Replaced Common Hepatic Artery From Superior Mesenteric Artery
... resectability. In addition, angiographic data sets can be rendered to create displays of the local venous and arterial anatomy that are familiar to surgeons(5-6). ...
... resectability. In addition, angiographic data sets can be rendered to create displays of the local venous and arterial anatomy that are familiar to surgeons(5-6). ...
23 - peritoneum2009-01-27 10:5210.0 MB
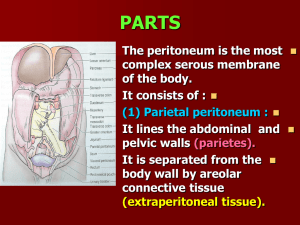
... It ascends onto the posterior abdominal wall and becomes continuous with the visceral peritoneum which covers the front and sides of the ascending and descending colon. ...
... It ascends onto the posterior abdominal wall and becomes continuous with the visceral peritoneum which covers the front and sides of the ascending and descending colon. ...
Lab 9 – Abdomen
... External abdominal oblique – continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its aponeurosis; most superficial of the muscles of the abdominal wall; immediately superficial to the internal abdominal ...
... External abdominal oblique – continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its aponeurosis; most superficial of the muscles of the abdominal wall; immediately superficial to the internal abdominal ...
Anatomy
... The oesophagus is a 25cm long tube that is continuous with the pharynx and stomach and it has three constrictions. The cervical constriction is at its junction with the pharynx, 15cm from the teeth and is the upper esophageal sphincter (C6). The bronchoaortic constriction is 25cm from the teeth ...
... The oesophagus is a 25cm long tube that is continuous with the pharynx and stomach and it has three constrictions. The cervical constriction is at its junction with the pharynx, 15cm from the teeth and is the upper esophageal sphincter (C6). The bronchoaortic constriction is 25cm from the teeth ...
GI Tract Physiologic Disturance
... • Observing number, location and mucosal pattern of the dilated bowel may roughly indicate the point of obstruction • Commonly due to post-surgical adhesion or hernia ...
... • Observing number, location and mucosal pattern of the dilated bowel may roughly indicate the point of obstruction • Commonly due to post-surgical adhesion or hernia ...
Intestinal Stomas
... # A transverse incision 8-10cm long, with removal of a disc of skin, is made for transverse colon (in the Rt. upper abdomen midway between the umbilicus and xiphisternum over the rectus abdominus muscle and extending laterally to the lateral border of the rectus muscle), while for the sigmoid colon ...
... # A transverse incision 8-10cm long, with removal of a disc of skin, is made for transverse colon (in the Rt. upper abdomen midway between the umbilicus and xiphisternum over the rectus abdominus muscle and extending laterally to the lateral border of the rectus muscle), while for the sigmoid colon ...
OMT in the Hospitalized Patient - American Academy of Osteopathy
... Only 1% of total body magnesium is in the plasma Essential for proper nerve & muscle functioning ...
... Only 1% of total body magnesium is in the plasma Essential for proper nerve & muscle functioning ...
Show List of Dissection Steps
... ❏ Identify the following parts of connecting peritoneum: ❏ lesser omentum ❏ hepatoduodenal ligament ❏ greater omentum ❏ omental bursa ❏ epiploic foramen ❏ mesoduodenum ❏ duodenocolic fold ❏ mesentery (mesojejunoileum) ❏ root of the mesentery ❏ mesocolon (ascending, transverse, descending) ❏ Attemp ...
... ❏ Identify the following parts of connecting peritoneum: ❏ lesser omentum ❏ hepatoduodenal ligament ❏ greater omentum ❏ omental bursa ❏ epiploic foramen ❏ mesoduodenum ❏ duodenocolic fold ❏ mesentery (mesojejunoileum) ❏ root of the mesentery ❏ mesocolon (ascending, transverse, descending) ❏ Attemp ...
Abdomen MCQs - WordPress.com
... a. Ascending is longer than descending – transverse is the longest > descending > ascending b. Only part suspended on mesentery is transverse colon – is all is c. Marginal artery is weakest at hepatic flexure - ? d. Lymphatic drainage is via superior and inferior mesenteric lymph nodes e. ? 26. wher ...
