A Universe of Dwarfs and Giants
... classed as proper stars. A star must produce its own light. These objects are either very dim or even black when looked at in visible light. The little they radiate is mainly infra-red light. Brown dwarfs can be thought of as failed stars; much bigger than a planet but just not big enough to make it ...
... classed as proper stars. A star must produce its own light. These objects are either very dim or even black when looked at in visible light. The little they radiate is mainly infra-red light. Brown dwarfs can be thought of as failed stars; much bigger than a planet but just not big enough to make it ...
PHYSICS 1500 - ASTRONOMY TOTAL: 100 marks Section A Please
... formation of new stars and galaxies. (d) the minimum density of matter and energy the Universe may have if it is open and infinite. (e) the maximum density of matter and energy the Universe may have if it is open and infinite. Question 20 Why do we think there was a slight imbalance between matter a ...
... formation of new stars and galaxies. (d) the minimum density of matter and energy the Universe may have if it is open and infinite. (e) the maximum density of matter and energy the Universe may have if it is open and infinite. Question 20 Why do we think there was a slight imbalance between matter a ...
Lecture 24 - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... from apparent brightness and distance (d). Apparent magnitude (old way). We can see about 1,000 stars in Northern Hemisphere with naked eye. Hipparchus rated them from 1 to 6. A '1' is 2.52 x brighter than a '2', etc. Range in brightness from the sun at '-26' magnitude to the faintest objects seen a ...
... from apparent brightness and distance (d). Apparent magnitude (old way). We can see about 1,000 stars in Northern Hemisphere with naked eye. Hipparchus rated them from 1 to 6. A '1' is 2.52 x brighter than a '2', etc. Range in brightness from the sun at '-26' magnitude to the faintest objects seen a ...
TY Course Day 2 Friday Constellations v1
... For the purpose of determining the constellations in contact with the ecliptic, the constellation boundaries as defined by the International Astronomical Union in 1930 are used. For example, the Sun enters the IAU boundary of Aries on April 19. Needless to say, the IAU defined the constellation bou ...
... For the purpose of determining the constellations in contact with the ecliptic, the constellation boundaries as defined by the International Astronomical Union in 1930 are used. For example, the Sun enters the IAU boundary of Aries on April 19. Needless to say, the IAU defined the constellation bou ...
Core Theme 2: Constellations
... For the purpose of determining the constellations in contact with the ecliptic, the constellation boundaries as defined by the International Astronomical Union in 1930 are used. For example, the Sun enters the IAU boundary of Aries on April 19. Needless to say, the IAU defined the constellation bou ...
... For the purpose of determining the constellations in contact with the ecliptic, the constellation boundaries as defined by the International Astronomical Union in 1930 are used. For example, the Sun enters the IAU boundary of Aries on April 19. Needless to say, the IAU defined the constellation bou ...
ppt
... 0K = -273 C (Absolute Zero) The light emitted by a hot plasma always has a characteristic spectrum – it's intensity (or brightness) is different at different energies (or frequencies, wavelengths, colours). Stars are almost blackbodies (i.e. they emit and absorb light equally) and so have a characte ...
... 0K = -273 C (Absolute Zero) The light emitted by a hot plasma always has a characteristic spectrum – it's intensity (or brightness) is different at different energies (or frequencies, wavelengths, colours). Stars are almost blackbodies (i.e. they emit and absorb light equally) and so have a characte ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... directly observable (such as temperature and some motions), while others (such as mass) require inference from other data. Of these characteristics, the most important are color, temperature, mass, and luminosity. Although most appear white to our eyes, most stars have a predominant color that is de ...
... directly observable (such as temperature and some motions), while others (such as mass) require inference from other data. Of these characteristics, the most important are color, temperature, mass, and luminosity. Although most appear white to our eyes, most stars have a predominant color that is de ...
BENNETT, Constraints on the Orbital Motion of OGLE-2006
... – Slight dependence on distance to the source star when converting to physical from Einstein Radii units ...
