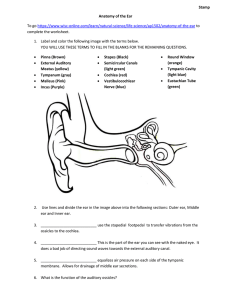
Physiology / sheet 7 The ear consists of three parts : external
... ear will consider it as half octave, one octave or two octaves which means that this is a musical sound. But if it happenes without harmony , then CNS will consider it as noise. ** Female’s and Male’s Voice : Female’s voice : high frequency and low amplitude (e.g : Fairouz) it is called Soprano soun ...
... ear will consider it as half octave, one octave or two octaves which means that this is a musical sound. But if it happenes without harmony , then CNS will consider it as noise. ** Female’s and Male’s Voice : Female’s voice : high frequency and low amplitude (e.g : Fairouz) it is called Soprano soun ...
CHAPTER 3
... One of a set of two receptor organs that detects changes in the tilt of the head. ...
... One of a set of two receptor organs that detects changes in the tilt of the head. ...
Medical Physics:Hearing - IB Objectives
... Ear protects itself from loud noises Reduces tight linkage between ossicles Can be too late if noise is too sudden Ear makes its own sounds Ringing (tinnitis) ...
... Ear protects itself from loud noises Reduces tight linkage between ossicles Can be too late if noise is too sudden Ear makes its own sounds Ringing (tinnitis) ...
Introduction to Tympanometry
... • Sound energy stimulates the TM (eardrum) vibrating the ossicular chain. Vibratory motion of the stapes is transmitted through the oval window into the cochlea. • Cochlea translates the sound energy into meaningful neuronal impulses to the brain. ...
... • Sound energy stimulates the TM (eardrum) vibrating the ossicular chain. Vibratory motion of the stapes is transmitted through the oval window into the cochlea. • Cochlea translates the sound energy into meaningful neuronal impulses to the brain. ...
1. Activation of the receptors by stimuli is called ______.
... b.the location of body parts in relation to the ground and to each other a.size constancy c.bitter, salty, sour, sweet, umami a.we have one canal to sense motion in each of the three planes c.sensory adaptation d.perceptual expectancy b.volume a.iris c.is a perception that does not correspond to rea ...
... b.the location of body parts in relation to the ground and to each other a.size constancy c.bitter, salty, sour, sweet, umami a.we have one canal to sense motion in each of the three planes c.sensory adaptation d.perceptual expectancy b.volume a.iris c.is a perception that does not correspond to rea ...
NOISE AND YOU - LIET-CLMC
... begins at 75 db. – Hearing damage begins at 90 db and can be permanent with one exposure of 120 db or more. – The average decibel levels at Montpelier High School are 7086; where damage to physical, psychological and communicative health begins. ...
... begins at 75 db. – Hearing damage begins at 90 db and can be permanent with one exposure of 120 db or more. – The average decibel levels at Montpelier High School are 7086; where damage to physical, psychological and communicative health begins. ...
Sensation & Perception
... tihng is taht the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae. The rset can be a toatl mses and you can sitll raed it wouthit porbelm. Tihs is bcuseae the huamn mnid deos not raed ervey lteter by istlef, but the ...
... tihng is taht the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae. The rset can be a toatl mses and you can sitll raed it wouthit porbelm. Tihs is bcuseae the huamn mnid deos not raed ervey lteter by istlef, but the ...
chapter 21 sound localization and temporal pattern analysis
... Figure 21.9. An example of sound processing and analysis in the inferior colliculus: Tuning to the direction of a frequency modulated (FM) sweep. The hypothetical neuron on the left receives inputs from 3 cells at a lower level, each of which is tuned to a different frequency (F1, F2 and F3, with F1 ...
... Figure 21.9. An example of sound processing and analysis in the inferior colliculus: Tuning to the direction of a frequency modulated (FM) sweep. The hypothetical neuron on the left receives inputs from 3 cells at a lower level, each of which is tuned to a different frequency (F1, F2 and F3, with F1 ...
Occupational Audiometric Testing 1: Overview
... Daily sound level check On an individual On an instrument ...
... Daily sound level check On an individual On an instrument ...
Hearing and Testing - Intermountain Healthcare
... Brainstem Response (ABR) test. This is especially helpful with infants and small children. Young babies can have this test while they sleep naturally. Sometimes a child will need medicine to sleep so they are completely still during the test. For ABR testing sounds are delivered to the child’s ear. ...
... Brainstem Response (ABR) test. This is especially helpful with infants and small children. Young babies can have this test while they sleep naturally. Sometimes a child will need medicine to sleep so they are completely still during the test. For ABR testing sounds are delivered to the child’s ear. ...
File
... 9. ___________________________ are the sense organs for equilibrium and balance. Hair cells within the canals perceive balance and position in space both aid in balance and have nothing to do with hearing. 10. ___________________________ helps with fluid motion and serves to equalize hydraulic press ...
