Participant Handout - Math Machines Home
... very powerful and it is relatively close--a mere 425 light years away. There are countless other stars in the sky which are actually more luminous than Betelgeuse, but which appear quite dim because they are very far away. There are also many nearby stars which appear relatively bright in our sky de ...
... very powerful and it is relatively close--a mere 425 light years away. There are countless other stars in the sky which are actually more luminous than Betelgeuse, but which appear quite dim because they are very far away. There are also many nearby stars which appear relatively bright in our sky de ...
Stellar Evolution and the Herzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Magnitudes: backwards (logarithmic) scale used for brightness. Negative numbers are brighter than positive! Each magnitude corresponds to a factor of about 2.51 A difference of 5 magnitudes corresponds exactly to a factor of 100 in brightness Apparent “visual” magnitudes: How bright a star appears t ...
... Magnitudes: backwards (logarithmic) scale used for brightness. Negative numbers are brighter than positive! Each magnitude corresponds to a factor of about 2.51 A difference of 5 magnitudes corresponds exactly to a factor of 100 in brightness Apparent “visual” magnitudes: How bright a star appears t ...
AST 207 Homework 5 Due 14 October 2011
... 2. Life on Deneb. Here you will find out what it means to live near a giant like Deneb. Recall that the luminosity of a star, where T is its temperature and R is its radius. Star ...
... 2. Life on Deneb. Here you will find out what it means to live near a giant like Deneb. Recall that the luminosity of a star, where T is its temperature and R is its radius. Star ...
Homework 1 SOLUTIONS - University of Colorado Boulder
... 1. All stars are called “fixed stars” because they are all at fixed celestial locations. This means that at any one specific location on Earth they have fixed rising and setting locations (setting locations ALWAYS symmetrical to rising locations around the meridian) and a fixed angle with respect to ...
... 1. All stars are called “fixed stars” because they are all at fixed celestial locations. This means that at any one specific location on Earth they have fixed rising and setting locations (setting locations ALWAYS symmetrical to rising locations around the meridian) and a fixed angle with respect to ...
Star Spectra - Renton School District
... High atmospheric pressures in a star cause spectral lines to be broadened, or “smeared out.” Giant stars, which have relatively low atmospheric pressures, are characterized by narrow spectral lines. ...
... High atmospheric pressures in a star cause spectral lines to be broadened, or “smeared out.” Giant stars, which have relatively low atmospheric pressures, are characterized by narrow spectral lines. ...
HR Diagram of One Solar Mass Evolution
... • In center of frame is 200,000K temp white dwarf • Mass loss from solar wind & esp. dust in atmosphere • 8 Solar masses can become 5 in 500,000 years ...
... • In center of frame is 200,000K temp white dwarf • Mass loss from solar wind & esp. dust in atmosphere • 8 Solar masses can become 5 in 500,000 years ...
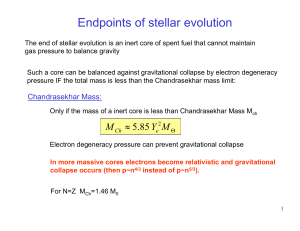
Endpoints of stellar evolution
... Type II: collapse of Fe core in a normal massive star (H envelope) Type I: ...
... Type II: collapse of Fe core in a normal massive star (H envelope) Type I: ...
Notes
... The star will settle into a hydrostatic and thermal equilibrium, where cooling is balanced by nuclear energy generation and there is no time dependence of any state variables. ...
... The star will settle into a hydrostatic and thermal equilibrium, where cooling is balanced by nuclear energy generation and there is no time dependence of any state variables. ...
Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics
... – Length of the waves determine the characteristics of the electromagnetic radiation. – The types of electromagnetic radiation can be arranged in a continuum called the Electromagnetic Spectrum (longest wavelengths at one end and shortest wavelengths at the other end) ...
... – Length of the waves determine the characteristics of the electromagnetic radiation. – The types of electromagnetic radiation can be arranged in a continuum called the Electromagnetic Spectrum (longest wavelengths at one end and shortest wavelengths at the other end) ...
Our Sun, Sol - Hobbs High School
... spinning neutron star with jets of particles moving almost at the speed of light streaming out above its magnetic poles. • These jets produce very powerful beams of light. • The precise periods of pulsars make them useful tools to astronomers. ...