... – Slight dependence on distance to the source star when converting to physical from Einstein Radii units ...
Basic data of CoRoT-Exo-2b - tls
... TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
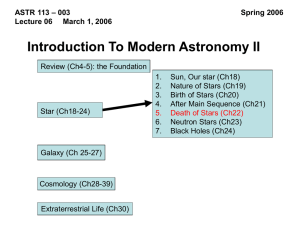
Stellar Evolution: the Death of Stars
... 1. What kinds of nuclear reactions occur within a star like the Sun as it ages? 2. Where did the carbon atoms in our bodies come from? 3. What is a planetary nebula, and what does it have to do with planets? 4. What is a white dwarf star? 5. Why do high-mass stars go through more evolutionary stages ...
... 1. What kinds of nuclear reactions occur within a star like the Sun as it ages? 2. Where did the carbon atoms in our bodies come from? 3. What is a planetary nebula, and what does it have to do with planets? 4. What is a white dwarf star? 5. Why do high-mass stars go through more evolutionary stages ...
Unit 3 - Lesson 8.9 Life of Stars Challenge
... These large stars have diameters between 10X and 100X that of the Sun. If the star is a Super Giant, their diameters can be up to 1000X of the Sun. A late-life stage sub-species star that emits a beam of electromagnetic radiation that can be only seen when the beam of emission is pointing toward the ...
... These large stars have diameters between 10X and 100X that of the Sun. If the star is a Super Giant, their diameters can be up to 1000X of the Sun. A late-life stage sub-species star that emits a beam of electromagnetic radiation that can be only seen when the beam of emission is pointing toward the ...
Lab 5: Searching for Extra-Solar Planets
... would appear if four equally spaced observations were made in one complete cycle of the star’s motion. (Be sure to show the direction of the observer in your sketch.) 2. By measuring wavelength shifts in the star’s spectrum, astronomers can determine the orbital parameters of the star and planet sys ...
... would appear if four equally spaced observations were made in one complete cycle of the star’s motion. (Be sure to show the direction of the observer in your sketch.) 2. By measuring wavelength shifts in the star’s spectrum, astronomers can determine the orbital parameters of the star and planet sys ...
The winter sky over Bosham
... the name itself is derived from the Arabic word ‘rijl’. Both are about ten million years old and near the end of their lives, but can you see a difference in colour? Rigel is a blue/white star roughly twice as hot as the Sun, whereas Betelgeuse is orange-red, showing it to be much cooler. Both stars ...
... the name itself is derived from the Arabic word ‘rijl’. Both are about ten million years old and near the end of their lives, but can you see a difference in colour? Rigel is a blue/white star roughly twice as hot as the Sun, whereas Betelgeuse is orange-red, showing it to be much cooler. Both stars ...
Chapter 29 Review
... As a star ages, its internal composition changes as nuclear reactions in the star’s core convert one element into another. 1. True 2. False ...
... As a star ages, its internal composition changes as nuclear reactions in the star’s core convert one element into another. 1. True 2. False ...
Star Birth
... • When thermonuclear reactions start at the center of a protostar, we say a new star is born. ...
... • When thermonuclear reactions start at the center of a protostar, we say a new star is born. ...
Astronomy 15 - Problem Set Number 4 1) Suppose one were to
... b) A star is found to have a displacement on the plates of almost half a pixel - 10 microns due to parallax, and simultaneously has a yearly displacement of 20 microns due to proper motion. Find its annual proper motion, its distance, and its transverse velocity. c) For this same star, a heliocentri ...
... b) A star is found to have a displacement on the plates of almost half a pixel - 10 microns due to parallax, and simultaneously has a yearly displacement of 20 microns due to proper motion. Find its annual proper motion, its distance, and its transverse velocity. c) For this same star, a heliocentri ...
d = 1 / p
... To do this in practice, first find the energy per second emitted by each unit of surface area, ε, using the relation given in class (ε = σ T 4). The luminosity of a star is given by the power emitted per unit area times its surface area (L = ε S); for a sphere, S = 4π R2, so L = ε S = (σ T4)(4π R2). ...
