MULTIPLICATION and DIVISION
... If children do not know what 15 divided by 3 equals, they can partition the 15 into numbers that they can divide by 3. Numbers that they know are divisible by 10 are called 'preferred multiples'. 'Preferred' because the child prefers them because they know them. 'Multiples' because when we multiply ...
... If children do not know what 15 divided by 3 equals, they can partition the 15 into numbers that they can divide by 3. Numbers that they know are divisible by 10 are called 'preferred multiples'. 'Preferred' because the child prefers them because they know them. 'Multiples' because when we multiply ...
Study Guide Adding and Subtracting Rational
... 1.) Mrs. Barnett has $11.75. She spends $5.20 at Dollar Mart. How much money does she have left? 2.) Mr. Crouch gains 10 yards, loses 3 yards, loses 10 yards, then gains 9 yards. How many overall yards has Mr. Crouch gained or lost? 3.) Mrs. Moriarity is baking cookies for her class. She needs to ad ...
... 1.) Mrs. Barnett has $11.75. She spends $5.20 at Dollar Mart. How much money does she have left? 2.) Mr. Crouch gains 10 yards, loses 3 yards, loses 10 yards, then gains 9 yards. How many overall yards has Mr. Crouch gained or lost? 3.) Mrs. Moriarity is baking cookies for her class. She needs to ad ...
8th Grade Math SCOS
... A square number, sometimes also called a perfect square, is an integer that is the square of an integer; in other words, it is the product of some integer with itself. For example, 9 is a square number, since it can be written as 3 × 3. Square numbers are non-negative. Another way of saying that a ( ...
... A square number, sometimes also called a perfect square, is an integer that is the square of an integer; in other words, it is the product of some integer with itself. For example, 9 is a square number, since it can be written as 3 × 3. Square numbers are non-negative. Another way of saying that a ( ...
Algebra 1.1, 1.2, 2.1-Expressions and Real Numbers day 2.notebook
... Perform any operations within grouping symbols. Evaluate exponents. Multiply or divide from left to right. Add or subtract from left to right. ...
... Perform any operations within grouping symbols. Evaluate exponents. Multiply or divide from left to right. Add or subtract from left to right. ...
Math 229 Inequalities and Absolute Value 06/02/2008 A. Interval
... Our goal is to use the properties of inequalities and other algebraic techniques to find which real numbers satisfy a given inequality. Examples: 1. 3 − 2x < 5 3 - 2x < ...
... Our goal is to use the properties of inequalities and other algebraic techniques to find which real numbers satisfy a given inequality. Examples: 1. 3 − 2x < 5 3 - 2x < ...
Physics 11 - Course Assessment Assignment Hand in the last two
... a measured or experimental value agrees with the standard value of the quantity. If a 500 g weight is placed on a scale we would expect the scale to read 500 g. If it does not, the scale is inaccurate. Digits that indicate an instrument’s degree of accuracy are called significant digits. Significant ...
... a measured or experimental value agrees with the standard value of the quantity. If a 500 g weight is placed on a scale we would expect the scale to read 500 g. If it does not, the scale is inaccurate. Digits that indicate an instrument’s degree of accuracy are called significant digits. Significant ...
Year 2 programme of study
... compare and order numbers from 0 up to 100 read and write numbers to at least 100 in numerals use place value and number facts to solve problems compare and order lengths, mass, volume/capacity compare and sequence intervals of time ...
... compare and order numbers from 0 up to 100 read and write numbers to at least 100 in numerals use place value and number facts to solve problems compare and order lengths, mass, volume/capacity compare and sequence intervals of time ...
Full text
... isn t often looking for an additional unit of work, but rather for short excursions into related material to spark student interest. This note describes such a bypath. When teaching the multiplication and division of polynomials, excellent interest-catchers are available. In multiplication, compute ...
... isn t often looking for an additional unit of work, but rather for short excursions into related material to spark student interest. This note describes such a bypath. When teaching the multiplication and division of polynomials, excellent interest-catchers are available. In multiplication, compute ...
UNIT 1: REAL NUMBERS Equivalent fractions Two fractions are
... To round down, just cut off the number at the place you want. See the table below. b) Rounding is the most usual kind of estimating. To round a decimal number, find the place value you want and look at the digit just to the right. If it is 5 or more, then round up. If it is 4 or less, round down. Th ...
... To round down, just cut off the number at the place you want. See the table below. b) Rounding is the most usual kind of estimating. To round a decimal number, find the place value you want and look at the digit just to the right. If it is 5 or more, then round up. If it is 4 or less, round down. Th ...
Review - Fundamental Concepts
... 5. n a m (n a ) a n 6. Notice that all the rules above do not have addition or subtraction in them. These rules do not apply when addition or subtraction are involved. Simplify each of the following: page 78 #12, 18, 24, 30 Fractions: 1. For addition and subtraction: find a common denominator, c ...
... 5. n a m (n a ) a n 6. Notice that all the rules above do not have addition or subtraction in them. These rules do not apply when addition or subtraction are involved. Simplify each of the following: page 78 #12, 18, 24, 30 Fractions: 1. For addition and subtraction: find a common denominator, c ...
1.5 Adding and Subtracting Real Numbers Template
... Ex.5: A robot submarine dives 803 feet to the ocean floor. It rises 215 feet as the water gets shallower. Then the submarine dives 2619 feet into a deep crevice. Next, it rises 734 feet to photograph a crack in the wall of the crevice. What is the location of the crack in relation to sea level? ...
... Ex.5: A robot submarine dives 803 feet to the ocean floor. It rises 215 feet as the water gets shallower. Then the submarine dives 2619 feet into a deep crevice. Next, it rises 734 feet to photograph a crack in the wall of the crevice. What is the location of the crack in relation to sea level? ...
Properties of Equality, Identity, and Operations
... multiplies it by everything inside the parentheses. • This property works over addition and subtraction. ...
... multiplies it by everything inside the parentheses. • This property works over addition and subtraction. ...
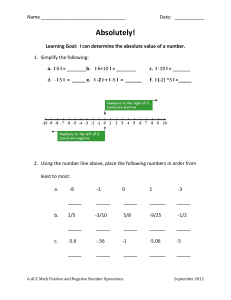
Name Date: ______ Absolutely! Learning Goal: I can determine the
... Learning Goal: I can determine the absolute value of a number. 1. Simplify the following: a. I 6 I = ...
... Learning Goal: I can determine the absolute value of a number. 1. Simplify the following: a. I 6 I = ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.