Hear for You is a national campaign designed to highlight the
... How Big is that Sound?: Use your sound level meter or real ear system to measure the levels of personal listening devices—participants will gain an understanding of how sound is measured and why it is important. What is Your SNR Hearing Loss?: Use a personal listening device such as a CD player w ...
... How Big is that Sound?: Use your sound level meter or real ear system to measure the levels of personal listening devices—participants will gain an understanding of how sound is measured and why it is important. What is Your SNR Hearing Loss?: Use a personal listening device such as a CD player w ...
The prominent frequency used by these devices seems to be 16KHz
... frequency. This level was set to avoid unpleasant but not necessarily harmful effects, such as nausea and tinnitus. The specified limits for the frequency band in question vary between 75-90dB unweighted. Frequencies up to 20KHz are the most studied and this is the cut-off point between very high fr ...
... frequency. This level was set to avoid unpleasant but not necessarily harmful effects, such as nausea and tinnitus. The specified limits for the frequency band in question vary between 75-90dB unweighted. Frequencies up to 20KHz are the most studied and this is the cut-off point between very high fr ...
middle ear
... • PLACE theory – high-frequency sounds vibrate most near the OPENING of the cochlea, whereas lower-frequency sounds vibrate more at the OTHER end. The brain interprets the pitch based on which nerves are firing. ...
... • PLACE theory – high-frequency sounds vibrate most near the OPENING of the cochlea, whereas lower-frequency sounds vibrate more at the OTHER end. The brain interprets the pitch based on which nerves are firing. ...
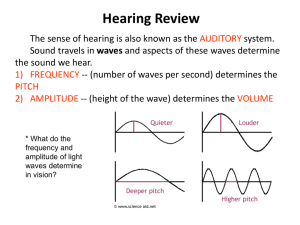
Sound and Pitch (Ch 11)
... – Hair cells at this point are stimulated the most strongly leading to the nerve fibers firing the most strongly at this location – Position of the peak is a function of frequency ...
... – Hair cells at this point are stimulated the most strongly leading to the nerve fibers firing the most strongly at this location – Position of the peak is a function of frequency ...
8L Sound and Hearing
... into electrical signals which are then sent to the brain. decibel – The unit for measuring the loudness of sound (dB). eardrum – The thin membrane in the ear which vibrates when sound reaches it. frequency – The number of waves per second, which shows the pitch of a sound. hertz – The unit of freque ...
... into electrical signals which are then sent to the brain. decibel – The unit for measuring the loudness of sound (dB). eardrum – The thin membrane in the ear which vibrates when sound reaches it. frequency – The number of waves per second, which shows the pitch of a sound. hertz – The unit of freque ...
harmonics
... the slinky-spring toy as a model, the high-pressure condition is analogous to the position where the coils of the spring are pressed close together, and the low-pressure condition is equivalent to the ends of the spring being stretched apart. If we were to draw a picture of these changes we would se ...
... the slinky-spring toy as a model, the high-pressure condition is analogous to the position where the coils of the spring are pressed close together, and the low-pressure condition is equivalent to the ends of the spring being stretched apart. If we were to draw a picture of these changes we would se ...
8L Sound and Hearing
... into electrical signals which are then sent to the brain. decibel – The unit for measuring the loudness of sound (dB). eardrum – The thin membrane in the ear which vibrates when sound reaches it. frequency – The number of waves per second, which shows the pitch of a sound. hertz – The unit of freque ...
... into electrical signals which are then sent to the brain. decibel – The unit for measuring the loudness of sound (dB). eardrum – The thin membrane in the ear which vibrates when sound reaches it. frequency – The number of waves per second, which shows the pitch of a sound. hertz – The unit of freque ...
How to Evaluate Noise Impact
... [2, 3]. The studies of noise at working places basically were only carried out at working places showing an A-weighted sound pressure level noticeably falling below 85 dB(A), thus guarantying that an ear damaging effect of noise could be excluded. In the context of this analysis many new cognitions ...