... a. Ascending is longer than descending – transverse is the longest > descending > ascending b. Only part suspended on mesentery is transverse colon – is all is c. Marginal artery is weakest at hepatic flexure - ? d. Lymphatic drainage is via superior and inferior mesenteric lymph nodes e. ? 26. wher ...
MedlinePlus
... This document is for informational purposes and is not intended to be a substitute for the advice of a doctor or healthcare professional or a recommendation for any particular treatment plan. Like any printed material, it may become out of date over time. The Patient Education Institute does not war ...
... This document is for informational purposes and is not intended to be a substitute for the advice of a doctor or healthcare professional or a recommendation for any particular treatment plan. Like any printed material, it may become out of date over time. The Patient Education Institute does not war ...
File - Sheffield Peer Teaching Society
... suspended from posterior abdominal wall by DORSAL mesentery HEPATIC DIVERTICULUM is a bud (arises ventrally) at the junction of the foregut and midgut. ...
... suspended from posterior abdominal wall by DORSAL mesentery HEPATIC DIVERTICULUM is a bud (arises ventrally) at the junction of the foregut and midgut. ...
DMS131 Abdominal Sonography I Multiple
... 4. What do the superior mesenteric vein and the splenic vein join together to form? a. celiac axis b. portal vein c. inferior vena cava d. main hepatic vein 5. The celiac axis is _______ to the origin of the superior mesenteric artery. a. cephalad b. caudal c. medial d. lateral 6. Which vessel lies ...
... 4. What do the superior mesenteric vein and the splenic vein join together to form? a. celiac axis b. portal vein c. inferior vena cava d. main hepatic vein 5. The celiac axis is _______ to the origin of the superior mesenteric artery. a. cephalad b. caudal c. medial d. lateral 6. Which vessel lies ...
Anatomy of the Abdomen, Pelvis
... Extension of serous membrane in the abdomino-pelvic cavity Mesentery: Double layer of peritoneum z Hold organs in place z Store fat z Route for vessels + nerves Retroperitoneal: some organs behind peritoneum (eg) distal esophagus, duodenum, ascending + descending colon, rectum, pancreas Peritoneal: ...
... Extension of serous membrane in the abdomino-pelvic cavity Mesentery: Double layer of peritoneum z Hold organs in place z Store fat z Route for vessels + nerves Retroperitoneal: some organs behind peritoneum (eg) distal esophagus, duodenum, ascending + descending colon, rectum, pancreas Peritoneal: ...
Acute or subacute renal failure after therapy with
... After the emergently surgical abdominal intervention was performed was discovered unexpected: break of the mesentery with haemoperitoneum and was solved. So the cause of the haemoperitoneum was break of the mesentery this was the reason that not a hematomas of the organs was the cause. All the organ ...
... After the emergently surgical abdominal intervention was performed was discovered unexpected: break of the mesentery with haemoperitoneum and was solved. So the cause of the haemoperitoneum was break of the mesentery this was the reason that not a hematomas of the organs was the cause. All the organ ...
clinical anatomy abdomen
... and peritoneal innervation) Somatosensory innervation : Intercostal nerves n. iliohypogastricus n. Ilioinguinalis Somatic pain : from abdominal wall and parietal peritoneum, sharp and well localized Visceral pain : from viscera, autonomic nerve fibers, distension, muscular contraction, vague, nausea ...
... and peritoneal innervation) Somatosensory innervation : Intercostal nerves n. iliohypogastricus n. Ilioinguinalis Somatic pain : from abdominal wall and parietal peritoneum, sharp and well localized Visceral pain : from viscera, autonomic nerve fibers, distension, muscular contraction, vague, nausea ...
1. Superficial Fascia (Camper`s)=fatty
... almost identical to the distribution of peripheral nerves. The spinal levels T7-T12 do not participate in plexus formation. The exception to this rule is at the L1 level (iliohypogastric & ilioinguinal). Here, the dermatome has two peripheral nerves and explains why a swift kick to Sam Sauce’s nuts ...
