Sound - WordPress.com
... 5. How does temperature, humidity and pressure affects the speed of sound in air? 6. Can you describe an experiment that shows sound cannot travel in vacuum? What is the name of the ...
... 5. How does temperature, humidity and pressure affects the speed of sound in air? 6. Can you describe an experiment that shows sound cannot travel in vacuum? What is the name of the ...
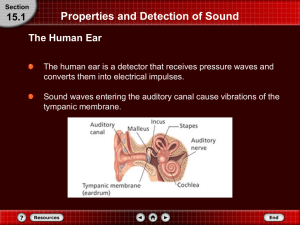
Properties and Detection of Sound
... Perceiving Sound – Loudness Exposure to loud sounds, in the form of noise or music, has been shown to cause the ear to lose its sensitivity, especially to high frequencies. The longer a person is exposed to loud sounds, the greater the effect. A person can recover from short-term exposure in a perio ...
... Perceiving Sound – Loudness Exposure to loud sounds, in the form of noise or music, has been shown to cause the ear to lose its sensitivity, especially to high frequencies. The longer a person is exposed to loud sounds, the greater the effect. A person can recover from short-term exposure in a perio ...
Structure of human ear
... hearing is considered 0 to 10 dB for young healthy human. The amplitude of sound pressure at which a painful sensation is starting is called pain threshold and this is accepted to 140 dB. However unpleasant sensation is starting to occur at 120dB. The difference between the weakest and the strongest ...
... hearing is considered 0 to 10 dB for young healthy human. The amplitude of sound pressure at which a painful sensation is starting is called pain threshold and this is accepted to 140 dB. However unpleasant sensation is starting to occur at 120dB. The difference between the weakest and the strongest ...
Audition
... Localization of Sound 1. Intensity differences 2. Time differences Time differences as small as 1/100,000 of a second can cause us to localize sound. The head acts as a “shadow” or partial sound barrier. ...
... Localization of Sound 1. Intensity differences 2. Time differences Time differences as small as 1/100,000 of a second can cause us to localize sound. The head acts as a “shadow” or partial sound barrier. ...
Slides from Lecture 11/24/2004 (Pascal Wallisch)
... • When it falls, it creates a pressure wave in the air. • If there is no organism with an auditory system present that interprets these oscillations in the air as a sound, it will make no noise. • Even if organisms with auditory systems are present, it will sound different to different organisms (if ...
... • When it falls, it creates a pressure wave in the air. • If there is no organism with an auditory system present that interprets these oscillations in the air as a sound, it will make no noise. • Even if organisms with auditory systems are present, it will sound different to different organisms (if ...
Midterm Exam #3 - Indiana HEP, Astrophysics and Theory
... Check out Figure 6-3 in your text. Higher frequencies will tend to excite the Basilar membrane closer to the oval window while lower frequencies will excite the membrane further down the cochlea/membrance. Therefore the 900 Hz tone will be the one that excites the membrane closer to the oval window. ...
... Check out Figure 6-3 in your text. Higher frequencies will tend to excite the Basilar membrane closer to the oval window while lower frequencies will excite the membrane further down the cochlea/membrance. Therefore the 900 Hz tone will be the one that excites the membrane closer to the oval window. ...
Musical Sounds - SFA Physics and Astronomy
... fundamental. Harmonics are integer multiples of the fundamental. Assignment of harmonic and overtone numbers works like this… ...
... fundamental. Harmonics are integer multiples of the fundamental. Assignment of harmonic and overtone numbers works like this… ...
Psychological Research Methods
... • Oval window: between middle and inner ear, passes vibrations to cochlea ...
... • Oval window: between middle and inner ear, passes vibrations to cochlea ...
Intro - University of Kentucky
... rate of 8 kHz). Let the Matlab function input arguments be the starting frequency and the time interval in seconds for each note in the scale. Let the output be a vector of samples that can be played with Matlab command “soundsc(v,8000)” (where v is the vector output of your function). A scale cov ...
... rate of 8 kHz). Let the Matlab function input arguments be the starting frequency and the time interval in seconds for each note in the scale. Let the output be a vector of samples that can be played with Matlab command “soundsc(v,8000)” (where v is the vector output of your function). A scale cov ...
Spatial Hearing
... The duplex theory suggests that sound localisation is based on interaural time differences at low frequencies and interaural intensity differences at high frequencies. However, for fluctuating high-frequency signals the envelope can carry good timing information. It is now thought that, for most sou ...
... The duplex theory suggests that sound localisation is based on interaural time differences at low frequencies and interaural intensity differences at high frequencies. However, for fluctuating high-frequency signals the envelope can carry good timing information. It is now thought that, for most sou ...
