Hearing part II
... • Rapid movements of the tympanic membrane in response to sound waves result in traveling waves that move in the basilar membrane from base to apex. • Because the basilar fibers are not similar, they increase in length from base to apex (12 folds) and decrease in stiffness from base to apex (100 fol ...
... • Rapid movements of the tympanic membrane in response to sound waves result in traveling waves that move in the basilar membrane from base to apex. • Because the basilar fibers are not similar, they increase in length from base to apex (12 folds) and decrease in stiffness from base to apex (100 fol ...
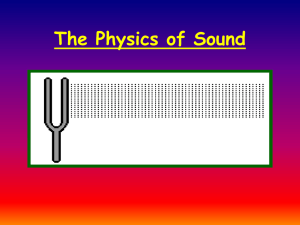
Sound
... more material so it vibrates more slowly and the wavelengths are longer = lower frequency. ...
... more material so it vibrates more slowly and the wavelengths are longer = lower frequency. ...
Chapter 10: Sound - Newark Catholic High School
... Section 1: The Nature of Sound sound waves occur when a vibrating object produces a wave when a radio speaker vibrates, it collides with some of the particles in the air, transferring energy to those particles. they collide with other particles, transferring energy to form a sound wave. Sound waves ...
... Section 1: The Nature of Sound sound waves occur when a vibrating object produces a wave when a radio speaker vibrates, it collides with some of the particles in the air, transferring energy to those particles. they collide with other particles, transferring energy to form a sound wave. Sound waves ...
Y8_Sound_Key Words - Ralph Thoresby School
... Word sheets that include new words from the ‘Focus on:’ pages are available on the Exploring Science website. ...
... Word sheets that include new words from the ‘Focus on:’ pages are available on the Exploring Science website. ...
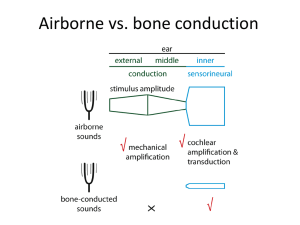
Auditory, Tactile, and Vestibular Systems
... Sound intensity (dB) = 20 log (P1/P2); where P2 is the threshold of hearing ...
... Sound intensity (dB) = 20 log (P1/P2); where P2 is the threshold of hearing ...
The EAR
... 1) The stereocilia are connected together through tip links. The tip links end on gating springs. 2) Fluid movement in one direction puts pressure on gating links, leading to ion channels opening. 3) Fluid movement in opposite direction reduces pressure on gating links, leading to ion channels closi ...
... 1) The stereocilia are connected together through tip links. The tip links end on gating springs. 2) Fluid movement in one direction puts pressure on gating links, leading to ion channels opening. 3) Fluid movement in opposite direction reduces pressure on gating links, leading to ion channels closi ...
Ultrasonics - Mitra.ac.in
... with a air column in it when the ultrasonic waves are passed the Kundt’s tube, the lycopodium powder sprinkled in the tube collects in the form of heaps at the nodal points and is blown off at the antinodal points. This method is used provided that the wavelength is not very small. ...
... with a air column in it when the ultrasonic waves are passed the Kundt’s tube, the lycopodium powder sprinkled in the tube collects in the form of heaps at the nodal points and is blown off at the antinodal points. This method is used provided that the wavelength is not very small. ...
Auditory, Tactile, and Vestibular Systems
... Sound intensity (dB) = 20 log (P1/P2); where P2 is the threshold of hearing ...
... Sound intensity (dB) = 20 log (P1/P2); where P2 is the threshold of hearing ...
03/12 PPT
... Frequency (wavelength/s): The number of sound pulses that travel past a fixed point in a second. Species - Frequency Range Humans 20 - 20,000 Hz Bats 1000-100,000 Hz ...
... Frequency (wavelength/s): The number of sound pulses that travel past a fixed point in a second. Species - Frequency Range Humans 20 - 20,000 Hz Bats 1000-100,000 Hz ...
The Auditory System
... 4. The ossicles: the malleus (hammer), the incus (anvil), & the stapes (stirrup) vibrate. These bones transmit the vibration from the middle ear to the inner ear. ...
... 4. The ossicles: the malleus (hammer), the incus (anvil), & the stapes (stirrup) vibrate. These bones transmit the vibration from the middle ear to the inner ear. ...
Hearing part I
... • Audition or hearing is the sense that allows us to communicate and hence interact with other organisms throughout the world • Sound waves are the adequate stimulus for hearing • The ear is the organ of hearing ...
