test - Scioly.org
... 65) Which ashonomical object on this year's list is described as "a spherical collection of hundreds of thousands of stars in the outer halo of the Large Magellanic Cloud that catbe seen from the southern fusmisphere." D) NGC 1846 A) SNR G1.9+0.3 E) SNR 0s09-67.s B) SS Cvgni c) NGC 2440 66) Which as ...
... 65) Which ashonomical object on this year's list is described as "a spherical collection of hundreds of thousands of stars in the outer halo of the Large Magellanic Cloud that catbe seen from the southern fusmisphere." D) NGC 1846 A) SNR G1.9+0.3 E) SNR 0s09-67.s B) SS Cvgni c) NGC 2440 66) Which as ...
Create a HR Diagram - EarthSpaceScience
... Luminosity and Spectral Class. Use circles or shading to correctly label the Main Sequence, Giants, and Dwarfs. Then use your diagram to answer the questions. ...
... Luminosity and Spectral Class. Use circles or shading to correctly label the Main Sequence, Giants, and Dwarfs. Then use your diagram to answer the questions. ...
Stages - A Summary - University of Dayton
... dwarfs) will be dim and cool and, as they grow older, will only grow dimmer and cooler, ultimately becoming black dwarfs (see STAGE 14). Astronomers have identified several brown dwarf candidates, and even have evidence for the presence of Jupiter-like planets in orbit around several nearby stars. R ...
... dwarfs) will be dim and cool and, as they grow older, will only grow dimmer and cooler, ultimately becoming black dwarfs (see STAGE 14). Astronomers have identified several brown dwarf candidates, and even have evidence for the presence of Jupiter-like planets in orbit around several nearby stars. R ...
Characteristics of Stars
... f. shines brightly in the center of a distant galaxy because of the friction of material spiraling around it ...
... f. shines brightly in the center of a distant galaxy because of the friction of material spiraling around it ...
Lec9_2D
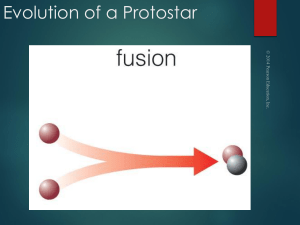
... two sources of energy, it becomes extremely bright. • The energy from this fusion (the radiation pressure) literally blows up (expands) the outer parts of the star many, many times. The surface of the star is moved far, far away from where the fusion is occurring, and so becomes cool. The star is no ...
... two sources of energy, it becomes extremely bright. • The energy from this fusion (the radiation pressure) literally blows up (expands) the outer parts of the star many, many times. The surface of the star is moved far, far away from where the fusion is occurring, and so becomes cool. The star is no ...
NAME_______________________________________
... ____ 10. Stars are assigned a spectral type, with M being the hottest stars. _________________________ ...
... ____ 10. Stars are assigned a spectral type, with M being the hottest stars. _________________________ ...
Stellar Properties
... 2. Star A and B have same luminosity. If star A is 4 times closer to Earth then star B, then _____ to earthly viewer.: a=A is 4 x brighter, b=B is 4x brighter, c=A is 16 times brighter d=B is 16 times brighter, e=A is 64x brighter 3. Apparent magnitude is measure of: a=light output, b=light received ...
... 2. Star A and B have same luminosity. If star A is 4 times closer to Earth then star B, then _____ to earthly viewer.: a=A is 4 x brighter, b=B is 4x brighter, c=A is 16 times brighter d=B is 16 times brighter, e=A is 64x brighter 3. Apparent magnitude is measure of: a=light output, b=light received ...
New York City Disciple Code - EarthSpaceScience-Keller
... A correct range within 10² of luminosity And the correct spectral class are included for each star ...
... A correct range within 10² of luminosity And the correct spectral class are included for each star ...
Stars Notes
... 4.b – Students know that the Sun is one of many stars in the Milky Way galaxy and that stars may differ in size, temperature and color 4.d – Students know that stars are the source of light for all bright objects in outer space and that the Moon and planets shine by reflected sunlight, not by thei ...
... 4.b – Students know that the Sun is one of many stars in the Milky Way galaxy and that stars may differ in size, temperature and color 4.d – Students know that stars are the source of light for all bright objects in outer space and that the Moon and planets shine by reflected sunlight, not by thei ...
The correct answers are written in bold, italic and underlined. The
... 15. Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen in which the nucleus contains one proton and two neutrons. How much more massive is this nucleus than that of ordinary hydrogen? • The same mass because this nucleus is still hydrogen • Three times as massive • Twice as massive 16. Electron transitions b ...
... 15. Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen in which the nucleus contains one proton and two neutrons. How much more massive is this nucleus than that of ordinary hydrogen? • The same mass because this nucleus is still hydrogen • Three times as massive • Twice as massive 16. Electron transitions b ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER 1
... B. Then they go through a sequence of situations where the core is contracting and heating up when no fusion is going on inside it and then stops contracting when the next type of fusion begins. Meanwhile the outer layers expand and cool while the core contracts. They contract and heat up when the c ...
... B. Then they go through a sequence of situations where the core is contracting and heating up when no fusion is going on inside it and then stops contracting when the next type of fusion begins. Meanwhile the outer layers expand and cool while the core contracts. They contract and heat up when the c ...
