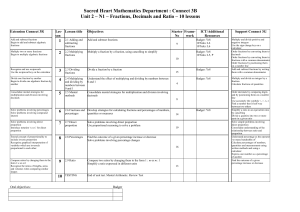
Unit 2 - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... Order fractions by converting them to decimals Order fractions by converting them to fractions with a common denominator Order fractions by positioning them on a number line Add and subtract fractions by writing them with a common denominator Multiply and divide an integer by a fraction Calculate fr ...
... Order fractions by converting them to decimals Order fractions by converting them to fractions with a common denominator Order fractions by positioning them on a number line Add and subtract fractions by writing them with a common denominator Multiply and divide an integer by a fraction Calculate fr ...
Lehigh 2006 (no calculators) 1. 1/(1/3
... 3. A bicyclist riding against the wind averages 10 mph from A to B, but with the wind averages 15 mph returning from B to A . What is his average speed for the trip? 4. What is the largest possible value for the sum of two fractions such that each of the four 1digit prime numbers occurs as one of th ...
... 3. A bicyclist riding against the wind averages 10 mph from A to B, but with the wind averages 15 mph returning from B to A . What is his average speed for the trip? 4. What is the largest possible value for the sum of two fractions such that each of the four 1digit prime numbers occurs as one of th ...
5th
... For example, create a story context for (1/3) ÷ 4, and use a visual fraction model to show the quotient. Use the relationship between multiplication and division to explain that (1/3) ÷ 4 = 1/12 because (1/12) × 4 = 1/3. b. Interpret division of a whole number by a unit fraction, and compute such qu ...
... For example, create a story context for (1/3) ÷ 4, and use a visual fraction model to show the quotient. Use the relationship between multiplication and division to explain that (1/3) ÷ 4 = 1/12 because (1/12) × 4 = 1/3. b. Interpret division of a whole number by a unit fraction, and compute such qu ...