... • Audition or hearing is the sense that allows us to communicate and hence interact with other organisms throughout the world • Sound waves are the adequate stimulus for hearing • The ear is the organ of hearing ...
Musical Sounds
... musical note is called the fundamental frequency. Any partial that is a whole number multiple of the fundamental frequency is called a ...
... musical note is called the fundamental frequency. Any partial that is a whole number multiple of the fundamental frequency is called a ...
15 SOUND
... with nearby molecules in the air, transferring some of its energy to them. These molecules then collide with other molecules in the air and pass the energy on to them. The energy originally transferred by the vibrating object continues to pass from one molecule to another. This process of collisions ...
... with nearby molecules in the air, transferring some of its energy to them. These molecules then collide with other molecules in the air and pass the energy on to them. The energy originally transferred by the vibrating object continues to pass from one molecule to another. This process of collisions ...
What is an audiogram?
... masking to find out which ear (cochlea) is hearing the test sound. Sound heard in a room reaches both ears at very similar levels. When very young children are tested with sounds played out of a loudspeaker, the sound is assumed to be heard by the “better ear”, regardless of which ear is nearest the ...
... masking to find out which ear (cochlea) is hearing the test sound. Sound heard in a room reaches both ears at very similar levels. When very young children are tested with sounds played out of a loudspeaker, the sound is assumed to be heard by the “better ear”, regardless of which ear is nearest the ...
Sound and Hearing
... The transducers (microphones) on sound level meters measure sound pressure (i.e., N/m2 or Pascals). Pressure needs to be converted to power prior to calculation of the decibel equivalent….i.e., acoustic power = pressure2 Finally, we need to agree upon a Reference value. By convention, we use 20 micr ...
... The transducers (microphones) on sound level meters measure sound pressure (i.e., N/m2 or Pascals). Pressure needs to be converted to power prior to calculation of the decibel equivalent….i.e., acoustic power = pressure2 Finally, we need to agree upon a Reference value. By convention, we use 20 micr ...
Chapter 16 PowerPoint
... Properties of Sound (con’t.) • Doppler effect - the apparent change in frequency as a wave source moves in relation to the listener • When a sound source moves, the frequency of the waves changes because of the motion of the source adds to the motion of the waves. ...
... Properties of Sound (con’t.) • Doppler effect - the apparent change in frequency as a wave source moves in relation to the listener • When a sound source moves, the frequency of the waves changes because of the motion of the source adds to the motion of the waves. ...
Sound - MsCharboneausWiki
... • When the object is moving, the frequency will not be the same to all listeners. • The shift in frequency caused by motion is called the Doppler effect. • You hear the Doppler effect when you hear a police or fire siren coming toward you, then going away from you. ...
... • When the object is moving, the frequency will not be the same to all listeners. • The shift in frequency caused by motion is called the Doppler effect. • You hear the Doppler effect when you hear a police or fire siren coming toward you, then going away from you. ...
Chapter 11 Section 1
... the spiral-shaped structure that is filled with liquid and contains tiny hair cells – When these hairs vibrate they send a signal to the auditory nerve which takes the signal to the brain for decoding and interpretation. – When a person experiences hearing loss is is usually because these hairs have ...
... the spiral-shaped structure that is filled with liquid and contains tiny hair cells – When these hairs vibrate they send a signal to the auditory nerve which takes the signal to the brain for decoding and interpretation. – When a person experiences hearing loss is is usually because these hairs have ...
Hearing
... pitches- explains high pitches 2. Frequency Theory: BM fires off neural messages at different ratesrate of firing accounts for differences in neural transmissions, which result in us hearing low frequencies ...
... pitches- explains high pitches 2. Frequency Theory: BM fires off neural messages at different ratesrate of firing accounts for differences in neural transmissions, which result in us hearing low frequencies ...
Document
... – If the bullet embeds in the pumpkin, how fast will the pumpkin be knocked off the post? – If the post is 1 meter tall, how much time will it take the pumpkin to strike the ground? – How far from the base of the post will the pumpkin strike the ground? – What will be the pumpkin's resultant impact ...
... – If the bullet embeds in the pumpkin, how fast will the pumpkin be knocked off the post? – If the post is 1 meter tall, how much time will it take the pumpkin to strike the ground? – How far from the base of the post will the pumpkin strike the ground? – What will be the pumpkin's resultant impact ...