Abdominal Viscera Basics - Page 1 of 10 Learning Modules
... certain gut structures during the return of the intestines into the abdominal cavity (discussed later). These organs include the pancreas, duodenum, ascending and descending colons, which are associated with fusion fascia adhering them to the posterior abdominal wall. In the accompanying movie of a ...
... certain gut structures during the return of the intestines into the abdominal cavity (discussed later). These organs include the pancreas, duodenum, ascending and descending colons, which are associated with fusion fascia adhering them to the posterior abdominal wall. In the accompanying movie of a ...
The Large Intestine Let`s continue on our wild journey through the GI
... -Completely surrounded by mesentery. -Mobile, needed for surgeries when there is a tumor in the colon or the rectum, anal canal. >>>>Colostomyopening within the transverse colon and any waste products/content is emptied out into an external sac that is fixed onto the anterior abdominal wall. from t ...
... -Completely surrounded by mesentery. -Mobile, needed for surgeries when there is a tumor in the colon or the rectum, anal canal. >>>>Colostomyopening within the transverse colon and any waste products/content is emptied out into an external sac that is fixed onto the anterior abdominal wall. from t ...
DigesCve System
... Epiploic appendages – small fat accumulations on the viscera Appendix (or vermiform appendix; also cecal (or caecal) appendix; also vermix Locations along the colon are: The ascending colon The right colic flexure (hepatic) The transverse colon The transverse mesocolon The left colic flexure (spleni ...
... Epiploic appendages – small fat accumulations on the viscera Appendix (or vermiform appendix; also cecal (or caecal) appendix; also vermix Locations along the colon are: The ascending colon The right colic flexure (hepatic) The transverse colon The transverse mesocolon The left colic flexure (spleni ...
general arrangement of the abdominal viscera
... partially covered with visceral peritoneum. The pancreas and the ascending and descending parts of the colon are examples of retroperitoneal organs. ...
... partially covered with visceral peritoneum. The pancreas and the ascending and descending parts of the colon are examples of retroperitoneal organs. ...
Nerve Supply
... mesoappendix and then into the superior mesenteric nodes. Nerve Supply The appendix is supplied by the sympathetic and parasympathetic (vagus) nerves from the superior mesenteric plexus. Afferent nerves for pain accompany the sympathetic plexus, enteres the spinal chord at the 10th ...
... mesoappendix and then into the superior mesenteric nodes. Nerve Supply The appendix is supplied by the sympathetic and parasympathetic (vagus) nerves from the superior mesenteric plexus. Afferent nerves for pain accompany the sympathetic plexus, enteres the spinal chord at the 10th ...
Peritoneum and abdominal cavity
... Midgut: distal duodenum, jejunum, ileum and large intestine up until the left colic flexure Hindgut: everything distal from left colic flexure Overview of veins of GI tract (Netter: Plate 294) The veins of the GI tract form a typical arrangement as described below: The splenic vein is joined about 1 ...
... Midgut: distal duodenum, jejunum, ileum and large intestine up until the left colic flexure Hindgut: everything distal from left colic flexure Overview of veins of GI tract (Netter: Plate 294) The veins of the GI tract form a typical arrangement as described below: The splenic vein is joined about 1 ...
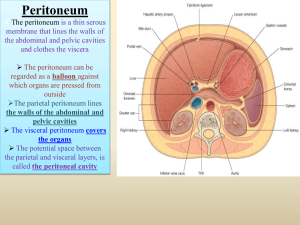
The peritoneum 腹膜
... Position: lies between the liver and duodenum, behind the lesser omentum and infront of the inferior vena cava The omental bursa (lesser sac) communicates with the greater sac through the omental foramen. ...
... Position: lies between the liver and duodenum, behind the lesser omentum and infront of the inferior vena cava The omental bursa (lesser sac) communicates with the greater sac through the omental foramen. ...
Abdomen-Part 3 - kylethornton.org
... ligament of Treitz- suspensory lig-around celiac axis Entry of small bowel into peritoneal cavity Lt upper abdomen/ umbilical region- absorption occurs- folds?? ...
... ligament of Treitz- suspensory lig-around celiac axis Entry of small bowel into peritoneal cavity Lt upper abdomen/ umbilical region- absorption occurs- folds?? ...
