Rational Numbers and Decimals
... • A rational number is a number that can be written a ratio of two integers and neither number can be zero. • A rational number that is terminating decimal means it ends. When dividing the remainder is zero. • A rational number that has a repeating decimal keep on going and going. ...
... • A rational number is a number that can be written a ratio of two integers and neither number can be zero. • A rational number that is terminating decimal means it ends. When dividing the remainder is zero. • A rational number that has a repeating decimal keep on going and going. ...
2.5a Translate to an Algebraic Expression
... numbers subtracted from 20 ____________ 9. The product of six and three less than the number ____________ 10. Twice the sum of a number and eight ...
... numbers subtracted from 20 ____________ 9. The product of six and three less than the number ____________ 10. Twice the sum of a number and eight ...
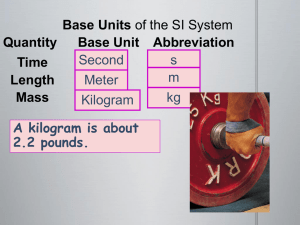
Scientific measurement - Campbell County Schools
... 2. In order for this to be a proper measurement, it must contain a number and a unit. B. Science is very dependent on measurements. C. Every time a scientist performs an experiment, something is being _____________________. D. The four things in the universe are commonly measured in chemistry. 1. Ma ...
... 2. In order for this to be a proper measurement, it must contain a number and a unit. B. Science is very dependent on measurements. C. Every time a scientist performs an experiment, something is being _____________________. D. The four things in the universe are commonly measured in chemistry. 1. Ma ...
MATH 0302
... Multiply monomials using the product rule. Divide monomials and write the answer using positive exponents only. Write decimals in scientific notation and convert numbers in scientific notation to decimal form. Translate verbal phrases into mathematical expressions. Evaluate algebraic expressions for ...
... Multiply monomials using the product rule. Divide monomials and write the answer using positive exponents only. Write decimals in scientific notation and convert numbers in scientific notation to decimal form. Translate verbal phrases into mathematical expressions. Evaluate algebraic expressions for ...
Lecture 2
... On the other hand if a product is repeated then it is clear that the pattern just seen will repeat so one gets an infinite repeating pattern in the fractional representation. ...
... On the other hand if a product is repeated then it is clear that the pattern just seen will repeat so one gets an infinite repeating pattern in the fractional representation. ...
Eg. 2
... • Rewriting a number as a product of a number between 1 and 10 and a whole number power of ten. • Helps eliminate using too many zeros. • Helps to correctly locate the decimal place when reporting a quantity. • Eg: Radius of earth = 6,380,000 m = 6.38 x 106 m Radius of a hydrogen atom = 0.000 000 00 ...
... • Rewriting a number as a product of a number between 1 and 10 and a whole number power of ten. • Helps eliminate using too many zeros. • Helps to correctly locate the decimal place when reporting a quantity. • Eg: Radius of earth = 6,380,000 m = 6.38 x 106 m Radius of a hydrogen atom = 0.000 000 00 ...
A number is divisible by
... 4 if the last to digits of the number is divisible by 4 5 if the number ends in 0 or 5 6 if the number is divisible by 2 AND 3 9 if the sum of the digits is divisible by 9 10 if the number ends in 0 ...
... 4 if the last to digits of the number is divisible by 4 5 if the number ends in 0 or 5 6 if the number is divisible by 2 AND 3 9 if the sum of the digits is divisible by 9 10 if the number ends in 0 ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.