DOC - Cool Cosmos
... a star really is. Simply put, a star is a large amount of gas and dust that is collapsing under the force of gravity. At first, this crush of gravity makes the inside of the star hot enough to ignite a nuclear explosion. This explosion supports the star against gravity and makes it shine. In our Sun ...
... a star really is. Simply put, a star is a large amount of gas and dust that is collapsing under the force of gravity. At first, this crush of gravity makes the inside of the star hot enough to ignite a nuclear explosion. This explosion supports the star against gravity and makes it shine. In our Sun ...
Characteristics of stars powerpoint
... • The brightness a star would have if it was a standard distance from Earth • This requires an astronomer to determine both the apparent magnitude and distance from Earth ...
... • The brightness a star would have if it was a standard distance from Earth • This requires an astronomer to determine both the apparent magnitude and distance from Earth ...
Forces in stars
... and a mass of 2 million million million million million kg (about 300 000 times that of the Earth). This enormous mass means a very high gravitational pull – a person weighing 600 N on the surface of the Earth would have the colossal weight of 16400N if they stood on the 'surface' of the Sun. As muc ...
... and a mass of 2 million million million million million kg (about 300 000 times that of the Earth). This enormous mass means a very high gravitational pull – a person weighing 600 N on the surface of the Earth would have the colossal weight of 16400N if they stood on the 'surface' of the Sun. As muc ...
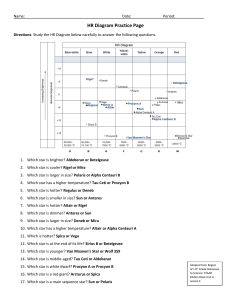
HR Diagram Practice Page
... 1. Which star is brighter? Aldeberan or Betelgeuse 2. Which star is cooler? Rigel or Mira 3. Which star is larger in size? Polaris or Alpha Centauri B 4. Which star has a higher temperature? Tau Ceti or Procyon B 5. Which star is hotter? Regulus or Deneb 6. Which star is smaller in size? Sun or Anta ...
... 1. Which star is brighter? Aldeberan or Betelgeuse 2. Which star is cooler? Rigel or Mira 3. Which star is larger in size? Polaris or Alpha Centauri B 4. Which star has a higher temperature? Tau Ceti or Procyon B 5. Which star is hotter? Regulus or Deneb 6. Which star is smaller in size? Sun or Anta ...
Astronomy Chapter 13 Name
... D. A type of binary star in which the spectrum lines exhibit a changing Doppler shift as a result of the orbital motion of one star around the other ...
... D. A type of binary star in which the spectrum lines exhibit a changing Doppler shift as a result of the orbital motion of one star around the other ...
Place in Space
... space. Light can travel about seven times around Earth in one second. Astronomers use the speed of light to measure how far away things are in space. They use light years. A light year is the distance that light can travel in one year. In one year light travels about 9,460,000,000,000 kilometres. So ...
... space. Light can travel about seven times around Earth in one second. Astronomers use the speed of light to measure how far away things are in space. They use light years. A light year is the distance that light can travel in one year. In one year light travels about 9,460,000,000,000 kilometres. So ...
The Lifecycle of Stars
... to document the stages of a star’s lifecycle. Using the paper I provide, you will have to design and ...
... to document the stages of a star’s lifecycle. Using the paper I provide, you will have to design and ...
01-ChapterRadiation
... which of the seven forms of light…. …does our Sun have its peak intensity? …does our eyes have the greatest sensitivity? …is the Earth’s atmosphere fairly transparent? ...
... which of the seven forms of light…. …does our Sun have its peak intensity? …does our eyes have the greatest sensitivity? …is the Earth’s atmosphere fairly transparent? ...
The life cycle of a star
... core is called a neutron star An extremely dense star made of neutrons ...
... core is called a neutron star An extremely dense star made of neutrons ...
Chapter 18 Study Guide
... 9. What type of star has a low temperature but a high luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) Red supergiant 10. According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, what relationship exist between the brightness and temperature of a main sequence star? The Hertzsprung- Russell diagram shows that main s ...
... 9. What type of star has a low temperature but a high luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) Red supergiant 10. According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, what relationship exist between the brightness and temperature of a main sequence star? The Hertzsprung- Russell diagram shows that main s ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... • When hot enough = nuclear fusion begins • Once the gas and dust blow away, the star can be seen • All stars (low and high mass) start out here ...
... • When hot enough = nuclear fusion begins • Once the gas and dust blow away, the star can be seen • All stars (low and high mass) start out here ...
Surface Environments of the Planets o+ our Solar System
... In this exercise, you will also become more familiar with the various naming systems for stars. Remember, only the brightest stars which form our constellations have been given proper names. There are thousands of stars that have either Bayer Greek letter names, and even more that have Flamsteed num ...
... In this exercise, you will also become more familiar with the various naming systems for stars. Remember, only the brightest stars which form our constellations have been given proper names. There are thousands of stars that have either Bayer Greek letter names, and even more that have Flamsteed num ...
12 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... maintained for a time interval t so that N = λt pulses are detected. If the observation is repeated several times there should be a standard deviation in the measurements of σ1 = (λt)½ = N ½, i.e., for a particular count N has a probability of about 2/3 of being with within σ1 of λt, or the uncertai ...