... [2, 3]. The studies of noise at working places basically were only carried out at working places showing an A-weighted sound pressure level noticeably falling below 85 dB(A), thus guarantying that an ear damaging effect of noise could be excluded. In the context of this analysis many new cognitions ...
ears v. eyes
... Whatever the preferred playlist, our auditory system is a superb piece of engineering, and indeed many auditory researchers have an engineering as well as a neuroscience background. The pressure waves that are sound enter the ears through the curved and lobed pinna, a structure as specific to each i ...
... Whatever the preferred playlist, our auditory system is a superb piece of engineering, and indeed many auditory researchers have an engineering as well as a neuroscience background. The pressure waves that are sound enter the ears through the curved and lobed pinna, a structure as specific to each i ...
WHITE PAPER: ACOUSTICS PRIMER FOR MUSIC SPACES
... All too often we are called in to help with rehearsal rooms that are too loud. Topping the list of concerns in a loud room is the effect on the hearing health of educators and students. According to OSHA standards, 90dB is the maximum acceptable level of noise in a workplace without hearing protecti ...
... All too often we are called in to help with rehearsal rooms that are too loud. Topping the list of concerns in a loud room is the effect on the hearing health of educators and students. According to OSHA standards, 90dB is the maximum acceptable level of noise in a workplace without hearing protecti ...
Chapter 24 Hearing and Noise
... for high mental tasks. Speech interference is measured by words missed. To reduce speech interference, reduce noise or improve the message, the speaker, the transmission system, or the listener. ISE 311 - Ch. 24 ...
... for high mental tasks. Speech interference is measured by words missed. To reduce speech interference, reduce noise or improve the message, the speaker, the transmission system, or the listener. ISE 311 - Ch. 24 ...
The anatomy of the hearing process involves the external, middle
... sound aid and residual hearing to develop oral communication skills. The oral approach emphasizes the use of amplified sound and residual hearing but also may employ lipreading, reading and writing, motokinesthetic speech training (feeling an individual’s face and reproducing breath and voice patter ...
... sound aid and residual hearing to develop oral communication skills. The oral approach emphasizes the use of amplified sound and residual hearing but also may employ lipreading, reading and writing, motokinesthetic speech training (feeling an individual’s face and reproducing breath and voice patter ...
Sound
... loudness are related Loudness is the way humans understand sound intensity. High intensity sounds make your eardrums vibrate further which in turn creates increased hair cell movements making you hear a loud sound instead of quiet one. ...
... loudness are related Loudness is the way humans understand sound intensity. High intensity sounds make your eardrums vibrate further which in turn creates increased hair cell movements making you hear a loud sound instead of quiet one. ...
Slides - UMD Physics
... Periodicity pitch and fundamental tracking (This is not Physics, it’s psychology) An overtone series like 2f, 3f, 4f, … which is missing the fundamental has a pitch equal to the f, 2f, 3f, 4f, … series (the brain “adds” the fundamental for the purpose of ...
... Periodicity pitch and fundamental tracking (This is not Physics, it’s psychology) An overtone series like 2f, 3f, 4f, … which is missing the fundamental has a pitch equal to the f, 2f, 3f, 4f, … series (the brain “adds” the fundamental for the purpose of ...
CHAPTER 19 ACOUSTICS AND THE EAR
... Hearing is the detection and analysis of vibrations generated by objects at some distance from the body transmitted to the ear as pressure waves in air, water, or other medium. Pressure waves in air or any other medium are a form of mechanical energy. Sound cannot travel through a vacuum because it ...
... Hearing is the detection and analysis of vibrations generated by objects at some distance from the body transmitted to the ear as pressure waves in air, water, or other medium. Pressure waves in air or any other medium are a form of mechanical energy. Sound cannot travel through a vacuum because it ...
Document
... • Inner ear reaches its full adult size when the fetus is 20-22 weeks old. • The ears are responsible for keeping the body in balance • Hearing loss is the number one disability in the world. – 76.3% of people loose their hearing at age 19 and over ...
