physical properties of the basilar ...
chapter11 (new window)
... – Hair cells at this point are stimulated the most strongly leading to the nerve fibers firing the most strongly at this location. – Position of the peak is a function of frequency. ...
... – Hair cells at this point are stimulated the most strongly leading to the nerve fibers firing the most strongly at this location. – Position of the peak is a function of frequency. ...
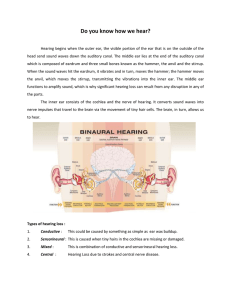
Do you know how we hear
... The inner ear consists of the cochlea and the nerve of hearing. It converts sound waves into nerve impulses that travel to the brain via the movement of tiny hair cells. The brain, in turn, allows us to hear. ...
... The inner ear consists of the cochlea and the nerve of hearing. It converts sound waves into nerve impulses that travel to the brain via the movement of tiny hair cells. The brain, in turn, allows us to hear. ...
Chapter 05
... Color of an object remains the same under different illuminations. However, when context changes the color of an object may look different. ...
... Color of an object remains the same under different illuminations. However, when context changes the color of an object may look different. ...
Chapter 13b Special Senses
... V. Myopia: Nearsightedness- eyeball too long. Correct w/concave lens ...
... V. Myopia: Nearsightedness- eyeball too long. Correct w/concave lens ...
Presentation_LigaAizsila
... SOUND THERAPY Noise plays a major part in people stress levels. The effect of Sound Therapy for the majority of people is to give a built-in defense against the effects of noise-induced stress. Sound healing is one of the best personal improvements. Sound therapy provides electrical energy flow and ...
... SOUND THERAPY Noise plays a major part in people stress levels. The effect of Sound Therapy for the majority of people is to give a built-in defense against the effects of noise-induced stress. Sound healing is one of the best personal improvements. Sound therapy provides electrical energy flow and ...
The Ear
... bony labyrinth • Suspended in its perilymph are two sacs: the saccule and utricle • The saccule extends into the cochlea ...
... bony labyrinth • Suspended in its perilymph are two sacs: the saccule and utricle • The saccule extends into the cochlea ...
What is sound? - Expressions Arts and Entertainment Centre
... The only part of the ear that we can see is the outer ear, which acts like a funnel to collect sound. Some animals have really big ears, or special shaped ears, to help them collect sound. The working of the inner ear is a story of vibrations. The outer ear channels sound waves to the eardrum, which ...
... The only part of the ear that we can see is the outer ear, which acts like a funnel to collect sound. Some animals have really big ears, or special shaped ears, to help them collect sound. The working of the inner ear is a story of vibrations. The outer ear channels sound waves to the eardrum, which ...
A.1.3.1GoodVibrations - Life Science Academy
... 1. Explain how sound travels through the air. 2. Draw a picture of a sound wave. Label both the amplitude and frequency on the picture and describe how these terms relate to how a person would hear this sound wave. 3. Describe the pathway of sound from the time a sound is generated to the time our b ...
... 1. Explain how sound travels through the air. 2. Draw a picture of a sound wave. Label both the amplitude and frequency on the picture and describe how these terms relate to how a person would hear this sound wave. 3. Describe the pathway of sound from the time a sound is generated to the time our b ...
VOM070 EN Noise - Universiteit Leiden
... Sounds are everywhere. They may be soft, such as a whisper or the rustling of corn in the wind, and they may be loud, such as an airplane flying over low. When sounds are unwanted or unintended, they are often referred to as ‘noise’. Sounds are produced by sources of sound (or noise) (such as a devi ...
... Sounds are everywhere. They may be soft, such as a whisper or the rustling of corn in the wind, and they may be loud, such as an airplane flying over low. When sounds are unwanted or unintended, they are often referred to as ‘noise’. Sounds are produced by sources of sound (or noise) (such as a devi ...
Document
... •Outer ear and middle ear functions •Inner ear: the cochlea - Frequency tuning and the cochlear amplifier - Hair cell damage •Neural coding of sound: frequency and timing •Sound localisation: brainstem processing •Auditory cortex ...
... •Outer ear and middle ear functions •Inner ear: the cochlea - Frequency tuning and the cochlear amplifier - Hair cell damage •Neural coding of sound: frequency and timing •Sound localisation: brainstem processing •Auditory cortex ...
Full size lecture slides (PowerPoint file, 7.2 MB)
... •Outer ear and middle ear functions •Inner ear: the cochlea - Frequency tuning and the cochlear amplifier - Hair cell damage •Neural coding of sound: frequency and timing •Sound localisation: brainstem processing •Auditory cortex ...
... •Outer ear and middle ear functions •Inner ear: the cochlea - Frequency tuning and the cochlear amplifier - Hair cell damage •Neural coding of sound: frequency and timing •Sound localisation: brainstem processing •Auditory cortex ...
sensation
... anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea’s oval window. Inner Ear: Innermost part of the ear, containing the cochlea, semicircular canals, and vestibular sacs. Transfers the sound to the brain. ...
... anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea’s oval window. Inner Ear: Innermost part of the ear, containing the cochlea, semicircular canals, and vestibular sacs. Transfers the sound to the brain. ...
Audition Outline - Villanova University
... at higher frequencies by reducing the transmission of low frequencies (again, the muscles play a role here) ...
... at higher frequencies by reducing the transmission of low frequencies (again, the muscles play a role here) ...
Sound

In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as a typically audible mechanical wave of pressure and displacement, through a medium such as air or water. In physiology and psychology, sound is the reception of such waves and their perception by the brain.