Max Axiom Sound Key
... Why can’t the worker hear Max’s neighbor, Al, talk? (Include a scientific answer not just the object) The worker can’t hear Max’s neighbor, Al, talk because he is wearing protective ear wear. The earmuffs keep the sound wave from hitting the workers ears. ...
... Why can’t the worker hear Max’s neighbor, Al, talk? (Include a scientific answer not just the object) The worker can’t hear Max’s neighbor, Al, talk because he is wearing protective ear wear. The earmuffs keep the sound wave from hitting the workers ears. ...
Chapter 5
... Where AiAi* is the photon flux of a wave, the physical meaning of this relation is that for each photon taken away from the pump beam, two photons are created: one at the signal frequency 1 and one at the idler with 2. This may also be expressed as the Manley-Rowe relation: ...
... Where AiAi* is the photon flux of a wave, the physical meaning of this relation is that for each photon taken away from the pump beam, two photons are created: one at the signal frequency 1 and one at the idler with 2. This may also be expressed as the Manley-Rowe relation: ...
Scoring Guide
... Read the left had side the page and make sure you do the loudness test. Be sure the volume on your computer is set at a normal range. Turn it down if it is uncomfortable or stop. What is the frequency range of your hearing? Answers will vary but should be between 20 and 20,000 Hz. o. Once hearing is ...
... Read the left had side the page and make sure you do the loudness test. Be sure the volume on your computer is set at a normal range. Turn it down if it is uncomfortable or stop. What is the frequency range of your hearing? Answers will vary but should be between 20 and 20,000 Hz. o. Once hearing is ...
SNSDP010 - DPOAE with SmartDPOAE.indd
... comfortably. Even though the patient does not need to be in a relaxed state for this test, it is recommended, in order to minimize noise. To obtain a better recording it is also ...
... comfortably. Even though the patient does not need to be in a relaxed state for this test, it is recommended, in order to minimize noise. To obtain a better recording it is also ...
Interaural Time Difference
... •Direction and rate of change of frequency modulation (FM) •Rate of change in amplitude modulation (AM) •The interval between two sounds •Other more complex sound patterns (not all are tuned to every parameter) ...
... •Direction and rate of change of frequency modulation (FM) •Rate of change in amplitude modulation (AM) •The interval between two sounds •Other more complex sound patterns (not all are tuned to every parameter) ...
mechanical waves, problem set #2
... ∑ Write down the rotational equilibrium condition, τO = 0, for a pole and find T . Neglect the mass of the wire for this part and assume that the wire is horizontal at all points. b) We pluck the wire at one end. How long it takes for the pulse to travel to the other end? c) Wind causes the wire to ...
... ∑ Write down the rotational equilibrium condition, τO = 0, for a pole and find T . Neglect the mass of the wire for this part and assume that the wire is horizontal at all points. b) We pluck the wire at one end. How long it takes for the pulse to travel to the other end? c) Wind causes the wire to ...
“Ears” - Kristen Livingston
... Save them to AUDIO SPRING 2015 folder in lab, where you will find an individual folder with your name containing “LAB ASSIGNMENT 1) Have each sound labeled ...
... Save them to AUDIO SPRING 2015 folder in lab, where you will find an individual folder with your name containing “LAB ASSIGNMENT 1) Have each sound labeled ...
Sound Notes
... • Outer Ear- collects sound waves and directs them into the ear canal • Middle Ear- the three bones act as levers to increase the size of vibration • Inner Ear- converts vibrations into electrical signals for the brain to ...
... • Outer Ear- collects sound waves and directs them into the ear canal • Middle Ear- the three bones act as levers to increase the size of vibration • Inner Ear- converts vibrations into electrical signals for the brain to ...
I. KATZ Chapter 3 PsychoacousticsStudy Guide
... Direct Psychophysical Scaling - We cannot directly measure the ______________ experience of an observer - We can however, quantify these experiences based on ______________ - “direct” psychophysical procedures involve the magnitude or quality of a perception being estimated directly by the observer ...
... Direct Psychophysical Scaling - We cannot directly measure the ______________ experience of an observer - We can however, quantify these experiences based on ______________ - “direct” psychophysical procedures involve the magnitude or quality of a perception being estimated directly by the observer ...
Hearing Loss
... Usable hearing is from 0-120 dB dBs are intensity ratios 20dB is not double of 10dB, but 100 times greater The strongest sounds an average person can hear without pain can be as much as 10 million times greater in intensity than a sound that is barely audible ...
... Usable hearing is from 0-120 dB dBs are intensity ratios 20dB is not double of 10dB, but 100 times greater The strongest sounds an average person can hear without pain can be as much as 10 million times greater in intensity than a sound that is barely audible ...