cat-funda-book… Click here to
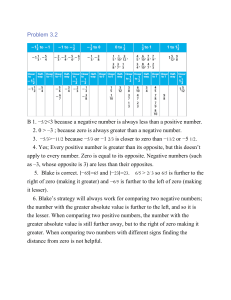
... If the numbers are not consecutive, with a common difference with a common difference of d, then the first number is x-nd and the last one is x+nd The middle number is always same as the average. Example: what is the 6thnumber in an AP, whose average of first 11 numbers is 24? ...
... If the numbers are not consecutive, with a common difference with a common difference of d, then the first number is x-nd and the last one is x+nd The middle number is always same as the average. Example: what is the 6thnumber in an AP, whose average of first 11 numbers is 24? ...
Indexed Collections Let I be a set (finite of infinite). If for each
... empty collection of sets is defined to be the universal set U. You should be able to supply a justification for these definitions, as was done above. Generalised DeMorgan’s Laws. You should memorize these, and know how to prove them. ∪ni=1 Ai = ∩ni=1 Ai and ∩ni=1 Ai = ∪ni=1 Ai The index set does not ha ...
... empty collection of sets is defined to be the universal set U. You should be able to supply a justification for these definitions, as was done above. Generalised DeMorgan’s Laws. You should memorize these, and know how to prove them. ∪ni=1 Ai = ∩ni=1 Ai and ∩ni=1 Ai = ∪ni=1 Ai The index set does not ha ...
Document
... 1.5 Simple Approximations Error function: (probability theory) It is not possible to evaluate this integral by means of ...
... 1.5 Simple Approximations Error function: (probability theory) It is not possible to evaluate this integral by means of ...
Mathematics Summer Session: Transition Math Chapter 1 Notes
... For example, if we needed the number 3,763: We would have: MMM + D + CC + L + X + III = MMMDCCLXIII Our decimal system works much the same, but it’s centered on the number ten. The whole numbers, in decimal notation, include: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5…all the way to infinity. Each digit represents a cert ...
... For example, if we needed the number 3,763: We would have: MMM + D + CC + L + X + III = MMMDCCLXIII Our decimal system works much the same, but it’s centered on the number ten. The whole numbers, in decimal notation, include: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5…all the way to infinity. Each digit represents a cert ...
Maths Workshop - St Michael`s C of E Primary School
... Know what each digit represents and partition three-digit numbers into a multiple of 100, a multiple of 10, and ones. Understand multiplication as repeated addition and as an array. ...
... Know what each digit represents and partition three-digit numbers into a multiple of 100, a multiple of 10, and ones. Understand multiplication as repeated addition and as an array. ...
Mastery Test 1 Study Guide
... Counting #’s: 1, 2, 3,…. Whole #’s: 0, 1, 2, 3,…. Integers: …., -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3,…. Positive #’s: all numbers greater than 0 Negative #’s: all numbers less than 0 Rational #’s: all Numbers that are NOT IRRATIONAL Irrational #’s: CRAZY, most well know example is Pi (3.1416……..) #’ ...
... Counting #’s: 1, 2, 3,…. Whole #’s: 0, 1, 2, 3,…. Integers: …., -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3,…. Positive #’s: all numbers greater than 0 Negative #’s: all numbers less than 0 Rational #’s: all Numbers that are NOT IRRATIONAL Irrational #’s: CRAZY, most well know example is Pi (3.1416……..) #’ ...
Name Chapter 1 Test Place Value, Add and Subtract Whole Number
... Directions: Circle the letter of the best answer. (1 pt. each) 1. The estimated population of Hong Kong 2. in 2006 was six million, nine hundred forty thousand, four hundred thirty-two. What is this number in standard form? ...
... Directions: Circle the letter of the best answer. (1 pt. each) 1. The estimated population of Hong Kong 2. in 2006 was six million, nine hundred forty thousand, four hundred thirty-two. What is this number in standard form? ...
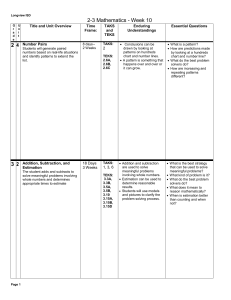
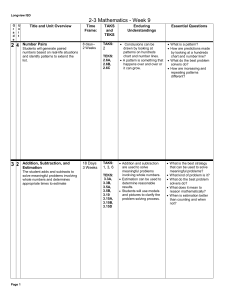
Week of 2-13-17 - Math
... Solve real world problems involving multiplication of fractions and mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the problem. 5.MD.1 Convert among different-sized standard measurement units within a given measurement system (e.g., convert 5 cm to 0.05 m), and use th ...
... Solve real world problems involving multiplication of fractions and mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the problem. 5.MD.1 Convert among different-sized standard measurement units within a given measurement system (e.g., convert 5 cm to 0.05 m), and use th ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.