Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • About half of stars orbit a companion • 3 classes of binaries ...
... • About half of stars orbit a companion • 3 classes of binaries ...
Ay123 Homework 1 Solutions
... form p(r) = pc × f (r/R), where f (x) is a function you will determine. What is the dependence of the central pressure pc in terms of M and R?. Express pc numerically with M and R in solar units. First we need the mass enclosed within radius r: ...
... form p(r) = pc × f (r/R), where f (x) is a function you will determine. What is the dependence of the central pressure pc in terms of M and R?. Express pc numerically with M and R in solar units. First we need the mass enclosed within radius r: ...
Unit 8 Chapter 30
... They are near the end of their lives as stars. If it flares up again, it becomes a Nova (new star) and can burn for a while longer. Super Nova: The center core of huge stars is mainly made up of heavy metals (U, Pb, Fe, Ni). When all of the fuel is used up the collapse of these metals is very rapid. ...
... They are near the end of their lives as stars. If it flares up again, it becomes a Nova (new star) and can burn for a while longer. Super Nova: The center core of huge stars is mainly made up of heavy metals (U, Pb, Fe, Ni). When all of the fuel is used up the collapse of these metals is very rapid. ...
Exam #2 Solutions
... to assist your memory. Points to mention The Bright Stars are All more luminous than the Sun. Either hotter main sequence stars or cooler giants. The hotter main sequence stars are mostly B and A stars with temperatures around 15,000 K and luminosities between 50 and 5,000 solar luminosities, ...
... to assist your memory. Points to mention The Bright Stars are All more luminous than the Sun. Either hotter main sequence stars or cooler giants. The hotter main sequence stars are mostly B and A stars with temperatures around 15,000 K and luminosities between 50 and 5,000 solar luminosities, ...
Lab 2: The Planisphere
... distortion, constellations in the sky will not appear as they do on the planisphere, but the planisphere can help us identify bright stars and give us a general idea of where to look for other stars. It's also very useful in figuring out when certain star will rise or set. The best way to get comfor ...
... distortion, constellations in the sky will not appear as they do on the planisphere, but the planisphere can help us identify bright stars and give us a general idea of where to look for other stars. It's also very useful in figuring out when certain star will rise or set. The best way to get comfor ...
SECTION 30.2 Measuring the Stars 1. Constellations are a. the
... c. measuring the position of the visible star in the pair and noting shifts as it orbits the center of mass between it and the unseen companion star. d. examining the stars’ absorption spectra. 5. When estimating the distance of stars from Earth, astronomers use the fact that nearby stars shift in p ...
... c. measuring the position of the visible star in the pair and noting shifts as it orbits the center of mass between it and the unseen companion star. d. examining the stars’ absorption spectra. 5. When estimating the distance of stars from Earth, astronomers use the fact that nearby stars shift in p ...
Observations and Theoretical Models of Subdwarfs
... distinguish subdwarfs from other stars has created until relatively recently. Because of this, differing criteria used by various observers has led to some confusion on the subject of subdwarfs in that one author may regard a star as being a subdwarf whereas another astronomer (using different crite ...
... distinguish subdwarfs from other stars has created until relatively recently. Because of this, differing criteria used by various observers has led to some confusion on the subject of subdwarfs in that one author may regard a star as being a subdwarf whereas another astronomer (using different crite ...
ph507-16-1exo2
... Direct imaging of planets is difficult because of the enormous difference in brightness between the star and the planet, and the small angular separation between them. Direct detection: must be large and distant from star Circumstellar dust discs. (Circumstantial evidence.) Disc of material around t ...
... Direct imaging of planets is difficult because of the enormous difference in brightness between the star and the planet, and the small angular separation between them. Direct detection: must be large and distant from star Circumstellar dust discs. (Circumstantial evidence.) Disc of material around t ...
Earth Science 25.2A : Stellar Evolution
... of our sun have relatively short life spans. These stars end in a brilliant explosion called a supernova. During a supernova, a star becomes millions of times brighter than it’s prenova stage. If one of the stars nearest to Earth produced a supernova, it would be brighter than our sun. ...
... of our sun have relatively short life spans. These stars end in a brilliant explosion called a supernova. During a supernova, a star becomes millions of times brighter than it’s prenova stage. If one of the stars nearest to Earth produced a supernova, it would be brighter than our sun. ...
Student 1
... .Barnard’s star was thought to have no flares, due to its age, but one was observed in 2011. The significance of Red Dwarfs to astronomy. Although intelligent life formed around a “G” star for us astronomers think that life will most likely be found around a Red Dwarf. Primarily because their energy ...
... .Barnard’s star was thought to have no flares, due to its age, but one was observed in 2011. The significance of Red Dwarfs to astronomy. Although intelligent life formed around a “G” star for us astronomers think that life will most likely be found around a Red Dwarf. Primarily because their energy ...
PowerPoint - Star Life Cycle
... Iron is the lightest element that doesn’t release energy when you attempt to fuse it together. You actually end up with less energy than you started with! So instead of generating pressure to hold up the outer layers, the iron fusion actually takes pressure out of the core. Thus, there is nothing ...
... Iron is the lightest element that doesn’t release energy when you attempt to fuse it together. You actually end up with less energy than you started with! So instead of generating pressure to hold up the outer layers, the iron fusion actually takes pressure out of the core. Thus, there is nothing ...