... 9. ___________________________ are the sense organs for equilibrium and balance. Hair cells within the canals perceive balance and position in space both aid in balance and have nothing to do with hearing. 10. ___________________________ helps with fluid motion and serves to equalize hydraulic press ...
Sound Worksheets
... repeatedly pushes against the air particles next to it. The pressure of the vibrating string causes these air particles to vibrate. The air particles alternately push together and spread apart. This starts waves of vibrations that travel through the air in all directions away from the strings. The v ...
... repeatedly pushes against the air particles next to it. The pressure of the vibrating string causes these air particles to vibrate. The air particles alternately push together and spread apart. This starts waves of vibrations that travel through the air in all directions away from the strings. The v ...
Auditory System
... medium such as air or water in which to move. Sound: vibratory energy caused by movement of physical objects • Rate of vibration is called frequency – What we hear is pitch (high or low) – We hear 20-20,000 Hz (cycles/sec) • Size (intensity) of vibration is amplitude – What we experience is loudness ...
... medium such as air or water in which to move. Sound: vibratory energy caused by movement of physical objects • Rate of vibration is called frequency – What we hear is pitch (high or low) – We hear 20-20,000 Hz (cycles/sec) • Size (intensity) of vibration is amplitude – What we experience is loudness ...
Psych B – Module 9
... • Other sensory messages go through another set of fibers. • The nonpain fibers can close the pain gates to stop the sense of pain. ...
... • Other sensory messages go through another set of fibers. • The nonpain fibers can close the pain gates to stop the sense of pain. ...
Cross Section Human Ear Model (418k PDF file)
... A. outer ear canal – the location in which sound travels from the outer ear to the eardrum B. eardrum – thin piece of skin separating the outer and middle ear that vibrates and amplifies sound waves before entering the middle ear C. hammer (malleus) – the first small bone of the ossicles; responsib ...
... A. outer ear canal – the location in which sound travels from the outer ear to the eardrum B. eardrum – thin piece of skin separating the outer and middle ear that vibrates and amplifies sound waves before entering the middle ear C. hammer (malleus) – the first small bone of the ossicles; responsib ...
HEARING HEARING We use our ears to hear different sounds.
... Sound vibrations go into the ...................................... and along the.......................... The vibrations reach the................................. It vibrates. The vibration of the eardrum moves the ................................................... They make the sound louder. Eq ...
... Sound vibrations go into the ...................................... and along the.......................... The vibrations reach the................................. It vibrates. The vibration of the eardrum moves the ................................................... They make the sound louder. Eq ...
The Inner Ear
... • On the basilar membrane sits the sensory organ of the ear, the organ of Corti which acts as a transducer (converting sound energy into electrical energy) • It is composed of a complex of supporting cells and sensory or hair cells atop the thin basilar membrane • There are some 16,000 -20,000 of th ...
... • On the basilar membrane sits the sensory organ of the ear, the organ of Corti which acts as a transducer (converting sound energy into electrical energy) • It is composed of a complex of supporting cells and sensory or hair cells atop the thin basilar membrane • There are some 16,000 -20,000 of th ...
ER-20 High-Fidelity Earplugs
... loss, depending on the intensity and duration of the noise. Some persons are more susceptible to hearing loss from high-level sound than others. The majority of eight-hour equivalent noise exposures fall between 85 and 95 dB. Many musicians and industrial workers can be adequately protected with as ...
... loss, depending on the intensity and duration of the noise. Some persons are more susceptible to hearing loss from high-level sound than others. The majority of eight-hour equivalent noise exposures fall between 85 and 95 dB. Many musicians and industrial workers can be adequately protected with as ...
open Gail Gudmunssen`s description of the ER20
... response of the ear, and reduce sound evenly across frequencies to preserve the intelligibility of speech and the timbre of music while providing protection from the cumulative effects of noise exposure over a lifetime. Sound heard through the earplugs is clear, but safer. ...
... response of the ear, and reduce sound evenly across frequencies to preserve the intelligibility of speech and the timbre of music while providing protection from the cumulative effects of noise exposure over a lifetime. Sound heard through the earplugs is clear, but safer. ...
Stapedectomy - West Suburban ENT
... stimulated sending a signal to the brain that we hear as sound. When the stapes bone is fixed by otosclerosis, this interrupts the transmission of the vibrations of sound into the cochlea of the inner ear and there is a hearing loss. When a prosthesis replaces the stapes, the sound vibrations are on ...
... stimulated sending a signal to the brain that we hear as sound. When the stapes bone is fixed by otosclerosis, this interrupts the transmission of the vibrations of sound into the cochlea of the inner ear and there is a hearing loss. When a prosthesis replaces the stapes, the sound vibrations are on ...
Sound

In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as a typically audible mechanical wave of pressure and displacement, through a medium such as air or water. In physiology and psychology, sound is the reception of such waves and their perception by the brain.