The Infracolic Compartment
... The space lies between the parietal peritoneum and the fascia and musculature of the posterior abdominal wall. It extends superiorly from the diaphragm, and inferiorly to the sacral promontory and the pelvis inlet. ...
... The space lies between the parietal peritoneum and the fascia and musculature of the posterior abdominal wall. It extends superiorly from the diaphragm, and inferiorly to the sacral promontory and the pelvis inlet. ...
25 -celiac_T2009-01-27 12:361.2 MB
... It is the artery of foregut, it supplies GIT from lower 1/3 of esophgus down as far as the middle of second part of duodenum. Origin : is very short and arises from front of abdominal aorta at level of lower border of T12 vertebra. It is surrounded by the celiac plexus of nerves. It lies behind ...
... It is the artery of foregut, it supplies GIT from lower 1/3 of esophgus down as far as the middle of second part of duodenum. Origin : is very short and arises from front of abdominal aorta at level of lower border of T12 vertebra. It is surrounded by the celiac plexus of nerves. It lies behind ...
PPT
... the ileocecal sphincter by physiologists) serves as a sphincter and controls the flow of contents from the ileum into the colon. • The smooth muscle tone is reflexly increased when the cecum is distended; the gastrin hormone, which is produced by the stomach, causes relaxation of the muscle ...
... the ileocecal sphincter by physiologists) serves as a sphincter and controls the flow of contents from the ileum into the colon. • The smooth muscle tone is reflexly increased when the cecum is distended; the gastrin hormone, which is produced by the stomach, causes relaxation of the muscle ...
Slides 7
... the ileocecal sphincter by physiologists) serves as a sphincter and controls the flow of contents from the ileum into the colon. • The smooth muscle tone is reflexly increased when the cecum is distended; the gastrin hormone, which is produced by the stomach, causes relaxation of the muscle ...
... the ileocecal sphincter by physiologists) serves as a sphincter and controls the flow of contents from the ileum into the colon. • The smooth muscle tone is reflexly increased when the cecum is distended; the gastrin hormone, which is produced by the stomach, causes relaxation of the muscle ...
superior mesenteric artery
... the ileocecal sphincter by physiologists) serves as a sphincter and controls the flow of contents from the ileum into the colon. • The smooth muscle tone is reflexly increased when the cecum is distended; the gastrin hormone, which is produced by the stomach, causes relaxation of the muscle ...
... the ileocecal sphincter by physiologists) serves as a sphincter and controls the flow of contents from the ileum into the colon. • The smooth muscle tone is reflexly increased when the cecum is distended; the gastrin hormone, which is produced by the stomach, causes relaxation of the muscle ...
Document
... Peritoneal folds are small peritoneal continuations, which sometimes are formed by the blood vessels, different ducts or fibrous ligaments. Peritoneal ligaments are two-layer folds of peritoneum that connects viscera to the abdominal and pelvic walls, or realize connections between organs. ◦ divided ...
... Peritoneal folds are small peritoneal continuations, which sometimes are formed by the blood vessels, different ducts or fibrous ligaments. Peritoneal ligaments are two-layer folds of peritoneum that connects viscera to the abdominal and pelvic walls, or realize connections between organs. ◦ divided ...
Abdomen and Pelvis
... 1. The rectus abdominis muscle is a flexor of the lumbar spine. 2. Direct inguinal hernias pass through the deep inguinal ring. 3. The stomach lies posterior to the lesser sac of the peritoneal cavity. 4. The liver is attached to the diaphragm and the anterior abdominal wall by the lesser omentum. 5 ...
... 1. The rectus abdominis muscle is a flexor of the lumbar spine. 2. Direct inguinal hernias pass through the deep inguinal ring. 3. The stomach lies posterior to the lesser sac of the peritoneal cavity. 4. The liver is attached to the diaphragm and the anterior abdominal wall by the lesser omentum. 5 ...
Total Mesorectal Excision: Tips and Techniques.
... mobilized by lateral to medial approach, begin at 2 mm anterior to the white line of Toldt. The left side colon was mobilized by lateral to medial approach, begin at 2 mm. above the white line of Toldt. By extending this plane upwardly, the splenic flexure was mobilized as in laparoscopic surgery. M ...
