2 n-1
... The binary number system uses base 2 This system use digit to represent the binary number 0 and 1 The binary number system is generally used in digital circuit area For example, a binary number is 1011012 ...
... The binary number system uses base 2 This system use digit to represent the binary number 0 and 1 The binary number system is generally used in digital circuit area For example, a binary number is 1011012 ...
Algebraic Expression
... One of the most commonly used variables is the letter x. Because the letter x looks so much like the multiplication sign , you will not use to represent multiplication when working with variables. Instead, you will use one of the methods above. ...
... One of the most commonly used variables is the letter x. Because the letter x looks so much like the multiplication sign , you will not use to represent multiplication when working with variables. Instead, you will use one of the methods above. ...
Table 1 Fill in the blank: Choose a word from the bank below to fill in
... A non repeating, non terminating decimal represents a/an _______________. All whole number and their opposites are called ______________. _______________ is a whole number but NOT a natural number. Answer each question carefully. Be sure to show all work when appropriate. Circle the choice that show ...
... A non repeating, non terminating decimal represents a/an _______________. All whole number and their opposites are called ______________. _______________ is a whole number but NOT a natural number. Answer each question carefully. Be sure to show all work when appropriate. Circle the choice that show ...
Document
... operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division to form other real numbers, two functions can be combined to create new functions. When f(x) = 2x – 3 ...
... operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division to form other real numbers, two functions can be combined to create new functions. When f(x) = 2x – 3 ...
Binary Numbers
... Two’s complement notation: The most popular system for presenting integers within today’s computers is two’s complement notation. Each value is represented by a pattern of 32 bits. Such a large system allows a wide range of numbers to be represented. ...
... Two’s complement notation: The most popular system for presenting integers within today’s computers is two’s complement notation. Each value is represented by a pattern of 32 bits. Such a large system allows a wide range of numbers to be represented. ...
integers intel
... INTEGERS INTEL Integers are also called SIGNED NUMBERS. These numbers are positive and negative with “0” being at the half way point. You’ve probably seen a number line with a zero in the middle and negative numbers to the left and positive numbers to the right. Please notice the arrows at the ends ...
... INTEGERS INTEL Integers are also called SIGNED NUMBERS. These numbers are positive and negative with “0” being at the half way point. You’ve probably seen a number line with a zero in the middle and negative numbers to the left and positive numbers to the right. Please notice the arrows at the ends ...
Math Notes for Chapter Three
... Dividing Fractions: you are trying to determine how many of one fraction can go into another fraction 2 – 1/4 = means you are trying to determine how many 4ths can fit into 2 ...
... Dividing Fractions: you are trying to determine how many of one fraction can go into another fraction 2 – 1/4 = means you are trying to determine how many 4ths can fit into 2 ...
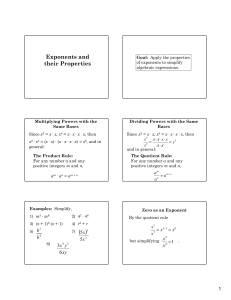
Exponents and their Properties
... For any numbers a and b and any whole number n: (ab)n = anbn Raising a Quotient to a Power: For any numbers a and b, b ≠ 0, and any whole number n: n an a = n b b ...
... For any numbers a and b and any whole number n: (ab)n = anbn Raising a Quotient to a Power: For any numbers a and b, b ≠ 0, and any whole number n: n an a = n b b ...
Words that Imply the Operations Operation
... Keep in mind that when you are going from words to symbols and numbers, always go one step at a time and read through the sentence one piece at a time to figure out the order! Example: When we read the sentence “17 less than a number” that tells us we are subtracting 17 from something else…. n - 17 ...
... Keep in mind that when you are going from words to symbols and numbers, always go one step at a time and read through the sentence one piece at a time to figure out the order! Example: When we read the sentence “17 less than a number” that tells us we are subtracting 17 from something else…. n - 17 ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.