... maintained for a time interval t so that N = λt pulses are detected. If the observation is repeated several times there should be a standard deviation in the measurements of σ1 = (λt)½ = N ½, i.e., for a particular count N has a probability of about 2/3 of being with within σ1 of λt, or the uncertai ...
WHAT IS A STAR? - cloudfront.net
... glowing sphere of gas that produces energy by fusion held together by gravity. Fusion means ‘joining together’. ...
... glowing sphere of gas that produces energy by fusion held together by gravity. Fusion means ‘joining together’. ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 9
... 27.1 & 27.2 – Formation & Models of the Solar System 1. What is a solar nebula? 2. What is the nebular hypothesis? 3. How did the land and atmosphere of Earth form? 4. How do the theories of Aristotle and Copernicus differ? 5. What did Ptolemy propose about the solar system? 6. What is a protoplanet ...
... 27.1 & 27.2 – Formation & Models of the Solar System 1. What is a solar nebula? 2. What is the nebular hypothesis? 3. How did the land and atmosphere of Earth form? 4. How do the theories of Aristotle and Copernicus differ? 5. What did Ptolemy propose about the solar system? 6. What is a protoplanet ...
When Stars Blow Up
... •At the base of the accreted layer, electrons become degenerate •When the temperature reaches a few MK, fusion begins •Degenerate fusion is a runaway. •All the H fuses to He and heavier elements in a soundcrossing time (a few minutes) •The star increases in brightness ~ 10,000 times •Most of the mat ...
... •At the base of the accreted layer, electrons become degenerate •When the temperature reaches a few MK, fusion begins •Degenerate fusion is a runaway. •All the H fuses to He and heavier elements in a soundcrossing time (a few minutes) •The star increases in brightness ~ 10,000 times •Most of the mat ...
Properties of Main Sequence Stars
... Calculate the density of an O5 and M5 main sequence star relative to the Sun’s density. Record your answer below and show your calculations on a separate page. O5: ...
... Calculate the density of an O5 and M5 main sequence star relative to the Sun’s density. Record your answer below and show your calculations on a separate page. O5: ...
Document
... 6. Explain why stars appear to move in the night sky. (MC) Because Earth moves 7. Understand how scientists can find the temperature and chemical composition of a star. (MC) They use a spectrum 8. The majority of the universe is made of ___dark______ matter and ____dark____ energy. Humans, stars, pl ...
... 6. Explain why stars appear to move in the night sky. (MC) Because Earth moves 7. Understand how scientists can find the temperature and chemical composition of a star. (MC) They use a spectrum 8. The majority of the universe is made of ___dark______ matter and ____dark____ energy. Humans, stars, pl ...
Homework Problems for Quiz 1 – AY 5 – Spring 2013
... 12. If a red star and a blue star both have the same radius and both are the same distance from the Earth, which one is brighter in the sky? The blue star produces more energy per unit surface area than the red star based on Stephan’s Law. If the two stars have the same radius, they have the same su ...
... 12. If a red star and a blue star both have the same radius and both are the same distance from the Earth, which one is brighter in the sky? The blue star produces more energy per unit surface area than the red star based on Stephan’s Law. If the two stars have the same radius, they have the same su ...
Microsoft Word Document
... 11. The Crab Nebula is an example of a ________________. It rotates 30 times per second and will continue doing that for __________ of years. ...
... 11. The Crab Nebula is an example of a ________________. It rotates 30 times per second and will continue doing that for __________ of years. ...
Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... Draw lines on the diagram to show the evolutionary paths of stars X and Y. ...
... Draw lines on the diagram to show the evolutionary paths of stars X and Y. ...
Mountain Skies
... its orbit. In April, we get a chance at both views. Tonight, as the sky darkens, it is in the west below Mars. But, recall that Mercury, because it is so close to the sun, moves very rapidly. Thus, we will have a favorable vie ...
... its orbit. In April, we get a chance at both views. Tonight, as the sky darkens, it is in the west below Mars. But, recall that Mercury, because it is so close to the sun, moves very rapidly. Thus, we will have a favorable vie ...
Star of Bethlehem

In Christian tradition, the Star of Bethlehem, also called the Christmas Star, revealed the birth of Jesus to the Biblical Magi, and later led them to Bethlehem. The star appears only in the nativity story of the Gospel of Matthew, where astrologers from the east are inspired by the star to travel to Jerusalem. There they meet King Herod of Judea, and ask where the king of the Jews had been born. Herod, following a verse from the Book of Micah interpreted as a prophecy, directs them to Bethlehem, to the south of Jerusalem. The star leads them to Jesus' home in the town, where they worship him and give him gifts. The wise men are then given a divine warning not to return to Herod so they return home by a different route.Many Christians see the star as a miraculous sign to mark the birth of the Christ (or messiah). Some theologians claimed that the star fulfilled a prophecy, known as the Star Prophecy. Astronomers have made several attempts to link the star to unusual astronomical events, such as a conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn, a comet or a supernova.Many modern scholars do not consider the story to be describing a historical event but a pious fiction created by the author of the Gospel of Matthew.The subject is a favorite at planetarium shows during the Christmas season, although the Biblical account describes Jesus with a broader Greek word, which can mean either ""infant"" or ""child"" (paidon), rather than the more specific word for infant (brephos), possibly implying that some time has passed since the birth. The visit is traditionally celebrated on Epiphany (January 6) in Western Christianity.