... To do this in practice, first find the energy per second emitted by each unit of surface area, ε, using the relation given in class (ε = σ T 4). The luminosity of a star is given by the power emitted per unit area times its surface area (L = ε S); for a sphere, S = 4π R2, so L = ε S = (σ T4)(4π R2). ...
d = 1 / p
... Expressing this in terms of radius, R = (L / (4π σ T )) . Never confuse the radius of the star R with the distance to the star d! Although both are measures of length that appear in our equations squared and multiplied by 4π, they are extremely different! In addition, keep in mind that the Stefan-Bo ...
... Expressing this in terms of radius, R = (L / (4π σ T )) . Never confuse the radius of the star R with the distance to the star d! Although both are measures of length that appear in our equations squared and multiplied by 4π, they are extremely different! In addition, keep in mind that the Stefan-Bo ...
Endpoints of Stellar Evolution
... • The result of a supernova that, according to Chinese and Japanese chronicles, exploded in 1054. Despite a distance of about 7,000 light-years, the supernova was brighter than Venus for weeks before fading from view after nearly two years. Interestingly, almost no European records of the event hav ...
... • The result of a supernova that, according to Chinese and Japanese chronicles, exploded in 1054. Despite a distance of about 7,000 light-years, the supernova was brighter than Venus for weeks before fading from view after nearly two years. Interestingly, almost no European records of the event hav ...
Star Formation, HR Diagram, and the Main Sequence (Professor
... Radial velocities are measured using the Doppler Shift of the star's spectrum: •Star moving towards Earth: Blueshift •Star moving away from Earth: Redshift •Star moving across our line of sight: No Shift In all cases, the Radial Velocity is Independent of Distance. ...
... Radial velocities are measured using the Doppler Shift of the star's spectrum: •Star moving towards Earth: Blueshift •Star moving away from Earth: Redshift •Star moving across our line of sight: No Shift In all cases, the Radial Velocity is Independent of Distance. ...
Supernova - Mid-Pacific Institute
... supported by the release of nuclear energy. If the star is particularly massive, then its core will collapse and in so doing will release a huge amount of energy. This will cause a blast wave that ejects the star's envelope into interstellar space. ...
... supported by the release of nuclear energy. If the star is particularly massive, then its core will collapse and in so doing will release a huge amount of energy. This will cause a blast wave that ejects the star's envelope into interstellar space. ...
Star of Bethlehem

In Christian tradition, the Star of Bethlehem, also called the Christmas Star, revealed the birth of Jesus to the Biblical Magi, and later led them to Bethlehem. The star appears only in the nativity story of the Gospel of Matthew, where astrologers from the east are inspired by the star to travel to Jerusalem. There they meet King Herod of Judea, and ask where the king of the Jews had been born. Herod, following a verse from the Book of Micah interpreted as a prophecy, directs them to Bethlehem, to the south of Jerusalem. The star leads them to Jesus' home in the town, where they worship him and give him gifts. The wise men are then given a divine warning not to return to Herod so they return home by a different route.Many Christians see the star as a miraculous sign to mark the birth of the Christ (or messiah). Some theologians claimed that the star fulfilled a prophecy, known as the Star Prophecy. Astronomers have made several attempts to link the star to unusual astronomical events, such as a conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn, a comet or a supernova.Many modern scholars do not consider the story to be describing a historical event but a pious fiction created by the author of the Gospel of Matthew.The subject is a favorite at planetarium shows during the Christmas season, although the Biblical account describes Jesus with a broader Greek word, which can mean either ""infant"" or ""child"" (paidon), rather than the more specific word for infant (brephos), possibly implying that some time has passed since the birth. The visit is traditionally celebrated on Epiphany (January 6) in Western Christianity.