The Evolution of Stars - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... keeps us safely planted here on Earth, but it is more that just that. Gravity, or gravitation, is the natural phenomenon by which all objects with mass attract other objects. Without gravity the universe would be a very different place. ...
... keeps us safely planted here on Earth, but it is more that just that. Gravity, or gravitation, is the natural phenomenon by which all objects with mass attract other objects. Without gravity the universe would be a very different place. ...
LL_starsCatalog
... Note that each Set method is overloaded so that they may be called with numeric or character parameters. Your program does not have to call both of these but it is good to include them both so that they are available to be used. The application must use an unordered linked list to hold all the stars ...
... Note that each Set method is overloaded so that they may be called with numeric or character parameters. Your program does not have to call both of these but it is good to include them both so that they are available to be used. The application must use an unordered linked list to hold all the stars ...
Stars
... • They look small because they are a long way away, but in fact many are bigger and brighter than our Sun. • The heat of the star is made in the center by nuclear fusion reactions. • There are lots of different colours and sizes of stars. ...
... • They look small because they are a long way away, but in fact many are bigger and brighter than our Sun. • The heat of the star is made in the center by nuclear fusion reactions. • There are lots of different colours and sizes of stars. ...
Deep Space Mystery Note Form 3
... indicating that it was the 367th[nb 1] supernova SN is the prefix for them. found in 2005.[40][41] Historical supernovae are known simply by the year they occurred: SN 185, SN 1006, SN 1054, SN 1572 (Tycho's Nova) and SN 1604 (Kepler's Star). Since 1885 the letter notation has been used, even if t ...
... indicating that it was the 367th[nb 1] supernova SN is the prefix for them. found in 2005.[40][41] Historical supernovae are known simply by the year they occurred: SN 185, SN 1006, SN 1054, SN 1572 (Tycho's Nova) and SN 1604 (Kepler's Star). Since 1885 the letter notation has been used, even if t ...
How Far To That Star?
... to find the distance to a relatively nearby star. (less than 250 parsecs, or 815 LY) It uses Triangulation to find the distance. The Standard Candle Method compares Apparent magnitude to Absolute Magnitude to find the distance to more distant stars and even ...
... to find the distance to a relatively nearby star. (less than 250 parsecs, or 815 LY) It uses Triangulation to find the distance. The Standard Candle Method compares Apparent magnitude to Absolute Magnitude to find the distance to more distant stars and even ...
Stellar Evolution (Powerpoint) 17
... fusion at once. What a star normally takes billions of years to burn, this star burns all at once. BIG explosion! ...
... fusion at once. What a star normally takes billions of years to burn, this star burns all at once. BIG explosion! ...
Bellringer - Madison County Schools
... kilometers times 4.5. That number won’t even fit in your calculator without the use of Scientific Notation. A light-year is a unit of DISTANCE, not time. You could also measure distance on Earth in terms of time. For example, if it takes you one hour to ride your bike to the mall, you could say the ...
... kilometers times 4.5. That number won’t even fit in your calculator without the use of Scientific Notation. A light-year is a unit of DISTANCE, not time. You could also measure distance on Earth in terms of time. For example, if it takes you one hour to ride your bike to the mall, you could say the ...
Lives of Stars - Madison County Schools
... Our solar system formed from this type of scenario. All of the material for everything in this solar system came from a supernova that exploded in this area of the Milky Way. ...
... Our solar system formed from this type of scenario. All of the material for everything in this solar system came from a supernova that exploded in this area of the Milky Way. ...
Birth and Death of Stars
... • After the supergiant stage, massive stars contract with a gravitational force much greater than low mass stars. The high pressures and temperatures that result causes nuclear fusion to begin again. This time the core fuses into heavier elements such as oxygen, magnesium, or silicon. Fusion continu ...
... • After the supergiant stage, massive stars contract with a gravitational force much greater than low mass stars. The high pressures and temperatures that result causes nuclear fusion to begin again. This time the core fuses into heavier elements such as oxygen, magnesium, or silicon. Fusion continu ...
Star of Bethlehem

In Christian tradition, the Star of Bethlehem, also called the Christmas Star, revealed the birth of Jesus to the Biblical Magi, and later led them to Bethlehem. The star appears only in the nativity story of the Gospel of Matthew, where astrologers from the east are inspired by the star to travel to Jerusalem. There they meet King Herod of Judea, and ask where the king of the Jews had been born. Herod, following a verse from the Book of Micah interpreted as a prophecy, directs them to Bethlehem, to the south of Jerusalem. The star leads them to Jesus' home in the town, where they worship him and give him gifts. The wise men are then given a divine warning not to return to Herod so they return home by a different route.Many Christians see the star as a miraculous sign to mark the birth of the Christ (or messiah). Some theologians claimed that the star fulfilled a prophecy, known as the Star Prophecy. Astronomers have made several attempts to link the star to unusual astronomical events, such as a conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn, a comet or a supernova.Many modern scholars do not consider the story to be describing a historical event but a pious fiction created by the author of the Gospel of Matthew.The subject is a favorite at planetarium shows during the Christmas season, although the Biblical account describes Jesus with a broader Greek word, which can mean either ""infant"" or ""child"" (paidon), rather than the more specific word for infant (brephos), possibly implying that some time has passed since the birth. The visit is traditionally celebrated on Epiphany (January 6) in Western Christianity.