... spinning neutron star with jets of particles moving almost at the speed of light streaming out above its magnetic poles. • These jets produce very powerful beams of light. • The precise periods of pulsars make them useful tools to astronomers. ...
class17
... How would the apparent brightness of Alpha Centauri change if it were three times farther away? ...
... How would the apparent brightness of Alpha Centauri change if it were three times farther away? ...
Lesson 4, Stars
... viewed from two locations is called parallax. Astronomers use parallax to find the distance ...
... viewed from two locations is called parallax. Astronomers use parallax to find the distance ...
STARS Chapter 8 Section 1
... Astronomers use units called light years to measure the distance of stars A light-year is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in a year Proxima Centauri, is the closest star to the sun. 9,461,000,000,000 trillion km or ...
... Astronomers use units called light years to measure the distance of stars A light-year is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in a year Proxima Centauri, is the closest star to the sun. 9,461,000,000,000 trillion km or ...
Stellar Temperature & Luminosity Student Page Purpose
... 1. If the peak in the black body curve of a star is at a longer wavelength than the peak wavelength for our Sun, how does the surface temperature of that star compare to our Sun’s surface temperature? 2. Which of the following events will have the largest effect on a star’s brightness — doubling its ...
... 1. If the peak in the black body curve of a star is at a longer wavelength than the peak wavelength for our Sun, how does the surface temperature of that star compare to our Sun’s surface temperature? 2. Which of the following events will have the largest effect on a star’s brightness — doubling its ...
Stargazing
... 9. Which would probably generate more light, a star that burns hydrogen quickly or a star that burns hydrogen slowly? ...
... 9. Which would probably generate more light, a star that burns hydrogen quickly or a star that burns hydrogen slowly? ...
Circumstellar Zones
... The top panel simulation displays a visualization of a star and its planets looking down onto the plane of the solar system. The habitable zone is displayed for the particular star being simulated. One can click and drag either toward the star or away from it to change the scale being displayed. ...
... The top panel simulation displays a visualization of a star and its planets looking down onto the plane of the solar system. The habitable zone is displayed for the particular star being simulated. One can click and drag either toward the star or away from it to change the scale being displayed. ...
Star Types
... - Red Giant stars are very large, cool and quite bright. Ex. Betelgeuse is 100,000 times more luminous than the Sun but is only 3,500K on the surface. It’s radius is 1,000 times that of the Sun. ...
... - Red Giant stars are very large, cool and quite bright. Ex. Betelgeuse is 100,000 times more luminous than the Sun but is only 3,500K on the surface. It’s radius is 1,000 times that of the Sun. ...
Classifying Stars - Concord Academy Boyne
... How is a Star Formed? Stars begin their lives as nebula ...
... How is a Star Formed? Stars begin their lives as nebula ...
FINAL EXAM Name: ASTRONOMY II - 79202 Spring 1995
... Star #1 is twice as hot at its surface than star #2. Star #1 is twice as large as star #2. Star #1 is four times hotter at its surface than star #2. Star #1 is four times larger than star #2. ...
... Star #1 is twice as hot at its surface than star #2. Star #1 is twice as large as star #2. Star #1 is four times hotter at its surface than star #2. Star #1 is four times larger than star #2. ...
Star of Bethlehem

In Christian tradition, the Star of Bethlehem, also called the Christmas Star, revealed the birth of Jesus to the Biblical Magi, and later led them to Bethlehem. The star appears only in the nativity story of the Gospel of Matthew, where astrologers from the east are inspired by the star to travel to Jerusalem. There they meet King Herod of Judea, and ask where the king of the Jews had been born. Herod, following a verse from the Book of Micah interpreted as a prophecy, directs them to Bethlehem, to the south of Jerusalem. The star leads them to Jesus' home in the town, where they worship him and give him gifts. The wise men are then given a divine warning not to return to Herod so they return home by a different route.Many Christians see the star as a miraculous sign to mark the birth of the Christ (or messiah). Some theologians claimed that the star fulfilled a prophecy, known as the Star Prophecy. Astronomers have made several attempts to link the star to unusual astronomical events, such as a conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn, a comet or a supernova.Many modern scholars do not consider the story to be describing a historical event but a pious fiction created by the author of the Gospel of Matthew.The subject is a favorite at planetarium shows during the Christmas season, although the Biblical account describes Jesus with a broader Greek word, which can mean either ""infant"" or ""child"" (paidon), rather than the more specific word for infant (brephos), possibly implying that some time has passed since the birth. The visit is traditionally celebrated on Epiphany (January 6) in Western Christianity.