... almost identical to the distribution of peripheral nerves. The spinal levels T7-T12 do not participate in plexus formation. The exception to this rule is at the L1 level (iliohypogastric & ilioinguinal). Here, the dermatome has two peripheral nerves and explains why a swift kick to Sam Sauce’s nuts ...
introduction to - yeditepe anatomy fhs 121
... Absorption of chemical compounds occurs principally in the small intestine, a coiled 5- to 6-m-long tube (shorter in life, when tonus is present, than in the cadaver) consisting of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. Peristalsis also occurs in the jejunum and ileum; however, it is not forceful unless ...
... Absorption of chemical compounds occurs principally in the small intestine, a coiled 5- to 6-m-long tube (shorter in life, when tonus is present, than in the cadaver) consisting of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. Peristalsis also occurs in the jejunum and ileum; however, it is not forceful unless ...
Intestinal Obstruction
... • Def. :- It is a congenital agangliosis of the intestine which result of disordered emberyogenesis involving the myenteric nervous system . • Etiology :- Lack of migratory nerve cells to develop . • Esophagus 6th week . • Transverse colon 8th week . • Rectum 12th week . • Incidence :- 1 per 5000 li ...
... • Def. :- It is a congenital agangliosis of the intestine which result of disordered emberyogenesis involving the myenteric nervous system . • Etiology :- Lack of migratory nerve cells to develop . • Esophagus 6th week . • Transverse colon 8th week . • Rectum 12th week . • Incidence :- 1 per 5000 li ...
digestive tract
... is an inflammatory disease of the intestines that may affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from anus to mouth, causing a wide variety of symptoms It can develop discontinously without sequence and skipping in all alimentary tract , terminal ileum. Peak onset is between ages 10 and 30 Cause ...
... is an inflammatory disease of the intestines that may affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from anus to mouth, causing a wide variety of symptoms It can develop discontinously without sequence and skipping in all alimentary tract , terminal ileum. Peak onset is between ages 10 and 30 Cause ...
Abdomen
... Intraperitoneal organs are almost completely covered with visceral peritoneum Extraperitoneal organs are outside the peritoneal cavity and are only partially covered with peritoneum. Retroperitoneal organs such as the kidneys are between the parietal peritoneum and the posterior abdominal wall ...
... Intraperitoneal organs are almost completely covered with visceral peritoneum Extraperitoneal organs are outside the peritoneal cavity and are only partially covered with peritoneum. Retroperitoneal organs such as the kidneys are between the parietal peritoneum and the posterior abdominal wall ...
What is Colorectal Cancer
... world it is the third most common cancer type. Usually it originates from adenomatous polyps in colon. It creates 10-15% of all cancers and it is the most common type among gastrointestinal system (digestive system) cancers. It is the second common cause of death among men following lung cancer and ...
... world it is the third most common cancer type. Usually it originates from adenomatous polyps in colon. It creates 10-15% of all cancers and it is the most common type among gastrointestinal system (digestive system) cancers. It is the second common cause of death among men following lung cancer and ...
ABDOMINAL CAVITY
... posterior to the stomach, the posterior wall of the stomach is in contact with the sac. • Thus any posterior ulceration of the stomach will cause fluid to pass into this sac. ...
... posterior to the stomach, the posterior wall of the stomach is in contact with the sac. • Thus any posterior ulceration of the stomach will cause fluid to pass into this sac. ...
Mesentery

The mesentery is a fold of membranous tissue that arises from the posterior wall of the peritoneal cavity and attaches to the intestinal tract. Within it are the arteries and veins that supply the intestine. The term can be used narrowly to denote just the material that supplies the jejunum and ileum of the small intestine, or broadly to include the right, left and transverse mesocolon, mesoappendix, mesosigmoid and mesorectum.The human mesentery, also called the mesenteric organ, mainly comprises the small intestinal mesentery, the right, left and transverse mesocolon, mesosigmoid and mesorectum. Conventional teaching has described the mesocolon as a fragmented structure; the small intestinal mesentery, transverse and sigmoid mesocolon all terminate at their insertion into the posterior abdominal wall. Recent advances in gastrointestinal anatomy have demonstrated that the mesenteric organ is actually a single, continuous structure that reaches from the duodenojejunal flexure to the level of the distal mesorectum. This simpler concept has been shown to have significant implications.