... mobilized by lateral to medial approach, begin at 2 mm anterior to the white line of Toldt. The left side colon was mobilized by lateral to medial approach, begin at 2 mm. above the white line of Toldt. By extending this plane upwardly, the splenic flexure was mobilized as in laparoscopic surgery. M ...
Document
... Main Branches of Sup. Mesenteric (Read Your Text) 1. Inf. pancreaticoduodenal a. anastomose with sup. Pancreaticoduodenal a. (comes from??) 2. Jejunal & ileal branches. 3. Ileocolic a.: to ileum, cecum & appendix, and part of ascending colon 4 branches ? gives off the appendicular a. from (which ar ...
... Main Branches of Sup. Mesenteric (Read Your Text) 1. Inf. pancreaticoduodenal a. anastomose with sup. Pancreaticoduodenal a. (comes from??) 2. Jejunal & ileal branches. 3. Ileocolic a.: to ileum, cecum & appendix, and part of ascending colon 4 branches ? gives off the appendicular a. from (which ar ...
File
... • Distinctive features, but a gradual change from one to other. • They are freely mobile & are attached to post. abdominal wall by fan-shaped mesentery. • Root of the mesentery permits entrance & exit of branches of superior mesenteric artery and vein, lymph vessels and nerves. • Small intestine wal ...
... • Distinctive features, but a gradual change from one to other. • They are freely mobile & are attached to post. abdominal wall by fan-shaped mesentery. • Root of the mesentery permits entrance & exit of branches of superior mesenteric artery and vein, lymph vessels and nerves. • Small intestine wal ...
Abdominal and peritoneal cavities
... from the duodenojejunal junction to the iliocecal junction d. mesocolon - mesentery associated with the large intestine (1) mesocolon associated with the ascending and descending colon fuses with peritoneum of the posterior body wall making the ascending and descending colon retroperitoneal (2) meso ...
... from the duodenojejunal junction to the iliocecal junction d. mesocolon - mesentery associated with the large intestine (1) mesocolon associated with the ascending and descending colon fuses with peritoneum of the posterior body wall making the ascending and descending colon retroperitoneal (2) meso ...
Abdomen
... The coronary ligaments represent reflections of the visceral peritoneum covering the liver onto the diaphragm. As such, between the two layers of the coronary ligament there is a large triangular surface of the liver devoid of peritoneal covering; this is named the bare area of the liver, and is att ...
... The coronary ligaments represent reflections of the visceral peritoneum covering the liver onto the diaphragm. As such, between the two layers of the coronary ligament there is a large triangular surface of the liver devoid of peritoneal covering; this is named the bare area of the liver, and is att ...
25 The peritoneum
... the supravesical fossae #the medial inguinal fossae the lateral inguinal fossae the infravesical fossae ! The supravesical fossae are situated between: the median umbilical fold and medial umbilical folds #the median umbilical fold and lateral umbilical folds the hepatogastric ligament and the hepat ...
... the supravesical fossae #the medial inguinal fossae the lateral inguinal fossae the infravesical fossae ! The supravesical fossae are situated between: the median umbilical fold and medial umbilical folds #the median umbilical fold and lateral umbilical folds the hepatogastric ligament and the hepat ...
Mesentery

The mesentery is a fold of membranous tissue that arises from the posterior wall of the peritoneal cavity and attaches to the intestinal tract. Within it are the arteries and veins that supply the intestine. The term can be used narrowly to denote just the material that supplies the jejunum and ileum of the small intestine, or broadly to include the right, left and transverse mesocolon, mesoappendix, mesosigmoid and mesorectum.The human mesentery, also called the mesenteric organ, mainly comprises the small intestinal mesentery, the right, left and transverse mesocolon, mesosigmoid and mesorectum. Conventional teaching has described the mesocolon as a fragmented structure; the small intestinal mesentery, transverse and sigmoid mesocolon all terminate at their insertion into the posterior abdominal wall. Recent advances in gastrointestinal anatomy have demonstrated that the mesenteric organ is actually a single, continuous structure that reaches from the duodenojejunal flexure to the level of the distal mesorectum. This simpler concept has been shown to have significant implications.