... • Inner ear reaches its full adult size when the fetus is 20-22 weeks old. • The ears are responsible for keeping the body in balance • Hearing loss is the number one disability in the world. – 76.3% of people loose their hearing at age 19 and over ...
Chapter 24 Hearing and Noise
... is probably unaffected by noise except for high mental tasks. Speech interference is measured by words missed. To reduce speech interference, reduce noise or improve the message, the speaker, the transmission system, or the listener. ISE 311 - 20 ...
... is probably unaffected by noise except for high mental tasks. Speech interference is measured by words missed. To reduce speech interference, reduce noise or improve the message, the speaker, the transmission system, or the listener. ISE 311 - 20 ...
Auditory System - PROFESSOR AC BROWN
... a. large area (relatively) so helps to amplify sound b. transmits sound vibrations to middle ear ossicles 3. Conduction by ossicles through middle ear a. ossicular function: sound transmission from tympanic membrane to oval window of the cochlea b. middle ear muscles (tensor tympani and stapedius): ...
... a. large area (relatively) so helps to amplify sound b. transmits sound vibrations to middle ear ossicles 3. Conduction by ossicles through middle ear a. ossicular function: sound transmission from tympanic membrane to oval window of the cochlea b. middle ear muscles (tensor tympani and stapedius): ...
Audition - Peoria Public Schools
... illuminations. However, when context changes the color of an object may look different. ...
... illuminations. However, when context changes the color of an object may look different. ...
Lesson 2.1: Critical Reading Name___________________
... that carries sound waves into the ear. The sound waves travel through the air inside the ear canal to the eardrum. The eardrum is like the head of a drum. It’s a thin membrane stretched tight across the end of the ear canal. The eardrum vibrates when sound waves strike it, and it sends the vibration ...
... that carries sound waves into the ear. The sound waves travel through the air inside the ear canal to the eardrum. The eardrum is like the head of a drum. It’s a thin membrane stretched tight across the end of the ear canal. The eardrum vibrates when sound waves strike it, and it sends the vibration ...
Vocal Formants
... of the waveform. What sample represents the same vowel sound as Sample E? How do you know? ...
... of the waveform. What sample represents the same vowel sound as Sample E? How do you know? ...
! Acoustics For Musicians! Maximilian Crosby! Music Technology!
... Frequency is the number of waves per unit time. For example a very low frequency means that the wave length is very long creating a lower pitch and a high frequency would have a very thin wave length, this creates a high pitched sound. If you look at a sign wave diagram Frequency applies to the X ex ...
... Frequency is the number of waves per unit time. For example a very low frequency means that the wave length is very long creating a lower pitch and a high frequency would have a very thin wave length, this creates a high pitched sound. If you look at a sign wave diagram Frequency applies to the X ex ...
PDF version - Medyna 2017
... The human hearing system is a complex mechanical system intended to capture acoustic waves in air and transmit them to the cochlea responsible for the transduction in a nerve signal. In its basic behaviour sound is collected by the pinna (ear) and conducted through the ear canal to the tympanic memb ...
... The human hearing system is a complex mechanical system intended to capture acoustic waves in air and transmit them to the cochlea responsible for the transduction in a nerve signal. In its basic behaviour sound is collected by the pinna (ear) and conducted through the ear canal to the tympanic memb ...
Part 1: Sound Waves - Science with Mr. Enns
... § At the outer ear, sound waves are focused by the pinna down the ear canal to the eardrum. § The sound waves make the eardrum vibrate. § The vibrations are amplified by the 3 middle ear bones: the hammer, anvil and stirrup. § The stirrup transfers the vibrations to the cochlea within the in ...
... § At the outer ear, sound waves are focused by the pinna down the ear canal to the eardrum. § The sound waves make the eardrum vibrate. § The vibrations are amplified by the 3 middle ear bones: the hammer, anvil and stirrup. § The stirrup transfers the vibrations to the cochlea within the in ...
Sound

In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as a typically audible mechanical wave of pressure and displacement, through a medium such as air or water. In physiology and psychology, sound is the reception of such waves and their perception by the brain.