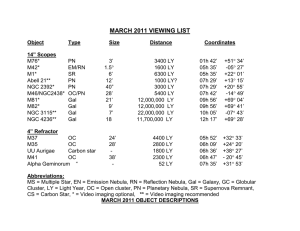
March
... sky. The expanding gas cloud is the result of an exploding star observed in 1054 A.D. At it’s brightest it was four times brighter than Venus and was a visible daylight object for 23 days. The gaseous shell is about 10 light years in diameter and is still expanding outward at the high rate of 1800 k ...
... sky. The expanding gas cloud is the result of an exploding star observed in 1054 A.D. At it’s brightest it was four times brighter than Venus and was a visible daylight object for 23 days. The gaseous shell is about 10 light years in diameter and is still expanding outward at the high rate of 1800 k ...
Astronomy 110 Announcements: 11.1 Properties of Stars
... It would be only 1/3 as bright It would be only 1/6 as bright It would be only 1/9 as bright It would be three times brighter ...
... It would be only 1/3 as bright It would be only 1/6 as bright It would be only 1/9 as bright It would be three times brighter ...
charts_set_8
... equivalent. So in freefall, light and ball also travel in straight lines. 3. Now imagine two people in freefall on Earth, passing a ball back and forth. From their perspective, they pass it in a straight line. From a stationary perspective, it follows a curved path. So will a flashlight beam, but cu ...
... equivalent. So in freefall, light and ball also travel in straight lines. 3. Now imagine two people in freefall on Earth, passing a ball back and forth. From their perspective, they pass it in a straight line. From a stationary perspective, it follows a curved path. So will a flashlight beam, but cu ...
Neutron Stars
... There Is No Way Iron Can Produce Any Energy to Push Back Against the Crush of Gravity in the Star’s Core The star is DOOMED!!! ...
... There Is No Way Iron Can Produce Any Energy to Push Back Against the Crush of Gravity in the Star’s Core The star is DOOMED!!! ...
Advances in Environmental Biology Approach Mahin Shahrivar and
... It is subjected to its off time [19]. It is stated that the sun will be turned off from its core and it will transform into the central layer as a labyrinth and it is showing its contraction formation at that time [10]. The sun produces about 564 million ton hydrogen per every second as its own cons ...
... It is subjected to its off time [19]. It is stated that the sun will be turned off from its core and it will transform into the central layer as a labyrinth and it is showing its contraction formation at that time [10]. The sun produces about 564 million ton hydrogen per every second as its own cons ...
HR Diagram
... 5. Our sun has a surface temperature of 6000 K and an absolute magnitude of + 4.7. Plot the Sun on the H-R diagram and label it ‘Sun’. 6. Betelgeuse is one of the largest stars in the night sky. It has a surface temperature of 3200 K and an absolute magnitude of – 5.5. To which group does Betelgeuse ...
... 5. Our sun has a surface temperature of 6000 K and an absolute magnitude of + 4.7. Plot the Sun on the H-R diagram and label it ‘Sun’. 6. Betelgeuse is one of the largest stars in the night sky. It has a surface temperature of 3200 K and an absolute magnitude of – 5.5. To which group does Betelgeuse ...
Physical Science Laboratory: Skyglobe
... Materials: A computer with the program Skyglobe, Klassm Software, by Mark Haney installed. Procedure: ...
... Materials: A computer with the program Skyglobe, Klassm Software, by Mark Haney installed. Procedure: ...
Distance
... • How much does the apparent brightness of stars we see in the sky vary? Why? • Stars have different colors? So is the amount of light at different wavelengths the same? • Can we tell the difference between a very luminous star that is far away and in intrinsically low luminosity star that is ...
... • How much does the apparent brightness of stars we see in the sky vary? Why? • Stars have different colors? So is the amount of light at different wavelengths the same? • Can we tell the difference between a very luminous star that is far away and in intrinsically low luminosity star that is ...
read in advance to speed your work
... 10b. What is the ratio of the number of total multiple star members to single stars? Again ignore brown dwarfs. 10c. Can you think of (or discover through research) a reason for the number of single stars as opposed to the number of multiple stars? HR Diagram: The Stars in the Direction of Orion ...
... 10b. What is the ratio of the number of total multiple star members to single stars? Again ignore brown dwarfs. 10c. Can you think of (or discover through research) a reason for the number of single stars as opposed to the number of multiple stars? HR Diagram: The Stars in the Direction of Orion ...
Star of Bethlehem

In Christian tradition, the Star of Bethlehem, also called the Christmas Star, revealed the birth of Jesus to the Biblical Magi, and later led them to Bethlehem. The star appears only in the nativity story of the Gospel of Matthew, where astrologers from the east are inspired by the star to travel to Jerusalem. There they meet King Herod of Judea, and ask where the king of the Jews had been born. Herod, following a verse from the Book of Micah interpreted as a prophecy, directs them to Bethlehem, to the south of Jerusalem. The star leads them to Jesus' home in the town, where they worship him and give him gifts. The wise men are then given a divine warning not to return to Herod so they return home by a different route.Many Christians see the star as a miraculous sign to mark the birth of the Christ (or messiah). Some theologians claimed that the star fulfilled a prophecy, known as the Star Prophecy. Astronomers have made several attempts to link the star to unusual astronomical events, such as a conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn, a comet or a supernova.Many modern scholars do not consider the story to be describing a historical event but a pious fiction created by the author of the Gospel of Matthew.The subject is a favorite at planetarium shows during the Christmas season, although the Biblical account describes Jesus with a broader Greek word, which can mean either ""infant"" or ""child"" (paidon), rather than the more specific word for infant (brephos), possibly implying that some time has passed since the birth. The visit is traditionally celebrated on Epiphany (January 6) in Western Christianity.